Abstract
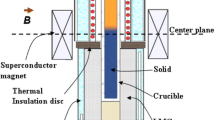
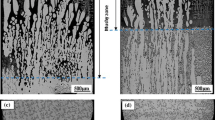
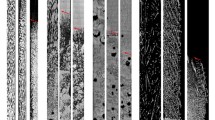
Effect of a transverse magnetic field on macrosegregation and growth of primary Al2Cu dendrites in directionally solidified Al-40 wt% Cu alloys was investigated experimentally. The experimental results indicated that the magnetic field caused the formation of channel-like and freckle segregations. It was also found that the application of the magnetic field benefited the growth of primary Al2Cu dendrites and the axial segregation. Moreover, the magnetic field decreased the primary dendrite spacing and the mushy zone length; however these effects weakened with the increase of the magnetic field intensity. The above experimental results should be attributed to the formation of the thermoelectric magnetic convection during directional solidification under the transverse magnetic field.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.I. Bergman, D.R. Fearn, J. Bloxham, and M.C. Shannon: Convection and channel formation in solidifying Pb-Sn alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 28, 859 (1997).
L. Yuan and P.D. Lee: A new mechanism for freckle initiation based on microstructural level simulation. Acta Mater. 60, 4917 (2012).
M.D. Dupouy, D. Camel, and J.J. Favier: Natural convective effects in directional dendritic solidification of binary metallic alloys: Dendritic array primary spacing. Acta Metall. Mater. 40, 1791 (1992).
P. Lehmann, R. Moreau, D. Camel, and R. Bolcato: A simple analysis of the effect of convection on the structure of the mushy zone in the case of horizontal Bridgman solidification. J. Cryst. Growth 183, 690 (1998).
M. Medina, Y. Du Terrail, F. Durand, and Y. Fautrelle: Channel segregation during solidification and the effects of an alternating traveling magnetic field. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 35, 743 (2004).
S. Boden, S. Eckert, and G. Gerbeth: Visualization of freckle formation induced by forced melt convection in solidifying GaIn alloys. Mater. Lett. 64, 1340 (2010).
S. Steinbach and L. Ratke: The influence of fluid flow on the microstructure of directionally solidified AlSi-base alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 38, 1388 (2007).
W.V. Youdelis and R.C. Dorward: Directional solidification of aluminium-copper alloys in a magnetic field. Can. J. Phys. 44, 139 (1966).
R. Moreau, O. Laskar, and M. Tanaka: Thermoelectric magnetohydrodynamic effects on solidification of metallic alloys in the dendritic regime. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 173, 93 (1993).
S.N. Tewari, R. Shah, and H. Song: Effect of magnetic field on the microstructure and macrosegregation in directionally solidified Pb-Sn alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 25, 1535 (1994).
P. Lehmann, R. Moreau, D. Camel, and R. Bolcato: Modification of interdendritic convection in directional solidification by a uniform magnetic field. Acta Mater. 46, 4067 (1998).
X. Li, Y. Fautrelle, and Z.M. Ren: Influence of thermoelectric effects on the solid–liquid interface shape and cellular morphology in the mushy zone during the directional solidification of Al–Cu alloys under a magnetic field. Acta Mater. 55, 3803 (2007).
C.A. Schneider, W.S. Rasband, and K.W. Eliceiri: NIH image to ImageJ: 25 Years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 671, 9 (2012).
A. Kao, P.D. Lee, and K. Pericleous: Influence of a slow rotating magnetic field in thermoelectric magnetohydrodynamic processing of alloys. ISIJ Int. 54, 1283 (2014).
A. Kao, N. Shevchenko, O. Roshchupinka, S. Eckert, and K. Pericleous: The effects of natural, forced and thermoelectric magnetohydrodynamic convection during the solidification of thin sample alloys. IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 84, 012018 (2015).
C. Beckermann: Modelling of macrosegregation: Applications and future needs. Int. Mater. Rev. 47, 243 (2002).
M.D. Dupouy, D. Camel, and J.J. Favier: Natural convective effects in directional dendritic solidification of binary metallic alloys: Dendritic array morphology. J. Cryst. Growth 126, 480 (1993).
L. Makkonen: Solid fraction in dendritic solidification of a liquid. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 091910 (2010).
S.N. Ojha, G. Ding, Y. Lu, J. Reye, and S.N. Tewari: Macrosegregation caused by thermosolutal convection during directional solidification of Pb-Sb alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 30, 2167 (1999).
M. Gündüz and E. Çadırlı: Directional solidification of aluminium–copper alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 327, 167 (2002).
X. Li, Z.M. Ren, A. Gagnoud, O. Budebkova, and Y. Fautrelle: Effects of thermoelectric magnetic convection on the solidification structure during directional solidification under lower transverse magnetic field. Metall. Trans. A 42, 3459 (2011).
C.Y. Ho, M.W. Ackerman, K.Y. Wu, T.N. Havill, and R.H. Bogaard: Electrical resistivity of ten selected binary alloy systems. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 12, 184 (1983).
J.L. Bretonnet, J. Auchet, and J.G. Gasser: Electrical transport properties of the liquid Al–Cu alloys. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 395, 117 (1990).
Y. Shen, Z.M. Ren, and X. Li: Effect of a low axial magnetic field on the primary Al2Cu phase growth in a directionally solidified Al–Cu hypereutectic alloy. J. Cryst. Growth 336, 67 (2011).
Y. Plevachuk, V. Sklyarchuk, and A. Yakymovychal: Density, Viscosity, and electrical conductivity of Hypoeutectic Al–Cu liquid alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 39, 3040 (2008).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work is supported partly by the European Space Agency through the Bl-inter 09_473220, National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51271109 and 51171106), and the Program for Professor of Special Appointment (Eastern Scholar) at Shanghai Institutions of Higher Learning.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Du, D., Gagnoud, A. et al. Effect of a transverse magnetic field on solidification structure in directionally solidified Al-40 wt% Cu alloys. Journal of Materials Research 31, 213–221 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.396
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.396