Abstract
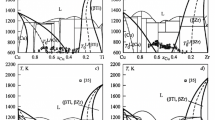
We propose a phenomenological Landau theory to describe polymorphic melting in binary solid solutions. We use the mean atomic displacement as the primary order parameter to represent the loss of the long-range order and the elastic strain induced by alloy component as the secondary order parameter. Under polymorphic constraint where alloy concentration fluctuation is restricted, the model predicts the melting line, also called T0-curve that is depressed by two factors, the static strain field caused by the solute, and the anharmonicity induced by the thermal vibration. We also obtain other thermodynamic properties at and around the melting point. The results confirm well with available experimental results for dilute solutions. We extrapolate the melting line to high concentration region for which no experimental data are available. From the results, we discuss the relation between polymorphic melting and glass transition, as well as glass formability.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.R. Ubbelhode: The Molten State of Matter: Melting and Crystal Structure (Wiley, New York, 1979).
M. Born: Thermodynamics of crystals and melting. J. Chem. Phys. 7, 591 (1939).
M. Born: On the stability of crystal lattices I. Proc. Cambridge Philos. Soc. 36, 160 (1940).
M. Born: Dynamical Theory of Crystal Lattices (Oxford University Press, 1998).
F.A. Lindemann: The calculation of molecular vibration frequencies. Phys. Z. 11, 609 (1910)
J.J. Gilvarry: The Lindemann and Grüneisen laws. Phys. Rev. 102, 308 (1956).
J.L. Tallon, W.H. Robinson, and S.I. Smedley: A melting criterion based on the dilatation dependence of shear modulii. Nature 266, 337 (1977)
J.L. Tallon: Crystal instability and melting. Nature 299, 188 (1982)
J.L. Tallon: A hierarchy of catastrophes as a succession of stability limits for the crystalline state. Nature 342, 658 (1989).
T. Gorecki: Vacancies and changes of physical-properties of metals at melting-point. Z. Metallkde. 65, 426 (1974)
T. Gorecki: Comments on vacancies and melting. Scr. Metall. 11, 1051 (1977).
J.E. Lennard and A.F. Devonshire: Critical and co-operative phenomena III. A theory of melting and the structure of liquids. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 169, 317 (1939)
K. Nordlund and R.S. Averback: Role of self-interstitial atoms on the high temperature properties of metals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 4201 (1998).
T. Ninomiya: Theory of melting, dislocation model I. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 44, 263 (1978).
A. Kanigel, J. Adler, and E. Polturak: Influence of point defects on the shear elastic coefficients and on the melting temperature of copper. Int. J. Mod. Phys. 12, 727 (2001)
X.M. Bai and M. Li: Ring-diffusion mediated homogeneous melting in the superheating regime. Phys. Rev. B 77, 134109 (2008).
D.R. Uhlmann: On the internal nucleation of melting. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 41, 347 (1980).
R.W. Cahn: Melting and the surface. Nature 323, 668 (1986).
M.A. Krivogla: Theory of X-Ray and Thermal Neutron Scattering by Real Crystals (Plenum Press, New York, 1969)
W.F. Kuhs: Generalized atomic displacements in the crystallographic structure analysis. Acta Cryst. A 48, 80 (1992).
A. Voronel, S. Rabinovich, A. Kisliuk, V. Steinburg, and T. Sverbilov: Universality of physical properties of disordered alloys. Phys. Rev. Lett. 60, 2402 (1988)
N.Q. Lam and P.R. Okamoto: A unified approach to solid-state amorphization and melting. Mater. Res. Soc. Bull. XIX 7, 41 (1994)
N.Q. Lam, P.R. Okamoto, and M. Li: Defect-induced crystal-to-glass transition. J. Nucl. Mater. 251, 89 (1997).
D.A. Porter and K.E. Easterling: Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloys, 2nd ed. (Chapman & Hall, 1992).
D.S. Kamenatskaya: in Growth of Crystals, Vol. 8, edited By N.N. Shefta (Consultants Bureau, New York, 1969), p. 271.
W.P. Allen, H.J. Fecht, and J.H. Perepezko: Melting behavior of Sn–Bi alloy droplets during continuous heating. Scr. Metall. 23, 643 (1989)
K.R. Lee, J.A. West, P.M. Smith, M.J. Aziz, and J.A. Knapp: Measurements of T0 temperatures of supersaturated Si–As alloys. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 205, 31 (1992).
W.L. Johnson: Thermodynamic and kinetic aspects of the crystal to glass transformation in metallic materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 30, 81 (1986).
M. Li, W.L. Johnson, and W.A. Goddard III: Configurationally frozen defects, random strains and Landau theory of crystal to glass transition. Mater. Forum 43, 246 (1995)
R.A. Cowley: Structural phase transitions. I. Landau theory. Adv. Phys. 29, 1 (1980)
R. Lipowsky: Critical surface phenomena at first order bulk transitions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 49, 1575 (1982)
H. Löwen and R. Lipowsky: Surface melting away from equilibrium. Phys. Rev. B 43, 3507 (1991).
C.E. Krill III, J. Li, C.M. Garland, C. Ettl, K. Samwer, W.B. Yelon, and W.L. Johnson: Precursors of amorphization in supersaturated Nb–Pd solid solutions. J. Mater. Res. 10, 280 (1995).
T.B. Massalski and H. Okamoto: Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams (ASM International, OH, 1992).
J.A. Kittz, R. Reitano, M.J. Aziz, D.P. Brunco, and M.O. Thompson: Time-resolved temperature measurements during rapid solidification of Si–As alloys induced by pulsed-laser melting. J. Appl. Phys. 73, 3725 (1993).
P.S. Peercy, M.O. Thompson, and J.Y. Tsao: Effects of As impurities on the solidification velocity of Si during pulsed laser annealing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 47, 244 (1985)
P. Baeri, R. Reitano, A.M. Malvezzi, and A. Borghesi: Pulsed laser melting of Si–As supersaturated solid solutions. J. Appl. Phys. 67, 1801 (1990).
L.V. Gurvich and I.V. Veyts: Thermodynamic Properties of Individual Substances: Elements and Compounds, Vol 2, 4th ed. (Hemisphere Pub. Corp., CRC Press, 1990).
S.P. Nikanorov, Yu.A. Burenkov, and A.V. Stepanov: Elastic properties of silicon. Sov. Phys. Solid State 13, 2516 (1971).
P.J. Mohr, B.N. Taylor, and D.B. Newell: CODATA recommended values of the fundamental physical constants. Rev. Mod. Phys. 80, 633 (2008).
R. Hull: Properties of Crystalline Silicon (INSPEC, London, 1999).
R.W. Cahn and P. Haasen: Physical Metallurgy, 4th ed. (North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1996), pp. 686–687.
J.L. Murray: Calculations of stable and metastable equilibrium diagrams of the Ag–Cu and Cd–Zn systems. Metall. Trans. A 15, 261 (1984).
M. Li and W.L. Johnson: Instability of metastable solid solutions and crystal to glass transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1120 (1993).
W.L. Johnson, M. Li, and C.E. Krill III: The crystal to glass transition in relation to melting. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 156-158, 481 (1993).
M. Li, W.L. Johnson, and W.A. Goddard III: Evidence of hexatic phase formation in 2-dimensional Lennard–Jones binary arrays. Phys. Rev. B 54, 12067 (1996).
M. Li: Defect-induced topological order-to-disorder transition in two-dimensional binary substitutional alloys: A molecular dynamics study. Phys. Rev. B 62, 13979 (2000).
P. Jalali and M. Li: Atomic size effect on critical cooling rate and glass formability. Phys. Rev. B 71, 013450 (2005).
H.J. Lee, T. Cagain, W.L. Johnson, and W.A. Goddard: Criteria for formation of metallic glasses: The role of atomic size ratio. J. Chem. Phys. 119, 9858 (2003).
T. Egami and Y. Waseda: Atomic size effect on the formability of metallic glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 64, 113 (1984).
T. Egami: Universal criterion for metallic glass formation. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 226, 261 (1993).
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support to this work provided partially by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. NSF-0907320. M.L. is also grateful for the partial support by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. PHY05-51164 at Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics in University of California, Santa Barbara, where a part of this work was done.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Li, M. A theory for polymorphic melting in binary solid solutions. Journal of Materials Research 26, 997–1005 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2011.55
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2011.55