Abstract
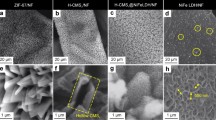
Electrocatalytic water splitting for the production of H2 is increasingly becoming a significant method to mitigate the current energy crisis and environmental pollution. However, oxygen evolution reaction (OER), a slow four-electron progress, is the bottle neck of water splitting. Thus, developing new, low cost, and effective catalysts for OER is a research hotspot in material and energy resource fields. Therefore, the research of nonprecious, metal-based OER catalysts has been popular. In this work, it is validated that 3D hollow Co(OH)2 nanoflowers synthesized by a facile template-based strategy at room temperature are effective electrocatalysts for OER. The catalysts display high activity with a current density of 10 mA/cm2 at an overpotential of 310 mV and a small Tafel slope of 68.9 mV/dec in alkaline condition. It’s noteworthy that this material is stable for over 20 h of chronopotentiometry. This work offers a simple and promising way to prepare efficient and durable electrocatalysts.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Zhang, W.Z. Lai, and R. Cao: Energy-related small molecule activation reactions: Oxygen reduction and hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions catalyzed by porphyrin- and corrole-based systems. Chem. Rev. 117, 3717 (2017).
J.R. Ran, J. Zhang, J.G. Yu, M. Jaroniec, and S.Z. Qiao: Earth-abundant cocatalysts for semiconductor-based photocatalytic water splitting. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 7787 (2014).
D. Gust, T.A. Moore, and A.L. Moore: Solar fuels via artificial photosynthesis. Acc. Chem. Res. 42, 1890 (2009).
V. Balzani, A. Credi, and M. Venturi: Photochemical conversion of solar energy. ChemSusChem 1, 26 (2008).
C. Xie, Y.Y. Wang, K. Hu, L. Tao, X.B. Huang, J. Huo, and S.Y. Wang: In situ confined synthesis of molybdenum oxide decorated nickel–iron alloy nanosheets from MoO42− intercalated layered double hydroxides for the oxygen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 87 (2017).
Z.J. Liu, Z.H. Zhao, Y.Y. Wang, S. Dou, D.F. Yan, D.D. Liu, Z.H. Xia, and S.Y. Wang: In situ exfoliated, edge-rich, oxygen-functionalized graphene from carbon fibers for oxygen electrocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 29, 1606207 (2017).
Y. Tachibana, L. Vayssieres, and J.R. Durrant: Artificial photosynthesis for solar water-splitting. Nat. Photonics 6, 511 (2012).
J. Ohi: Hydrogen energy cycle: An overview. J. Mater. Res. 20, 3180 (2005).
C.G. Morales-Guio, L.A. Stern, and X.L. Hu: Nanostructured hydrotreating catalysts for electrochemical hydrogen evolution. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 6555 (2014).
Y.M. Shi and B. Zhang: Recent advances in transition metal phosphide nanomaterials: Synthesis and applications in hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Soc. Rev. 45, 1529 (2016).
R. Zhang, X.X. Wang, S.J. Yu, T. Wen, X.W. Zhu, F.X. Yang, X.N. Sun, X.K. Wang, and W.P. Hu: Ternary NiCo2Px nanowires as pH-universal electrocatalysts for highly efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv. Mater. 29, 1605502 (2017).
J. Yin, Q.H. Fan, Y.X. Li, F.Y. Cheng, P.P. Zhou, P.X. Xi, and S.H. Sun: Ni–C–N nanosheets as catalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 14546 (2016).
L. An, L. Huang, P.P. Zhou, J. Yin, H.Y. Liu, and P.X. Xi: A self-standing high-performance hydrogen evolution electrode with nanostructured NiCo2O4/CuS heterostructures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 25, 6814 (2015).
M.X. Chen, J. Qi, W. Zhang, and R. Cao: Electrosynthesis of NiPx nanospheres for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution from a neutral aqueous solution. Chem. Commun. 53, 5507 (2017).
H.T. Lei, H.Y. Fang, Y.Z. Han, W.Z. Lai, X.F. Fu, and R. Cao: Reactivity and mechanism studies of hydrogen evolution catalyzed by copper corroles. ACS Catal. 5, 5145 (2015).
Y.Z. Han, H.Y. Fang, H.Z. Jing, H.L. Sun, H.T. Lei, W.Z. Lai, and R. Cao: Singly versus doubly reduced nickel porphyrins for proton reduction: Experimental and theoretical evidence for a homolytic hydrogen-evolution reaction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 55, 5457 (2016).
M.G. Walter, E.L. Warren, J.R. McKone, S.W. Boettcher, Q. Mi, E.A. Santori, and N.S. Lewis: Solar water splitting cells. Chem. Rev. 110, 6446 (2010).
D.Y. Guo, J. Qi, W. Zhang, and R. Cao: Surface electrochemical modification of a nickel substrate to prepare a NiFe-based electrode for water oxidation. ChemSusChem 10, 394 (2017).
S-C. Lin, Y-F. Chiu, P-W. Wu, Y-F. Hsieh, and C-Y. Wu: Templated fabrication of nanostructured Ni brush for hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Res. 25, 2001 (2010).
S.H. Shen: Toward efficient solar water splitting over hematite photoelectrodes. J. Mater. Res. 29, 29 (2013).
Y. Zhang, Y. Xie, Y.T. Zhou, X.W. Wang, and K. Pan: Well dispersed Fe2N nanoparticles on surface of nitrogen-doped reduced graphite oxide for highly efficient electrochemical hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Res. 32, 1770 (2017).
C.J. Gagliardi, B.C. Westlake, C.A. Kent, J.J. Paul, J.M. Papanikolas, and T.J. Meyer: Integrating proton coupled electron transfer (PCET) and excited states. Coord. Chem. Rev. 254, 2459 (2010).
M.X. Chen, Y.Z. Wu, Y.Z. Han, X.H. Lin, J.L. Sun, W. Zhang, and R. Cao: An iron-based film for highly efficient electrocatalytic oxygen evolution from neutral aqueous solution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 21852 (2015).
R. Cao, W.Z. Lai, and P.W. Du: Catalytic water oxidation at single metal sites. Energy Environ. Sci. 5, 8134 (2012).
Y.Z. Wu, M.X. Chen, Y.Z. Han, H.X. Luo, X.J. Su, M.T. Zhang, X.H. Lin, J.L. Sun, L. Wang, L. Deng, W. Zhang, and R. Cao: Fast and simple preparation of iron-based thin films as highly efficient water-oxidation catalysts in neutral aqueous solution. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 54, 4870 (2015).
T.R. Cook, D.K. Dogutan, S.Y. Reece, Y. Surendranath, T.S. Teets, and D.G. Nocera: Solar energy supply and storage for the legacy and nonlegacy worlds. Chem. Rev. 110, 6474 (2010).
Y. Lee, J. Suntivich, K.J. May, E.E. Perry, and Y. Shao-Horn: Synthesis and activities of rutile IrO2 and RuO2 nanoparticles for oxygen evolution in acid and alkaline solutions. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 3, 399 (2012).
D.F. Yan, Y.X. Li, J. Huo, R. Chen, L.M. Dai, and S.Y. Wang: Defect chemistry of nonprecious-metal electrocatalysts for oxygen reactions. Adv. Mater. 29, 1606459 (2017).
S. Chen and S.Z. Qiao: Hierarchically porous nitrogen-doped graphene–NiCo2O4 hybrid paper as an advanced electrocatalytic water-splitting material. ACS Nano 7, 10190 (2013).
G.S. Hutchings, Y. Zhang, J. Li, B.T. Yonemoto, X.G. Zhou, K.K. Zhu, and F. Jiao: In situ formation of cobalt oxide nanocubanes as efficient oxygen evolution catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 4223 (2015).
J. Kim, J.S. Kim, H. Baik, K. Kang, and K. Lee: Porous β-MnO2 nanoplates derived from MnCO3 nanoplates as highly efficient electrocatalysts toward oxygen evolution reaction. RSC Adv. 6, 26535 (2016).
J. Qi, W. Zhang, R.J. Xiang, K.Q. Liu, H.Y. Wang, M.X. Chen, Y.Z. Han, and R. Cao: Porous nickel-iron oxide as a highly efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. Adv. Sci. 2, 1500199 (2015).
C.H. Kuo, I.M. Mosa, A.S. Poyraz, S. Biswas, A.M. E-Sawy, W.Q. Song, Z. Luo, S.Y. Chen, J.F. Rusling, J. He, and S.L. Suib: Robust mesoporous manganese oxide catalysts for water oxidation. ACS Catal. 5, 1693 (2015).
K. Fominykh, J.M. Feckl, J. Sicklinger, M. Doblinger, S. Bocklein, J. Ziegler, L. Peter, J. Rathousky, E.W. Scheidt, T. Bein, and D. Fattakhova-Rohlfing: Ultrasmall dispersible crystalline nickel oxide nanoparticles as high-performance catalysts for electrochemical water splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 24, 3123 (2014).
R.D. Smith, M.S. Prevot, R.D. Fagan, S. Trudel, and C.P. Berlinguette: Water oxidation catalysis: Electrocatalytic response to metal stoichiometry in amorphous metal oxide films containing iron, cobalt, and nickel. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 11580 (2013).
L. Kuai, J. Geng, C.Y. Chen, E.J. Kan, Y.D. Liu, Q. Wang, and B.Y. Geng: A reliable aerosol-spray-assisted approach to produce and optimize amorphous metal oxide catalysts for electrochemical water splitting. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 53, 7547 (2014).
H.T. Wang, H.W. Lee, Y. Deng, Z.Y. Lu, P.C. Hsu, Y.Y. Liu, D.C. Lin, and Y. Cui: Bifunctional non-noble metal oxide nanoparticle electrocatalysts through lithium-induced conversion for overall water splitting. Nat. Commun. 6, 7261 (2015).
S. Jung, C.C.L. McCrory, I.M. Ferrer, J.C. Peters, and T.F. Jaramillo: Benchmarking nanoparticulate metal oxide electrocatalysts for the alkaline water oxidation reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 3068 (2016).
G.Q. Han, Y.R. Liu, W.H. Hu, B. Dong, X. Li, X. Shang, Y.M. Chai, Y.Q. Liu, and C.G. Liu: Crystallographic structure and morphology transformation of MnO2 nanorods as efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction. J. Electrochem. Soc. 163, H67 (2015).
W. Zhang, J. Qi, K.Q. Liu, and R. Cao: A nickel-based integrated electrode from an autologous growth strategy for highly efficient water oxidation. Adv. Energy Mater. 6, 1502489 (2016).
W. Zhang, Y.Z. Wu, J. Qi, M.X. Chen, and R. Cao: A thin NiFe hydroxide film formed by stepwise electrodeposition strategy with significantly improved catalytic water oxidation efficiency. Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1602547 (2017).
M.R. Gao, W.C. Sheng, Z.B. Zhuang, Q.R. Fang, S. Gu, J. Jiang, and Y.S. Yan: Efficient water oxidation using nanostructured α-nickel–hydroxide as an electrocatalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 7077 (2014).
M.W. Louie and A.T. Bell: An investigation of thin-film Ni–Fe oxide catalysts for the electrochemical evolution of oxygen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 12329 (2013).
L. Trotochaud, S.L. Young, J.K. Ranney, and S.W. Boettcher: Nickel–iron oxyhydroxide oxygen-evolution electrocatalysts: The role of intentional and incidental iron incorporation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 6744 (2014).
D. Friebel, M.W. Louie, M. Bajdich, K.E. Sanwald, Y. Cai, A.M. Wise, M.J. Cheng, D. Sokaras, T.C. Weng, R. Alonso-Mori, R.C. Davis, J.R. Bargar, J.K. Norskov, A. Nilsson, and A.T. Bell: Identification of highly active Fe sites in (Ni,Fe)OOH for electrocatalytic water splitting. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 1305 (2015).
P.F. Liu, S. Yang, B. Zhang, and H.G. Yang: Defect-rich ultrathin cobalt-iron layered double hydroxide for electrochemical overall water splitting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 34474 (2016).
F. Song and X.L. Hu: Ultrathin cobalt-manganese layered double hydroxide is an efficient oxygen evolution catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 16481 (2014).
Y. Zhang, B. Cui, C.S. Zhao, H. Lin, and J.B. Li: Co–Ni layered double hydroxides for water oxidation in neutral electrolyte. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15, 7363 (2013).
C. Zhang, M.F. Shao, L. Zhou, Z.H. Li, K.M. Xiao, and M. Wei: Hierarchical NiFe layered double hydroxide hollow microspheres with highly-efficient behavior toward oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 33697 (2016).
Y.Y. Wang, Y.Q. Zhang, Z.J. Liu, C. Xie, S. Feng, D.D. Liu, M.F. Shao, and S.Y. Wang: Layered double hydroxide nanosheets with multiple vacancies obtained by dry exfoliation as highly efficient oxygen evolution electrocatalysts. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 56, 5867 (2017).
R. Liu, Y.Y. Wang, D.D. Liu, Y.Q. Zou, and S.Y. Wang: Water-plasma-enabled exfoliation of ultrathin layered double hydroxide nanosheets with multivacancies for water oxidation. Adv. Mater. 29, 1701546 (2017).
J. Zhang, T. Wang, D. Pohl, B. Rellinghaus, R.H. Dong, S.H. Liu, X.D. Zhuang, and X.L. Feng: Interface engineering of MoS2/Ni3S2 heterostructures for highly enhanced electrochemical overall-water-splitting activity. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 55, 6702 (2016).
G.F. Chen, T.Y. Ma, Z.Q. Liu, N. Li, Y.Z. Su, K. Davey, and S.Z. Qiao: Efficient and stable bifunctional electrocatalysts Ni/NixMy (M = P, S) for overall water splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 26, 3314 (2016).
T.T. Liu, Y.H. Liang, Q. Liu, X.P. Sun, Y.Q. He, and A.M. Asiri: Electrodeposition of cobalt–sulfide nanosheets film as an efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. Electrochem. Commun. 60, 92 (2015).
W.J. Zhou, X.J. Wu, X.H. Cao, X. Huang, C.L. Tan, J. Tian, H. Liu, J.Y. Wang, and H. Zhang: Ni3S2 nanorods/Ni foam composite electrode with low overpotential for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution. Energy Environ. Sci. 6, 2921 (2013).
Z. Gao, J. Qi, M.X. Chen, W. Zhang, and R. Cao: An electrodeposited NiSe for electrocatalytic hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions in alkaline solution. Electrochim. Acta 224, 412 (2017).
D.S. Kong, H.T. Wang, Z.Y. Lu, and Y. Cui: CoSe2 nanoparticles grown on carbon fiber paper: An efficient and stable electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 4897 (2014).
A.T. Swesi, J. Masud, and M. Nath: Enhancing electrocatalytic activity of bifunctional Ni3Se2 for overall water splitting through etching-induced surface nanostructuring. J. Mater. Res. 31, 2888 (2016).
Y.W. Liu, H. Cheng, M.J. Lyu, S.J. Fan, Q.H. Liu, W.S. Zhang, Y.D. Zhi, C.M. Wang, C. Xiao, S.Q. Wei, B.J. Ye, and Y. Xie: Low overpotential in vacancy-rich ultrathin CoSe2 nanosheets for water oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 15670 (2014).
R. Xu, R. Wu, Y.M. Shi, J.F. Zhang, and B. Zhang: Ni3Se2 nanoforest/Ni foam as a hydrophilic, metallic, and self-supported bifunctional electrocatalyst for both H2 and O2 generations. Nano Energy 24, 103 (2016).
C. Tang, N.Y. Cheng, Z.H. Pu, W. Xing, and X.P. Sun: NiSe nanowire film supported on nickel foam: An efficient and stable 3D bifunctional electrode for full water splitting. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 54, 9351 (2015).
A.J. Esswein, Y. Surendranath, S.Y. Reece, and D.G. Nocera: Highly active cobalt phosphate and borate based oxygen evolving catalysts operating in neutral and natural waters. Energy Environ. Sci. 4, 499 (2011).
J. Masa, P. Weide, D. Peeters, I. Sinev, W. Xia, Z.Y. Sun, C. Somsen, M. Muhler, and W. Schuhmann: Amorphous cobalt boride (Co2B) as a highly efficient nonprecious catalyst for electrochemical water splitting: Oxygen and hydrogen evolution. Adv. Energy Mater. 6, 1502313 (2016).
Y.J. Tang, C.H. Liu, W. Huang, X.L. Wang, L.Z. Dong, S.L. Li, and Y.Q. Lan: Bimetallic carbides-based nanocomposite as superior electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 16977 (2017).
P.Z. Chen, K. Xu, Z.W. Fang, Y. Tong, J.C. Wu, X.L. Lu, X. Peng, H. Ding, C.Z. Wu, and Y. Xie: Metallic Co4N porous nanowire arrays activated by surface oxidation as electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 54, 14710 (2015).
K. Xu, P.Z. Chen, X.L. Li, Y. Tong, H. Ding, X.J. Wu, W.S. Chu, Z.M. Peng, C.Z. Wu, and Y. Xie: Metallic nickel nitride nanosheets realizing enhanced electrochemical water oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 4119 (2015).
D. Li, H. Baydoun, B. Kulikowski, and S.L. Brock: Boosting the catalytic performance of iron phosphide nanorods for the oxygen evolution reaction by incorporation of manganese. Chem. Mater. 29, 3048 (2017).
M.J. Liu and J.H. Li: Cobalt phosphide hollow polyhedron as efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for the evolution reaction of hydrogen and oxygen. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 2158 (2016).
C.G. Read, J.F. Callejas, C.F. Holder, and R.E. Schaak: General strategy for the synthesis of transition metal phosphide films for electrocatalytic hydrogen and oxygen evolution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 12798 (2016).
S.T. Wei, K. Qi, Z. Jin, J.S. Cao, W.T. Zheng, H. Chen, and X.Q. Cui: One-step synthesis of a self-supported copper phosphide nanobush for overall water splitting. ACS Omega 1, 1367 (2016).
X.G. Wang, W. Li, D.H. Xiong, and L.F. Liu: Fast fabrication of self-supported porous nickel phosphide foam for efficient, durable oxygen evolution and overall water splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 5639 (2016).
X.Y. Yu, Y. Feng, B.Y. Guan, X.W. Lou, and U. Paik: Carbon coated porous nickel phosphides nanoplates for highly efficient oxygen evolution reaction. Energy Environ. Sci. 9, 1246 (2016).
E.J. Popczun, J.R. McKone, C.G. Read, A.J. Biacchi, A.M. Wiltrout, N.S. Lewis, and R.E. Schaak: Nanostructured nickel phosphide as an electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 9267 (2013).
D. Li, H. Baydoun, C.N. Verani, and S.L. Brock: Efficient water oxidation using CoMnP nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 4006 (2016).
G. Zhang, G.C. Wang, Y. Liu, H.J. Liu, J.H. Qu, and J.H. Li: Highly active and stable catalysts of phytic acid-derivative transition metal phosphides for full water splitting. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 14686 (2016).
M. Ledendecker, S. Krick Calderon, C. Papp, H.P. Steinruck, M. Antonietti, and M. Shalom: The synthesis of nanostructured Ni5P4 films and their use as a non-noble bifunctional electrocatalyst for full water splitting. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 54, 12361 (2015).
W.Z. Lai, R. Cao, G. Dong, S. Shaik, J.N. Yao, and H. Chen: Why is cobalt the best transition metal in transition-metal hangman corroles for O–O bond formation during water oxidation? J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 3, 2315 (2012).
V. Artero, M. Chavarot-Kerlidou, and M. Fontecave: Splitting water with cobalt. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 50, 7238 (2011).
S.H. Wan, J. Qi, W. Zhang, W.N. Wang, S.K. Zhang, K.Q. Liu, H.Q. Zheng, J.L. Sun, S.Y. Wang, and R. Cao: Hierarchical Co(OH)F superstructure built by low-dimensional substructures for electrocatalytic water oxidation. Adv. Mater. 29, 1700286 (2017).
D.Y. Guo, F.F. Chen, W. Zhang, and R. Cao: Phase-transfer synthesis of α-Co(OH)2 and its conversion to CoO for efficient electrocatalytic water oxidation. Sci. Bull. 62, 626 (2017).
J.H. Wang, W. Cui, Q. Liu, Z.C. Xing, A.M. Asiri, and X.P. Sun: Recent progress in cobalt-based heterogeneous catalysts for electrochemical water splitting. Adv. Mater. 28, 215 (2016).
S. Dou, C.L. Dong, Z. Hu, Y.C. Huang, J.l. Chen, L. Tao, D.F. Yan, D.W. Chen, S.H. Shen, S.L. Chou, and S.Y. Wang: Atomic-scale CoOx species in metal-organic frameworks for oxygen evolution reaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 27, 1702546 (2017).
R.M. Liu, Z.X. Jiang, J.P. Ma, L. Ni, X.Y. Sun, Y. Liu, H.X. Chen, and Q. Liu: Al3+-induced growth of α-Co(OH)2 nanoplates as high-capacity supercapacitors and water oxidation electrocatalysts. RSC Adv. 7, 3783 (2017).
L. Wang, Z.H. Dong, Z.G. Wang, F.X. Zhang, and J. Jin: Layered α-Co(OH)2 nanocones as electrode materials for pseudocapacitors: Understanding the effect of interlayer space on electrochemical activity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 23, 2758 (2013).
Y.M. Jiang, X. Li, T.X. Wang, and C.M. Wang: Enhanced electrocatalytic oxygen evolution of α-Co(OH)2 nanosheets on carbon nanotube/polyimide films. Nanoscale 8, 9667 (2016).
P.F. Liu, S. Yang, L.R. Zheng, B. Zhang, and H.G. Yang: Electrochemical etching of α-cobalt hydroxide for improvement of oxygen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 9578 (2016).
M.A. Sayeed, T. Herd, and A.P. O’Mullane: Direct electrochemical formation of nanostructured amorphous Co(OH)2 on gold electrodes with enhanced activity for the oxygen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 991 (2016).
J.T. Zhang, J.F. Liu, Q. Peng, X. Wang, and Y.D. Li: Nearly monodisperse Cu2O and CuO nanospheres: Preparation and applications for sensitive gas sensors. Chem. Mater. 18, 867 (2006).
J.W. Nai, Y. Tian, X. Guan, and L. Guo: Pearson’s principle inspired generalized strategy for the fabrication of metal hydroxide and oxide nanocages. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 16082 (2013).
Y.P. Zhu, T.Y. Ma, M. Jaroniec, and S.Z. Qiao: Self-templating synthesis of hollow Co3O4 microtube arrays for highly efficient water electrolysis. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 56, 1324 (2017).
H.B. Li, M.H. Yu, X.H. Lu, P. Liu, Y. Liang, J. Xiao, Y.X. Tong, and G.W. Yang: Amorphous cobalt hydroxide with superior pseudocapacitive performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 745 (2014).
A. Bergmann, E. Martinez-Moreno, D. Teschner, P. Chernev, M. Gliech, J.F. de Araujo, T. Reier, H. Dau, and P. Strasser: Reversible amorphization and the catalytically active state of crystalline Co3O4 during oxygen evolution. Nat. Commun. 6, 8625 (2015).
Z.P. Liu, R.Z. Ma, M. Osada, K. Takada, and T. Sasaki: Selective and controlled synthesis of α- and β-cobalt hydroxides in highly developed hexagonal platelets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 13869 (2005).
J. Yang, H.W. Liu, W.N. Martens, and R.L. Frost: Synthesis and characterization of cobalt hydroxide, cobalt oxyhydroxide, and cobalt oxide nanodiscs. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 111 (2010).
T. Xue, X. Wang, and J.M. Lee: Dual-template synthesis of Co(OH)2 with mesoporous nanowire structure and its application in supercapacitor. J. Power Sources 201, 382 (2012).
Y.Q. Lai, Y. Li, L.X. Jiang, W. Xu, X.J. Lv, J. Li, and Y.X. Liu: Electrochemical behaviors of co-deposited Pb/Pb–MnO2 composite anode in sulfuric acid solution—Tafel and EIS investigations. J. Electroanal. Chem. 671, 16 (2012).
H.Y. Jin, S.J. Mao, G.P. Zhan, F. Xu, X.B. Bao, and Y. Wang: Fe incorporated α-Co(OH)2 nanosheets with remarkably improved activity towards the oxygen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 1078 (2017).
F. Song and X.L. Hu: Exfoliation of layered double hydroxides for enhanced oxygen evolution catalysis. Nat. Commun. 5, 4477 (2014).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21101170, 21503126, and 21573139), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (GK201603037), the Starting Research Funds of Shaanxi Normal University, and the “Thousand Talents Program” of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Guo, D., Zhang, W. et al. Co(OH)2 hollow nanoflowers as highly efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction. Journal of Materials Research 33, 568–580 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.390
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.390