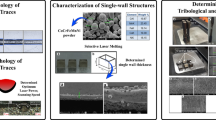
Abstract
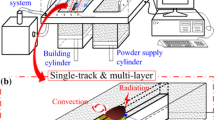
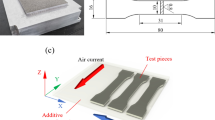
A systematic investigation of influence of the laser hatch style on densification behavior, microstructure, and tribological performance of aluminum parts’ preparation by selective laser melting (SLM) was implemented in this study. The scans with checker board (CB) style left better processing quality of surface morphology and few metallurgical defects to SLM parts in comparison with single fill and cross fill styles, hence leading to a relatively high densification level (99.42%). The CB style of shorter scan length left higher undercooling degree in small checker areas compared with other longer scan lengths, leading to finer equiaxed grains to the solidification microstructure. Accordingly, an enhanced mean microhardness of 129.7 HV0.1 was obtained in this hatch style, due to the grain refinement strengthening effect. The lowest coefficient of friction of 0.49 and wear rate of 2.43 × 10−4 mm3/(N m) were obtained. The improved densification level and formation of refined equiaxed grain and evenly distributed ring-shaped Si particles formed in CB parts changed the mechanism of material removal during sliding from the abrasion to adhesion of the tribolayer, significantly improving the wear resistance of SLM aluminum parts.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.D. Gu, H.Q. Wang, D.H. Dai, F. Chang, W. Meiners, Y.C. Hagedorn, K. Wissenbach, I. Kelbassa, and R. Poprawe: Densification behavior, microstructure evolution, and wear property of TiC nanoparticle reinforced AlSi10Mg bulk-form nanocomposites prepared by selective laser melting. J. Laser Appl. 27, S17003 (2015).
S. Siddique, M. Awd, J. Tenkamp, and F. Walther: High and very high cycle fatigue failure mechanisms in selective laser melted aluminum alloys. J. Mater. Res. 32, 1 (2017).
H.Y. Chen, D.D. Gu, D.H. Dai, C.L. Ma, and M.J. Xia: Microstructure and composition homogeneity, tensile property, and underlying thermal physical mechanism of selective laser melting tool steel parts. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 682, 279 (2017).
H. Attar, M. Bonisch, M. Calin, L.C. Zhang, K. Zhuravleva, A. Funk, S. Scudino, C. Yang, and J. Eckert: Comparative study of microstructures and mechanical properties of in situ Ti–TiB composites produced by selective laser melting, powder metallurgy, and casting technologies. J. Mater. Res. 29, 1941 (2014).
D.D. Gu and Y.F. Shen: Balling phenomena during direct laser sintering of multi-component Cu-based metal powder. J. Alloys Compd. 432, 163 (2007).
S.B. Sun, L.J. Zheng, Y.Y. Liu, J.H. Liu, and H. Zhang: Characterization of Al–Fe–V–Si heat-resistant aluminum alloy components fabricated by selective laser melting. J. Mater. Res. 30, 1661 (2015).
C.L. Ma, D.D. Gu, D.H. Dai, W.H. Chen, F. Chang, P.P. Yuan, and Y.F. Shen: Aluminum-based nanocomposites with hybrid reinforcements prepared by mechanical alloying and selective laser melting consolidation. J. Mater. Res. 30, 2816 (2015).
M. Simonelli, Y.Y. Tse, and C. Tuck: The formation of alpha plus beta microstructure in as-fabricated selective laser melting of Ti–6Al–4V. J. Mater. Res. 29, 2028 (2014).
S.A. Khairallah, A.T. Anderson, A. Rubenchik, and W.E. King: Laser powder-bed fusion additive manufacturing: Physics of complex melt flow and formation mechanisms of pores, spatter, and denudation zones. Acta Mater. 108, 36 (2016).
E.A. Jagle, P.P. Choi, J. Van Humbeeck, and D. Raabe: Precipitation and austenite reversion behavior of a maraging steel produced by selective laser melting. J. Mater. Res. 29, 2072 (2014).
A. Raghavan, H.L. Wei, T.A. Palmer, and T. DebRoy: Heat transfer and fluid flow in additive manufacturing. J. Laser Appl. 25, 052006 (2013).
H.Y. Chen, D.D. Gu, J.P. Xiong, and M.J. Xia: Improving additive manufacturing processability of hard-to-process overhanging structure by selective laser melting. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 250, 99 (2017).
Y. Sun, A. Moroz, and K. Alrbaey: Sliding wear characteristics and corrosion behaviour of selective laser melted 316L stainless steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 23, 518 (2014).
Z.W. Chen, M.A.L. Phan, and K. Darvish: Grain growth during selective laser melting of a Co–Cr–Mo alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 52, 7415 (2017).
L. Thijs, S. Montero, L. Maria, R. Wauthle, Q. Xie, J.P. Kruth, and J. Van Humbeeck: Strong morphological and crystallographic texture and resulting yield strength anisotropy in selective laser melted tantalum. Acta Mater. 61, 4657 (2013).
C. Tan, K. Zhou, W. Ma, P. Zhang, M. Liu, and T. Kuang: Microstructural evolution, nanoprecipitation behavior and mechanical properties of selective laser melted high-performance grade 300 maraging steel. Mater. Des. 134, 23 (2017).
K.N. Amato, S.M. Gaytan, L.E. Murr, E. Martinez, P.W. Shindo, J. Hernandez, S. Collins, and F. Medina: Microstructures and mechanical behavior of Inconel 718 fabricated by selective laser melting. Acta Mater. 60, 2229 (2012).
D.D. Gu, Y-C. Hagedorn, W. Meiners, G.B. Meng, R.J.S. Batista, K. Wissenbach, and R. Poprawe: Densification behavior, microstructure evolution, and wear performance of selective laser melting processed commercially pure titanium. Acta Mater. 60, 3849 (2012).
D.D. Gu and D.H. Dai: Role of melt behavior in modifying oxidation distribution using an interface incorporated model in selective laser melting of aluminum-based material. J. Appl. Phys. 120, 083104 (2016).
D.D. Gu, W. Meiners, K. Wissenbach, and R. Poprawe: Laser additive manufacturing of metallic components: Materials, processes and mechanisms. Int. Mater. Rev. 57, 133 (2012).
J.P. Kruth, L. Froyen, V.J. Van, P. Mercelis, M. Rombouts, and B. Lauwers: Selective laser melting of iron-based powder. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 149, 616 (2004).
H.Y. Chen and D.D. Gu: Effect of metallurgical defect and phase transition on geometric accuracy and wear resistance of iron-based parts fabricated by selective laser melting. J. Mater. Res. 31, 1477 (2016).
D.D. Gu, Y-C. Hagedorn, W. Meiners, K. Wissenbach, and R. Poprawe: Nanocrystalline TiC reinforced Ti matrix bulk-form nanocomposites by Selective Laser Melting (SLM): Densification, growth mechanism and wear behavior. Compos. Sci. Technol. 71, 1612 (2011).
A. Simchi: Direct laser sintering of metal powders: Mechanism, kinetics and microstructural features. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 428, 148 (2006).
J. Suryawanshi, K.G. Prashanth, S. Scudino, J. Eckert, O. Prakash, and U. Ramamurty: Simultaneous enhancements of strength and toughness in an Al–12Si alloy synthesized using selective laser melting. Acta Mater. 115, 285 (2016).
K. Arafune and A. Hirata: Thermal and solutal Marangoni convection in In–Ga–Sb system. J. Cryst. Growth 197, 811 (1999).
R.D. Li, J.H. Liu, Y.S. Shi, L. Wang, and W. Jiang: Balling behavior of stainless steel and nickel powder during selective laser melting process. Int. J. Adv. Des. Manuf. Technol. 59, 1025 (2012).
D. Wang, C. Song, Y. Yang, and Y. Bai: Investigation of crystal growth mechanism during selective laser melting and mechanical property characterization of 316L stainless steel parts. Mater. Des. 100, 291 (2016).
S.F. Wen, S. Li, Q.S. Wei, C.Z. Yan, S. Zhang, and Y.S. Shi: Effect of molten pool boundaries on the mechanical properties of selective laser melting parts. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 214, 2660 (2014).
E.O. Olakanmi, R.F. Cochrane, and K.W. Dalgarno: A review on selective laser sintering/melting (SLS/SLM) of aluminium alloy powders: Processing, microstructure, and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 74, 401 (2015).
K.G. Prashanth, S. Scudino, and J. Eckert: Defining the tensile properties of Al–12Si parts produced by selective laser melting. Acta Mater. 126, 25 (2017).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51405082), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant No. 2014A030310301), and the Science and Technology Innovation Platform of Foshan City, Guangdong Province, China. (Grant No. 2016AG100341).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Zhou, Y., Fan, Y. et al. Effect of laser hatch style on densification behavior, microstructure, and tribological performance of aluminum alloys by selective laser melting. Journal of Materials Research 33, 1713–1722 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.166
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.166