Abstract
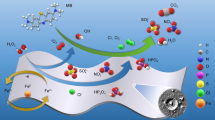
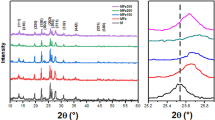
We report on the high catalytic activity of iron based metallic glass (MG) particles in dissociating direct blue dye (C32H20N6Na4O14S4) (DBD), a toxic water pollutant. We adopted high speed mechanical milling to activate the FeMG particles (of nominal composition Fe48Cr15Mo14Y2C15B6) and optimized the morphology and the particle size to achieve complete degradation of DBD in less than 20 min. The surface morphology and the particle size of the activated particles were characterized using scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. They were found to have corrugated edge like catalytically active surfaces after mechanical activation. The dye degradation rate of the activated MG powder was characterized via UV–visible absorption spectroscopy. The rate of dye degradation was significantly faster for the activated particles (within 20 min), compared to both pristine FeMG particles as well as elemental iron particles. In addition, the dye degradation mechanism was studied using Raman and infrared spectroscopy. The catalytically activated surfaces are believed to break the–C–H–,–C–N–, and–N=N–bonds, resulting in complete degradation of DBD.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Mester and M. Tien: Oxidation mechanism of ligninolytic enzymes involved in the degradation of environmental pollutants. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 46, 51–59, (2000).
R.G. Saratale, G.D. Saratale, J.S. Chang, and S.P. Govindwar: Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes: A review. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 42, 138–157 (2011).
A. Agrawal and P.G. Tratnyek: Reduction of nitro aromatic compounds by zero-valent iron metal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 30, 153–160 (1995).
G.R. Eykholt and D.T. Davenport: Dechlorination of the chloroacetanilide herbicides alachlor and metolachlor by iron metal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 32, 1482–1487 (1998).
W-x. Zhang: Nanoscale iron particles for environmental remediation: An overview. J. Nanopart. Res. 5, 323–332 (2003).
J. Cao, L. Wei, Q. Huang, L. Wang, and S. Han: Reducing degradation of azo dye by zero-valent iron in aqueous solution. Chemosphere 38, 565–571 (1999).
Y. Yoshida, S. Ogata, S. Nakamatsu, T. Shimamune, K. Kikawa, H. Inoue, and C. Iwakura: Decoloration of azo dye using atomic hydrogen permeating through a Pt-modified palladized Pd sheet electrode. Electrochim. Acta 45, 409–414 (1999).
S. Nam and P.G. Tratnyek: Reduction of azo dyes with zero-valent iron. Water Res. 34, 1837–1845 (2000).
T. Bigg and S.J. Judd: Kinetics of reductive degradation of azo dye by zero-valent iron. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 79, 297–303 (2001).
W.A. Arnold and A.L. Roberts: Pathways and kinetics of chlorinated ethylene and chlorinated acetylene reaction with Fe(0) particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 34, 1794–1805 (2000).
S. Choe, Y-Y. Chang, K-Y. Hwang, and J. Khim: Kinetics of reductive denitrification by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 41, 1307–1311 (2000).
J. Schroers: On the formability of bulk metallic glass in its supercooled liquid state. Acta Mater. 56, 471–478 (2008).
A.L. Greer: Metallic glasses. Science 267, 1947–1953 (1995).
M. Carmo, R.C. Sekol, S. Ding, G. Kumar, J. Schroers, and A.D. Taylor: Bulk metallic glass nanowire architecture for electrochemical applications. ACS Nano 5, 2979–2983 (2011).
R.C. Sekol, G. Kumar, M. Carmo, F. Gittleson, N. Hardesty-Dyck, S. Mukherjee, J. Schroers, and A.D. Taylor: Bulk metallic glass micro fuel cell. Small 9, 2081–2085 (2013).
J-Q. Wang, Y-H. Liu, M-W. Chen, G-Q. Xie, D.V. Louzguine-Luzgin, A. Inoue, and J.H. Perepezko: Rapid degradation of azo dye by Fe-based metallic glass powder. Adv. Funct. Mater. 22, 2567–2570 (2012).
P. Liu, J.L. Zhang, M.Q. Zha, and C.H. Shek: Synthesis of an Fe rich amorphous structure with a catalytic effect to rapidly decolorize azo dye at room temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 5500–5505 (2014).
C. Zhang, Z. Zhu, H. Zhang, and Z. Hu: Rapid decolorization of Acid Orange II aqueous solution by amorphous zero-valent iron. J. Environ. Sci. 24, 1021–1026 (2012).
C. Zhang, Z. Zhu, H. Zhang, and Z. Hu: On the decolorization property of Fe–Mo–Si–B alloys with different structures. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 358, 61–64 (2012).
S. Özkar: Enhancement of catalytic activity by increasing surface area in heterogeneous catalysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 1272–1277 (2009).
N.D. Lang and W. Kohn: Theory of metal surfaces: Charge density and surface energy. Phys. Rev. B 1, 4555–4568 (1970).
O. Rodriguez de la Fuente, M.A. Gonzalez-Barrio, V. Navarro, B.M. Pabon, I. Palacio, and A. Mascaraque: Surface defects and their influence on surface properties. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 25, 484008 (2013).
B. Hammer and J.K. Nørskov: Theoretical surface science and catalysis—calculations and concepts. In Advances in Catalysis, Vol. 45, H.K. Bruce and C. Gates eds. (Academic Press, New York, NY, 2000); pp. 71–129.
E.J. Weber: Iron-mediated reductive transformations: Investigation of reaction mechanism. Environ. Sci. Technol. 30, 716–719 (1996).
L.J. Matheson and P.G. Tratnyek: Reductive dehalogenation of chlorinated methanes by iron metal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 28, 2045–2053 (1994).
Y. Xia, Y. Xiong, B. Lim, and S.E. Skrabalak: Shape-controlled synthesis of metal nanocrystals: Simple chemistry meets complex physics?Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 48, 60–103 (2009).
N. Tian, Z-Y. Zhou, S-G. Sun, Y. Ding, and Z.L. Wang: Synthesis of tetrahexahedral platinum nanocrystals with high-index facets and high electro-oxidation activity. Science 316, 732–735 (2007).
Y. Ma, Q. Kuang, Z. Jiang, Z. Xie, R. Huang, and L. Zheng: Synthesis of trisoctahedral gold nanocrystals with exposed high-index facets by a facile chemical method. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 47, 8901–8904 (2008).
R. Abazari, F. Heshmatpour, and S. Balalaie: Pt/Pd/Fe trimetallic nanoparticle produced via reverse micelle technique: Synthesis, characterization, and its use as an efficient catalyst for reductive hydrodehalogenation of aryl and aliphatic halides under mild conditions. ACS Catal. 3, 139–149 (2013).
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Center for Advanced Research & Technology (CART) at the University of North Texas (UNT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, S., Bandi, V., Arora, H.S. et al. Synergistic catalytic effect of iron metallic glass particles in direct blue dye degradation. Journal of Materials Research 30, 1121–1127 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.90
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.90