Abstract
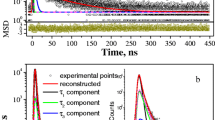
Positron annihilation lifetime measurements are performed for sol–gel-derived 70 mol% SiO2–30 mol% CaO bioactive glass. Strong positronium formation processes are shown to be an inherent feature for these kinds of materials. Observed orthopositronium (o-Ps) lifetimes show a three-modal distribution with lifetime values weighed at ∼2, ∼18, and ∼70 ns. The exposure of the investigated sol–gel-derived bioactive glasses to water vapor significantly modifies o-Ps lifetime distribution due to the penetration of water molecules into the nanopores, indicating high ratio of their interconnectivity. Classic Tao–Eldrup equation is used to relate the o-Ps lifetimes with the size of nanopores, whose distribution is verified by nitrogen adsorption porosimetry.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Li, A.E. Clark, and L.L. Hench: An investigation of bioactive glass powders by sol-gel processing. J. Appl. Biomater. 2, 231 (1991).
J.R. Jones, O. Tsigkou, E.E. Coates, M.M. Stevens, J.M. Polak, and L.L. Hench: Extracellular matrix formation and mineralization on a phosphate-free porous bioactive glass scaffold using primary human osteoblast (HOB) cells. Biomaterials 28, 1653 (2007).
A.C. Marques, R. Almeida, A. Thiema, S. Wang, M.M. Falk, and H. Jain: Sol-gel-derived glass scaffold with high pore interconnectivity and enhanced bioactivity. J. Mater. Res. 24, 3495 (2009).
S. Wang, M.M. Falk, A. Rashad, M.M. Saad, A.C. Marques, R.M. Almeida, M.K. Marei, and H. Jain: Evaluation of 3D nano/macroporous bioactive glass scaffold for hard tissue engineering. J. Mater. Sci. - Mater. Med. 22, 1195 (2011).
P. Sepulveda, J.R. Jones, and L.L. Hench: Bioactive sol-gel foams for tissue repair. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 59, 340 (2002).
D. Zhang, H. Jain, M. Hupa, and L. Hupa: In vitro degradation and bioactivity of tailored amorphous multi porous (TAMP) scaffold structure. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. (2012, in press).
V. Karageorgiou and D. Kaplan: Porosity of 3D biomaterial scaffolds and osteogenesis. Biomaterials 26, 5474 (2005).
K. Nakanishi: Pore structure control of silica gels based on phase separation. J. Porous Mater. 4, 67 (1997).
A. Yachi, R. Takahashi, S. Sato, T. Sodesawa, K. Oguma, K. Matsutani, and N. Mikami: Silica gel with continuous macropores prepared from water glass in the presence of poly(acrylic acid). J. Non-Cryst. Solids 351, 331 (2005).
J.R. Jones, L.M. Ehrenfried, and L.L. Hench: Optimizing bioactive glass scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 27, 964 (2006).
H. Maekawa, J. Esquena, S. Bishop, C. Solans, and B.F. Chmelka: Meso/macroporous inorganic oxide monoliths from polymer, foams. Adv. Mater. 15, 591 (2003).
W. Liang and C. Russel: Porous glass scaffolds by a salt sintering process. J. Mater. Sci. 41, 3787 (2006).
H.M. Moawad and H. Jain: Fabrication ofnano/macro porous glass-ceramic bioscaffold with a water-soluble pore former. J. Mater. Sci. - Mater. Med. 23, 307 (2012).
H. Yun, S. Kim, and Y. Hyeon: Design and preparation of bioactive glasses with hierarchical pore networks. Chem. Commun. 21, 2139 (2007).
A.C. Marques, H. Jain, and R.M. Almeida: Sol-gel derived nano/macroporous scaffolds. Phys. Chem. Glasses-Eur. J. Glass Sci. Technol., Part B 48, 65 (2007).
P.A. Webb and C. Orr: Analytical Methods in Fine Particle Technology (Micromeritics Instrument Corporation, Norcross, 1997).
S. Brunauer, P.H. Emmett, and E. Teller: Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 60, 309 (1938).
E.P. Barrett, L.G. Joyner, and P.P. Halenda: The determination of pore volume and area distributions in porous substances. 1. Computations from nitrogen isotherms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 73, 373 (1951).
R.W. Rice: Evaluation of extension of physical property-porosity models based on minimum solid area. J. Mater. Sci. 31, 102 (1996).
G. Ondracek: Human, medicine and materials: Biomaterials. Keram. Z. 40, 169 (1988).
R. Krause-Rehberg and H. Leipner: Positron Annihilation in Semiconductors (Springer, Heidelberg, 1999).
Y.C. Jean, P.E. Mallon, and D.M. Schrader: Principles and Application of Positron and Positronium Chemistry (World Scientific, Singapore, 2003).
O.E. Mogensen: Positron Annihilation in Chemistry (Springer, Berlin, 1995).
H. Nakanishi, Y.C. Jean, D.M. Schrader, and Y.C. Jean: In Positron and Positronium Chemistry (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1998).
G. Dlubek, Sen A. Gupta, J. Pionteck, R. Hassler, Krause-R. Rehberg, H. Kaspar, and K.H. Lochhaas: High-pressure dependence of the free volume in fluoroelastomers from positron lifetime and PVT experiments. Polymer 46, 6075 (2005).
O. Shpotyuk and J. Filipecki: Free volume in Vitreous Chalcogenide Semiconductors: Possibilities of Positron Annihilation Lifetime Study (WWSzP, Czestochowa, 2003). ISBN 83-7098-984-5.
Y. Vueva, A. Gama, A.V. Teixeira, R.M. Almeida, S. Wang, M.M. Falk, and H. Jain: Monolithic glass scaffolds with dual porosity prepared by polymer-induced phase separation and sol–gel. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93, 1945 (2010).
J. Kansy: Microcomputer program for analysis of positron annihilation lifetime spectra. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 374, 235 (1996).
S.J. Tao: Positronium annihilation in molecular substance. J. Chem. Phys. 56, 5499 (1972).
M. Eldrup, D. Lightbody, and J.N. Sherwood: The temperature dependence of positron lifetimes in solid pivalic acid. Chem. Phys. 63, 51 (1981).
T. Goworek, K. Ciesieslski, B. Jasinska, and J. Wawryszczuk: Positronium states in the pores of silica gel. Chem. Phys. 230, 305 (1998).
N. Djourelov, T. Suzuki, V. Shantarovich, and K. Kondo: Positronium formation in sol-gel-prepared silica-based glasses: Temperature and positron-irradiation effect. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 72, 723 (2005).
M. Misheva, N. Djourelov, F.M.A. Margaca, and Miranda I.M. Salvado: Positronium decay of zirconia-silica sol-gels. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 272, 209 (2000).
H. Klym, A. Ingram, O. Shpotyuk, J. Filipecki, and I. Hadzaman: Extended positron-trapping defects in insulating MgAl2O4 spinel-type ceramics. Phys. Status Solidi C 4, 715 (2007).
D. Dutta, S. Chatterjee, K.T. Pujari, and B.N. Ganguly: Pore structure of silica gel: A comparative study through BET and PALS. Chem. Phys. 312, 319 (2005).
D.W. Gidley, W.E. Frieze, T.L. Dull, A.F. Yee, E.T. Ryen, and H.M. Ho: Positronium annihilation in mesoporous thin films. Phys. Rev. B 60, R5157 (1999).
A.K. Varshneya: Fundamentals of Inorganic Glasses, 2nd ed. (Society of Glass Technology, Sheffield, UK, 2006).
A.C. Marques, H. Jain, C. Kiely, K. Song, C.J. Kiely, and R.M. Almeida: Nano/macroporous monolithic scaffolds prepared by the sol–gel method. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 51, 42 (2009).
L.L. Hench and J.K. West: The sol-gel process. Chem. Rev. 90, 33 (1990).
W.F. Magalhaes, J.C. Abbe, and G. Duplatre: Solvent and temperature effects on positronium annihilation parameters and on its quenching reactions with the free radical HTEMPO. Struct. Chem. 2, 399 (1991).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank U.S. National Science Foundation through IMI-NFG (Grant No. DMR-0844014), for initiating the international collaboration and providing partial financial support for this work. SW and HJ thank the National Science Foundation for support via the Materials World Network (DMR-0602975) program
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This author was an editor of this journal during the review and decision stage. For the JMR policy on review and publication of manuscripts authored by editors, please refer to http://www.mrs.org/jmr-editor-manuscripts/
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golovchak, R., Wang, S., Jain, H. et al. Positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy of nano/macroporous bioactive glasses. Journal of Materials Research 27, 2561–2567 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.252
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.252