Abstract
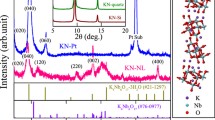
Ferroelectric K0.5Na0.5NbO3 (KNN) thin films were prepared by a chemical solution deposition approach with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) of different molecular weights introduced in the precursor solutions. The volatilization of the alkali ions and the effects of the molecular weight of PVP were examined with x-ray diffraction (XRD), thermal analysis, mass spectrometry, and x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The results clearly showed that the volatilization of the alkali ions mainly happened at moderate temperatures before the crystallization of the KNN perovskite phase. Loss of Na was more significant than K ions during the heating process of KNN. The introduction of PVP with the appropriate molecular weight could effectively promote the crystallization of the KNN perovskite phase at reduced temperature and substantially suppress the loss of the alkali ions before crystallization. Therefore, a high dielectric constant, piezoelectric coefficient, and well saturated ferroelectric hysteresis loops were obtained in the KNN films in which PVP of the right molecular weight were introduced.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.F. Li, K. Wang, B.P. Zhang, and L.M. Zhang: Ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties of fine-grained Na0.5K0.5NbO3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics prepared by spark plasma sintering. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 89, 706 (2006).
M. Matsubara, K. Kikuta, and S. Hirano: Piezoelectric properties of (K0.5Na0.5)(Nb1-xTax) O3-K5.4CuTa10O29 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 114105 (2005).
Y. Saito, H. Takao, T. Tani, T. Nonoyama, K. Takatori, T. Homma, T. Nagaya, and M. Nakamura: Lead-free piezoceramics. Nature 432, 84 (2004).
C. Zaldo, D.S. Gill, R.W. Eason, J. Mendiola, and P.J. Chandler: Growth of KNbO3 thin films on MgO by pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 65, 502 (1994).
Z. Yin, P. Zhang, and M.S. Zhang: Lattice matching, phase matching, and constituent consistency of optical waveguide Ba2NaNb5O15 films on KTiOPO4. Appl. Phys. Lett. 68, 2303 (1996).
Y. Nakashima, W. Sakamoto, H. Maiwai, T. Shimura, and T. Yogo: Lead-free piezoelectric (K,Na)NbO3 thin films derived from metal alkoxide precursors. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 46, L311 (2007).
Y. Nakashima, W. Sakamoto, T. Shimura, and T. Yogo: Chemical processing and characterization of ferroelectric (K,Na)NbO3 thin films. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 46, 6971 (2007).
F.P. Lai and J.F. Li: Sol-gel processing of lead-free (Na,K)NbO3 ferroelectric films. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 42, 287 (2007).
K. Tanaka, H. Hayashi, K.I. Kakimoto, H. Ohsato, and T. Iijima: Effect of (Na,K)-excess precursor solutions on alkoxy-derived (Na,K)NbO3 powders and thin films. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 46, 6964(2007).
C.R. Cho and A. Grishi: Background oxygen effects on pulsed laser deposited Na0.5K0.5NbO3 films: From superparaelectric state to ferroelectricity. J. Appl. Phys. 87, 4439 (2000).
M.V. Romanov, I.E. Korsakov, A.R. Kaul, S.Y. Stefanvich, I.A. Bolshakov, and G. Wahl: MOCVD of KNbO3 ferroelectric films and their characterization. Chem. Vap. Deposition 10, 318 (2004).
T. Lu, X.M. Chen, D.Z. Jin, and X. Hu: Dielectric and ferroelectric properties of (1–x) (Na0.5K0.5)NbO3-xBaTiO3 ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 40, 1847 (2005).
L.Y. Wang, K. Yao, and W. Ren: Piezoelectric K0.5Na0.5 NbO3 thick films derived from polyvinylpyrrolidone-modified chemical solution deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 092903 (2008).
K. Yao and F.E.H. Tay: Measurement of longitudinal piezoelectric coefficient of thin films by a laser-scanning vibrometer. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 50, 113 (2003).
Y. Narendar and G.L. Messing: Kinetic analysis of combustion synthesis of lead magnesium niobate from metal carboxylate gels. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80, 915 (1997).
S.H. Yu, K. Yao, and F.E.H. Tay: Structure and properties of (1–x)PZN -xPT thin films with perovskite phase promoted by polyethylene glycol. Chem. Mater. 18, 5343 (2006).
S.H. Yu, K. Yao, S. Shannigrahi, and F.E.H. Tay: Effects of polyethylene glycol) additive molecular weight on the micro-structure and properties of sol-gel-derived lead zirconate titanate thin films. J. Mater. Res. 18, 737 (2003).
Y.H. Lee, J.H. Cho, B.I. Kim, and D.K. Choi: Piezoelectric properties and densification based on control of volatile mass of potassium and sodium in (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3 ceramics. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 47, 4620 (2008).
N. Kaufherr, D.J. Eichorst, and D.A. Payne: X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy studies of alkoxide-derived lithium niobate. J. Vac. Sci. Technol.A, 14, 299 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Yao, K., Phoi Chin, G. et al. Volatilization of alkali ions and effects of molecular weight of polyvinylpyrrolidone introduced in solution-derived ferroelectric K0.5Na0.5NbO3 films. Journal of Materials Research 24, 3516–3522 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0433
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0433