Abstract
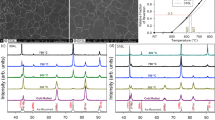
In the present work, specimens of the metastable austenitic stainless steel AISI 347 with different surface morphologies were investigated in stress-controlled fatigue tests in the high cycle fatigue (HCF) regime at ambient temperature. Specific surface morphologies were generated by cryogenic turning with CO2 snow cooling. As a result of the metastable austenite microstructure, phase changes from paramagnetic austenite to ferromagnetic martensite take place in the near-surface regime during cryogenic turning as well as in the whole specimen volume during monotonic and/or cyclic elastic–plastic deformation. The metastability of AISI 347 was characterized according to the MS-temperature determined from the chemical composition and by X-ray diffraction measurements with in situ cooling. Microhardness and strength of both phases were measured. Near-surface microstructure was analyzed by optical and scanning electron microscopy after focused ion beam preparation. Besides a partially martensitic surface layer, a thin nanocrystalline layer, both induced by cryogenic turning, was observed. In case of cyclic loading, the martensitic surface layer leads to a reduction of plastic strain amplitude as well as a retardation of crack initiation and consequently to an increase in fatigue life.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.K. Leuk Lai, K.H. Lo, and C.H. Shek: Stainless Steels: An Introduction and Their Recent Developments (Bentham Science Publishers, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2012).
P. Marshall: Austenitic Stainless Steels: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties (Elsevier Applied Science Publishers Ltd, London and New York, 1984).
S. Martin, S. Wolf, U. Martin, L. Kruger, and D. Rafaja: Deformation mechanisms in austenitic TRIP/TWIP steel as a function of temperature. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 47, 49 (2016).
S. Ackermann, S. Martin, M.R. Schwarz, C. Schimpf, D. Kulawinski, C. Lathe, S. Henkel, D. Rafaja, H. Biermann, and A. Weidner: Investigation of phase transformations in high-alloy austenitic TRIP steel under high pressure (up to 18 GPa) by in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 47, 95 (2016).
M. Smaga, F. Walther, and D. Eifler: Deformation-induced martensitic transformation in metastable austenitic steels. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 483–484, 394 (2008).
J. Man, M. Smaga, I. Kubena, D. Eifler, and J. Polák: Effect of metallurgical variables on the austenite stability in fatigued AISI 304 type steels. Eng. Fract. Mech. (2017), in press. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2017.04.041.
M. Smaga and D. Eifler: Fatigue life caclulation of metastable austenitic stainless steels on the basis of magnetic measurements. Mater. Test. 51, 370 (2009).
F. Hahnenberger, M. Smaga, and D. Eifler: Microstructural investigation of the fatigue behavior and phase transformation in metastable austenitic steels at ambient and lower temperatures. Int. J. Fatigue 69, 36 (2014).
J. Man, I. Kubena, M. Smaga, O. Man, A. Jaevenpaa, A. Weidner, Z. Chlup, and J. Polak: Microstructural changes during deformation of AISI 300 grade austenitic stainless steels: Impact of chemical heterogeneity. Proc. Struct. Integr. 2, 2299 (2016).
K.H. Lo, C.H. Shek, and J.K.L. Lai: Recent developments in stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Eng., R 65, 39 (2009).
H. Mughrabi: Cyclic slip irreversibilities and the evolution of fatigue damage. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 40, 1258 (2009).
J. Man and J. Polák: Mechanisms of extrusion and intrusion formation in fatigued crystalline materials. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 596, 15 (2014).
C. Ye, S. Suslov, D. Lin, and G.J. Cheng: Deformation-induced martensite and nanotwins by cryogenic laser shock peening of AISI 304 stainless steel and the effects on mechanical properties. Philos. Mag. 92, 1369 (2012).
H.W. Zhang, Z.K. Hei, G. Liu, J. Lu, and K. Lu: Formation of nanostructured surface layer on AISI 304 stainless steel by means of surface mechanical attrition treatment. Acta Mater. 51, 71 (2003).
D. Meyer: Cryogenic deep rolling—An energy based approach for enhanced cold surface hardening. CIRP Ann. 61, 543 (2012).
J.C. Aurich, P. Mayer, B. Kirsch, D. Eifler, M. Smaga, and R. Skorupski: Characterization of deformation induced surface hardening during cryogenic turning of AISI 347. CIRP Ann. 63, 65 (2014).
P. Mayer, B. Kirsch, and J.C. Aurich: Investigations on cryogenic turning to achieve surface hardening of metastable austenitic steel AISI 347. Adv. Mater. Res. 1018, 153 (2014).
P. Mayer, R. Skorupski, M. Smaga, D. Eifler, and J.C. Aurich: Deformation induced surface hardening when turning metastable austenitic steel AISI 347 with different cryogenic cooling strategies. Proc. CIRP 14, 101 (2014).
S. Martin, O. Fabrichnaya, and D. Rafaja: Prediction of the local deformation mechanisms in metastable austenitic steels from the local concentration of the main alloying elements. Mater. Lett. 159, 484 (2015).
H. Becker, H. Brandis, and W. Küppers: Zur Verfestigung instabil austenitischer nichtrostender Stähle und ihre Auswirkung auf das Umformverhalten von Feinblechen. Thyssen Edelstahl Tech. Ber. 12, 35 (1986).
G.H. Eichelmann and F.C. Hull: The effect of composition on the temperature of spontaneous transformation of austenite to martensite in 18-8 type stainless steel. Trans. ASM 45, 77 (1953).
T. Angel: Formation of martensite in austenitic stainless steels—Effects of deformation, temperature, and composition. J. Iron Steel Inst. 177, 165 (1954).
J. Talonen, P. Aspegren, and P. Hänninen: Comparison of different methods for measuring strain induced α-martensite content in austenitic steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 20, 1506 (2004).
D.L. Bish and S.A. Howard: Quantitative phase analysis using the rietveld method. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 21, 86 (1988).
A. Basa, C. Thaulow, and A. Barnoush: Chemically induced phase transformation in austenite by focused ion beam. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 45, 1189 (2014).
R. Skorupski: Einfluss der oberflächennahen Martensitbildung auf das LCF- und HCF-Ermüdungsverhalten sowie die Verschleißfestigkeit des metastabilen austenitischen Stahls X6CrNiNb1810. Ph.D. thesis, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, TU, Kaiserslautern, 2017.
M. Smaga, R. Skorupski, A. Boemke, P. Mayer, B. Kirsch, J.C. Aurich, I. Raid, J. Seewig, J. Man, D. Eifler, and T. Beck: Influences of surface morphology of fatigue behavior of metastable austenitic stainless steel AISI 347 at ambient temperature and 300 °C. Structural Integrity Procedia, 2nd International Conference on Structural Integrity, ICSI (2017), in press.
M. Kumagai, K. Akita, Y. Itano, M. Imafuku, and S.I. Ohya: X-ray diffraction study on microstructures of shot/laser-peened AISI316 stainless steel. J. Nucl. Mater. 443, 107 (2013).
I. Nikitin, B. Scholtes, H.J. Maier, and I. Altenberger: High temperature fatigue behavior and residual stress stability of laser-shock peened and deep rolled austenitic steel AISI 304. Scr. Mater. 50, 1345 (2004).
L. Trško, O. Bokůvka, F. Nový, and M. Guagliano: Effect of severe shot peening on ultra-high-cycle fatigue of a low alloy steel. Mater. Des. 57, 103 (2014).
I. Altenberger, B. Scholtes, U. Martin, and H. Oettel: Cyclic deformation and near surface microstructures of shot peened or deep rolled austenitic stainless steel AISI 304. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 264, 1 (1999).
H.J. Bassler and D. Eifler: Cyclic deformation behaviour and plasticity-induced martensite formation of the austenitic steel X6CrNiTi1810. Fatigue 99 (1), 205 (1999).
A. Sorich, M. Smaga, and D. Eifler: Influence of cyclic deformation induced phase transformation on the fatigue behavior of the austenitic steel X6CrNiNb1810. Adv. Mater. Res. 891–892, 1231 (2014).
M. Bayerlein, H-J. Christ, and H. Mughrabi: Plasticity-induced martensitic transformation during cyclic deformation of AISI 304L stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 114, L11 (1989).
R. Skorupski, M. Smaga, and D. Eifler: Low cycle fatigue behavior of AISI 347 with varied surface morphology. Proc. LCF7 39 (2013).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank the German Research Foundation (DFG) for the financial support within the CRC 926 “Microscale Morphology of Component Surfaces”. The fatigue specimens were turned at the Institute for Manufacturing Technology and Production Systems (FBK), TU Kaiserslautern, Germany. They thank Prof. J.C. Aurich and P. Mayer for their support. The focus ion beam (FIB) preparation and SEM investigation of nanocrystalline surface structures were performed at Nano Structuring Center (NSC) TU Kaiserslautern, Germany. They thank Dr. T. Löber for his support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smaga, M., Skorupski, R., Eifler, D. et al. Microstructural characterization of cyclic deformation behavior of metastable austenitic stainless steel AISI 347 with different surface morphology. Journal of Materials Research 32, 4452–4460 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.318
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.318