Abstract
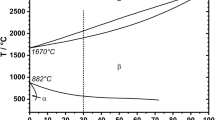
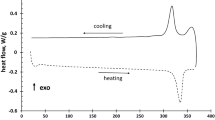
Titanium-tantalum based alloys can demonstrate a martensitic transformation well above 100 °C, which makes them attractive for shape memory applications at elevated temperatures. In addition, they provide for good workability and contain only reasonably priced constituents. The current study presents results from functional fatigue experiments on a binary Ti-25Ta high-temperature shape memory alloy. This material shows a martensitic transformation at about 350 °C along with a transformation strain of 2 pct at a bias stress of 100 MPa. The success of most of the envisaged applications will, however, hinge on the microstructural stability under thermomechanical loading. Thus, light and electron optical microscopy as well X-ray diffraction were used to uncover the mechanisms that dominate functional degradation in different temperature regimes. It is demonstrated the maximum test temperature is the key parameter that governs functional degradation in the thermomechanical fatigue tests. Specifically, ω-phase formation and local decomposition in Ti-rich and Ta-rich areas dominate when Tmax does not exceed ≈430 °C. As Tmax is increased, the detrimental phases start to dissolve and functional fatigue can be suppressed. However, when Tmax reaches ≈620 °C, structural fatigue sets in, and fatigue life is again deteriorated by oxygen-induced crack formation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Otsuka and X. Ren: Recent developments in the research of shape memory alloys. Intermetallics 7 (5), 511 (1999).
J. Ma, I. Karaman, and R.D. Noebe: High temperature shape memory alloys. Int. Mater. Rev. 55 (5), 257 (2010).
P.G. Lindquist and C.M. Wayman: Shape memory and transformation behavior of martensitic Ti–Pd–Ni and Ti–Pt–Ni alloys. In Engineering Aspects of Shape Memory Alloys, T.W. Duerig, K.N. Melton, D. Stöckel, and C.M. Wayman, eds. (Butterworth-Heinemann, London, Boston, Singapore, Sydney, Toronto, Wellington, 1990); p. 58.
J. Van Humbeeck: High temperature shape memory alloys. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 121 (1), 98 (1999).
R. Noebe, D. Gaydosh, S. Padula, II, A. Garg, T. Biles, M. Nathal, and W.D. Armstrong: Properties and potential of two (Ni, Pt) Ti alloys for use as high-temperature actuator materials. Smart Mater. Struct. 5761, 364 (2005).
K.C. Atli, I. Karaman, and R.D. Noebe: Influence of tantalum additions on the microstructure and shape memory response of Ti50.5Ni24Pd25 high-temperature shape memory alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 613, 250 (2014).
X.L. Meng, Y.F. Zheng, W. Cai, and L.C. Zhao: Two-way shape memory effect of a TiNiHf high temperature shape memory alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 372 (1–2), 180 (2004).
S. Besseghini, E. Villa, and A. Tuissi: Ni–Ti–Hf shape memory alloy: Effect of aging and thermal cycling. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 273, 390 (1999).
S.M. Saghaian, H.E. Karaca, M. Souri, A.S. Turabi, and R.D. Noebe: Tensile shape memory behavior of Ni50.3Ti29.7Hf20 high temperature shape memory alloys. Mater. Des. 101, 340 (2016).
S.M. Saghaian, H.E. Karaca, H. Tobe, M. Souri, R. Noebe, and Y.I. Chumlyakov: Effects of aging on the shape memory behavior of Ni-rich Ni50.3Ti29.7Hf20 single crystals. Acta Mater. 87, 128 (2015).
D. Canadinc, W. Trehern, H. Oscan, C. Hayrettin, O. Karakoc, I. Karaman, F. Sun, and Z. Chaudhry: On the deformation response and cyclic stability of Ni50Ti35Hf15 high temperature shape memory alloy wires. Scr. Mater. 135, 92 (2017).
P.J.S. Buenconsejo, H.Y. Kim, H. Hosoda, and S. Miyazaki: Shape memory behavior of Ti–Ta and its potential as a high-temperature shape memory alloy. Acta Mater. 57 (4), 1068 (2009).
J. Zhang, R. Rynko, J. Frenzel, C. Somsen, and G. Eggeler: Ingot metallurgy and microstructural characterization of Ti–Ta alloys. Int. J. Mater. Res. 105, 156 (2014).
P.J.S. Buenconsejo: Development and characterization of Ti–Ni based and Ti–Ta based shape memory alloys for novel applications. Ph.D. thesis, University of Tsukuba, Japan, 2009.
B.S. Hickman: The formation of omega phase in titanium and zirconium alloys: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 4, 554 (1969).
J.L. Murray: The Ta–Ti (tantalum–titanium) system. Bull. Alloy Phase Diagrams 2 (1), 62 (1981).
T. Niendorf, P. Krooß, C. Somsen, R. Rynko, A. Paulsen, E. Batyrshina, J. Frenzel, G. Eggeler, and H.J. Maier: Cyclic degradation of titanium–tantalum high-temperature shape memory alloys—The role of dislocation activity and chemical decomposition. Funct. Mater. Lett. 8, 1550062 (2015).
T. Niendorf, P. Krooß, E. Batyrsina, A. Paulsen, Y. Motemani, A. Ludwig, P. Buenconsejo, J. Frenzel, G. Eggeler, and H.J. Maier: Functional and structural fatigue of titanium tantalum high temperature shape memory alloys (HTSMAs). Mater. Sci. Eng., A 620, 359 (2015).
T. Niendorf, P. Krooß, E. Batyrsina, A. Paulsen, J. Frenzel, G. Eggeler, and H.J. Maier: On the functional degradation of binary titanium–tantalum high-temperature shape memory alloys—A new concept for fatigue life extension. Funct. Mater. Lett. 7, 1450042 (2014).
P.J.S. Buenconsejo, H.Y. Kim, and S. Miyazaki: Novel β-TiTaAl alloys with excellent cold workability and a stable high-temperature shape memory effect. Scr. Mater. 64, 1114 (2011).
R. Rynko, A. Marquardt, A. Paulsen, J. Frenzel, C. Somsen, and G. Eggeler: Microstructural evolution in a Ti–Ta high-temperature shape memory alloy during creep. Int. J. Mater. Res. 106, 331 (2015).
H.Y. Kim, T. Fukushima, P.J. Buenconsejo, T. Nam, and S. Miyazaki: Martensitic transformation and shape memory properties of Ti–Ta–Sn high temperature shape memory alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 528, 7238 (2011).
W. Siegert, K. Neuking, M. Mertmann, and G. Eggele: First cycle shape memory effect in the ternary NiTiNb system. J. Phys. 112, 739 (2003).
T.B. Massalski, H. Okamato, P.R. Subramanian, and L. Kacprzak: Phasen-Diagramm Ti–Ta, Binary Alloys Phase Diagrams (ASM International, Metals Park, Ohio, 1990).
J.C. Williams, B.S. Hickman, and D.H. Leslie: The effect of ternary additions on the decomposition of metastable beta-phase Ti alloys. Metall. Trans. 2, 477 (1971).
B.S. Hickman: Omega phase precipitation in alloys of titanium with transition metals. Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 245, 1329 (1969).
R. Rynko: Mikrostrukturelle Untersuchungen von thermisch und thermomechanisch induzierten Strukturbildungsprozessen in Ti–Ta Hochtemperatur-Formgedächtnislegierungen. Ph.D. thesis, Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Bochum, Germany, 2015.
J. Albrecht, T. Duering, and D. Richter: Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Bauteils aus einer Titanlegierung, sowie Bauteil und Verwendung des Bauteils. Europäische Patentanmeldung Patent Number 0062365, 7, 1982.
K.C. Atli, I. Karaman, R.D. Noebe, and D. Gaydosh: The effect of training on two-way shape memory effect of binary NiTi and NiTi based ternary high temperature shape memory alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 560, 653 (2013).
J. Dadda, H.J. Maier, I. Karaman, and Y. Chumlyakov: High-temperature in situ microscopy during stress-induced phase transformations in Co49Ni21Ga30 shape memory alloy single crystals. Int. J. Mater. Res. 101, 1503 (2010).
J. Dadda, H.J. Maier, I. Karaman, and Y.I. Chumlyakov: Cyclic deformation and austenite stabilization in Co35Ni35Al30 single crystalline high-temperature shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 57, 6123 (2009).
Ch. Grossmann, J. Frenzel, V. Sampath, T. Depka, and G. Eggeler: Elementary transformation and deformation processes and the cyclic stability of NiTi and NiTiCu shape memory spring actuators. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 40, 2530 (2009).
Y. Al-Zain, Y. Sato, H.Y. Kim, H. Hosoda, T.H. Nam, and S. Miyazaki: Room temperature aging behavior of Ti–Nb–Mo-based superelastic alloys. Acta Mater. 60, 2437 (2012).
M. Peters, J. Hemptenmacher, J. Kumpfert, and C. Leyens: Titan und Titanlegierungen: Struktur, Gefüge, Eigenschaften. In Titan und Titanlegierungen, M. Peters and C. Leyens, eds. (WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2002); p. 1.
R. Boyer, G. Welsch, and E.W. Collings: Materials Properties Handbook: Titanium Alloys (ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1994).
T.R. Bieler, R.M. Trevino, and L. Zeng: Alloys: Titanium. In F. Bassani, G.L. Liedl, and P. Wyder, eds., Encyclopedia of Condensed Matter Physics (Elsevier, 2005); p. 65.
R.F. Vojtovich and Eh.I. Golovko: Oxidation of Ti–Ta and Ti–Nb alloys. Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Met. 1, 222 (1979).
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Financial support by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft within the Research Unit Program “Hochtemperatur-Formgedächtnislegierungen” (Contract nos. MA1175/34-2, LU1175/11-2, and NI1327/2-2) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This author was an editor of this journal during the review and decision stage. For the JMR policy on review and publication of manuscripts authored by editors, please refer to http://www.mrs.org/editor-manuscripts/.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maier, H.J., Karsten, E., Paulsen, A. et al. Microstructural evolution and functional fatigue of a Ti-25Ta high-temperature shape memory alloy. Journal of Materials Research 32, 4287–4295 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.319
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.319