Abstract
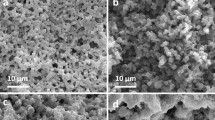
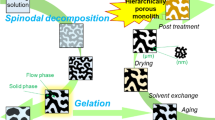
Nanocasting into silica templates for preparation of mesoporous materials has up to now been limited to those metal oxides and metals that can withstand the harsh silica etching processes currently used. Two new methods of removing the silica template are reported, either by dissolving the silica in methanolic base or by dissolution in aqueous base under an external potential. The utility of these methods is demonstrated in the synthesis of hierarchically porous zinc oxide, nickel oxide, and copper monoliths that would dissolve or react using other template removal methods. The successful etching of monolithic zinc oxide using methanolic base etching can be explained by the reduced solubility of zinc oxide in methanol compared with an aqueous base, while it also reduces the formation of hydroxides when etching the nickel oxide and copper monoliths. Alternatively, the formation of highly soluble copper oxide/hydroxide can be avoided by holding the copper monolith at a sufficiently negative potential while etching with an aqueous base.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hierarchically Structured Porous Materials, edited by B-L. Su, C. Sanchez, and X-Y. Yang (Wiley-VCH Verlag, Berlin, 2012).
Y. Li, Z-Y. Fu, and B-L. Su: Hierarchically structured porous materials for energy conversion and storage. Adv. Funct. Mater. 22, 4634 (2012).
J. Banhart: Metal foams: Production and stability Adv. Eng. Mater. 8(9), 781 (2006).
J. Biener, M. Stadermann, M. Suss, M.A. Worsley, M.M. Biener, K.A. Rose, and T.F. Baumann: Advanced carbon aerogels for energy applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 4, 656 (2011).
K. Nakanishi: Hierarchically porous materials by phase separation: Monoliths, in Hierarchically Structured Porous Materials: From Nanoscience to Catalysis, Separation, Optic, Energy, and Life Science, edited by S. Bao-Lian, C. Sanchez, and Y. Xiao-Yu (Wiley-VCH Verlag, Berlin, 2012), p. 241.
C.H. Ko and R. Ryoo: Imaging the channels in mesoporous molecular sieves with platinum. Chem. Commun. 21, 2467 (1996).
R. Ryoo, S.H. Joo, and S. Jun: Synthesis of highly ordered carbon molecular sieves via template-mediated structural transformation J. Phys. Chem. B 103, 7743 (1999).
H. Yang, Q. Shi, X. Liu, S. Xie, D. Jiang, F. Zhang, C. Yu, B. Tu, and D. Zhao: Synthesis of ordered mesoporous carbon monoliths with bicontinuous cubic pore structure of Ia3d symmetry. Chem. Commun. 23,2842 (2002).
F. Dao, Q. Lu, and D. Zhao: Synthesis of crystalline mesoporous CdS semiconductor nanoarrays through a mesoporous SBA-15 silica template technique. Adv. Mater. 15(9), 739 (2003).
A-H. Lu, D. Zhao, and Y. Wan: Nanocasting: A Versatile Strategy for Creating Nanostructured Porous Materials (Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, 2010).
A-H. Lu and F. Schüth: Nanocasting: A versatile strategy for creating nanostructured porous materials. Adv. Mater. 18, 1793 (2006).
J-H. Smått, F.M. Sayler, A. Grano, and M.G. Bakker: Formation of hierarchically porous metal oxide and metal monoliths by nanocasting into silica monoliths. Adv. Eng. Mater. 14(12), 1059 (2012).
Y. Ren, Z. Ma, and P.G. Bruce: Ordered mesoporous metal oxides: Synthesis and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 4909 (2012).
N. Linares, S. Hartmann, A. Galarneau, and P. Barbaro: Continuous partial hydrogenation reactions by Pd@unconventional bimodal porous titania monolith catalysts. ACS Catal. 2, 2194 (2012).
K. Cabrera, D. Lubda, H-M. Eggenweiler, H. Minakuchi, and K. Nakanishi: A new monolithic-type HPLC column for fast separations. J. High Resolut. Chromatogr. 23(1), 93 (2000).
N. Tanaka, H. Nagayama, H. Kobayashi, T. Ikegami, K. Hosoya, N. Ishizuka, H. Minakuchi, K. Nakanishi, K. Cabrera, and D. Lubda: Monolithic silica columns for HPLC, micro-HPLC, and CEC. J. High Resolut. Chromatogr. 23(1), 111 (2000).
A. Taguchi, J-H. Smått, and M. Lindén: Carbon monoliths possessing a hierarchical, fully interconnected porosity. Adv. Mater. 15(14), 1209 (2003).
J-H. Smått, C. Weidenthaler, J.B. Rosenholm, and M. Lindén: Hierarchically porous metal oxide monoliths prepared by the nanocasting route. Chem. Mater. 18, 1443 (2006).
S. Polarz, A.V. Orlov, F. Schüth, and A-H. Lu: Preparation of high-surface-area zinc oxide with ordered porosity, different pore sizes, and nanocrystalline walls. Chem. Euro. J. 13, 592 (2007).
T. Waitz, M. Tiemann, P.J. Klar, J. Sann, J. Stehr, and B.K. Meyer: Crystalline ZnO with an enhanced surface area obtained by nanocasting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 123108 (2007).
M. Tiemann: Repeated templating. Chem. Mater. 20, 961 (2008).
S. Lepoutre, B. Julián-López, C. Sanchez, H. Amenitsch, M. Linden, and D. Grosso: Nanocasted mesoporous nanocrystalline ZnO thin films. J. Mater. Chem. 20, 537 (2010).
J-H. Smått, S.A. Schunk, and M. Lindén: Versatile double-templating synthesis route to silica monoliths exhibiting a multimodal hierarchical porosity. Chem. Mater. 15, 2354 (2003).
A-H. Lu, J-H. Smått, S. Backlund, and M. Lindén: Easy and flexible preparation of nanocasted carbon monoliths exhibiting a multimodal hierarchical porosity. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 72, 59 (2004).
C. Liu and Y. Li: Synthesis and characterization of amorphous α-nickel hydroxide. J. Alloy Compd. 478, 415 (2009).
J.A. Moulijn, A.E. van Diepen, and F. Kapteijn: Catalyst deactivation: Is it predictable? What to do? Appl. Catal., A. 212, 3 (2001).
A. Cao, R. Lu, and G. Veser: Stabilizing metal nanoparticles for heterogeneous catalysis. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 12, 13499 (2010).
R.H. Lamoreaux, D.L. Hildenbrand, and L. Brewer: High-temperature vaporization behavior of oxides II. Oxides of Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, B, Al, Ga, Tl, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb, Zn, Cd, and Hg. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 16, 419 (1987).
D.R. Lide: Crc Handbook of Chemistry and Physics: A Ready-Reference Book of Chemical and Physical Data, 85 ed. (CRC Press, London, 2004).
W. Yue and W. Zhou: Porous crystals of cubic metal oxides templated by cage-containing mesoporous silica. J. Mater. Chem. 17, 4947 (2007).
M.E. Cabo, E. Pellicer, E. Rossinyol, O. Castell, S. Surinach, and M.D. Baro: Mesoporous NiCo2O4 spinel: Influence of calcination temperature over phase purity and thermal stability. Cryst. Growth Des. 9, 4814 (2009).
H. Liu, G. Wang, J. Liu, S. Qiao, and H. Ahn: Highly ordered mesoporous NiO anode material for lithium ion batteries with an excellent electrochemical performance. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 3046 (2011).
F. Jiao, A.H. Hill, A. Harrison, A. Berko, A.V. Chadwick, and P.G. Bruce: Synthesis of ordered mesoporous NiO with crystalline walls and a bimodal pore size distribution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 5262 (2008).
G.J. Kim and X-F. Guo: Fabrication and application of highly ordered mesoporous Co3O4, NiO, and their metals. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 71, 612 (2010).
W. Yue and W. Zhou: Synthesis of porous single crystals of metal oxides via a solid-liquid route. Chem. Mater. 19, 2359 (2007).
K.H. Gayer and A.B. Garrett: The equilibria of nickel hydroxide, Ni(OH)2, in solutions of hydrocholic acid and sodium hydroxide at 25º. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 71(9), 2973 (1949).
F.M. Sayler, A.J. Grano, S. Wiedmer, J-H. Smått, and M.G. Bakker: Application of 3-D hierarchically porous silver, cobalt oxide and zinc oxide monoliths to chromatographic separations. MRS Proc. 1389, g03–16 (2012). doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1557/opl.2012.525.
H. Yen, Y. Seo, R. Guillet-Nicolas, S. Kaliaguinec, and F. Kleitz: One-step-impregnation hard templating synthesis of high-surface-area nanostructured mixed metal oxides (NiFe2O4, CuFe2O4 and Cu/CeO2). Chem. Commun. 47, 10473 (2011).
M. Pourbaix: Atlas of Electrochemical Equilibria in Aqueous Solutions (National Association of Corrosion Engineers, Houston, Texas, 1974).
Acknowledgments
The use of Central Analytical Facility instruments (SEM, XRD) is greatly acknowledged. This work was partially supported by NSF under Grant No. CHE-0719398 (MGB) and by the Academy of Finland through Grant No. 259310 (JHS). The technical assistance of Ms. Kate Price in the development of the voltage stabilized etch, Mr. Jake Mims for sample preparation, and Mr. Clifton Watkins for running Raman spectroscopy are also much appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material
Supplementary materials can be viewed in this issue of the Journal of Materials Research by visiting http://journals.cambridge.org/jmr.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grano, A.J., Sayler, F.D., Smått, JH. et al. Alternative etching methods to expand nanocasting, and use in the synthesis of hierarchically porous nickel oxide, zinc oxide, and copper monoliths. Journal of Materials Research 28, 2483–2489 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2013.153
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2013.153