Abstract
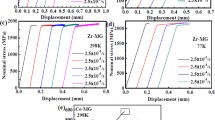
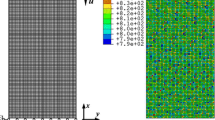
A constitutive theory for metallic glasses is established that is based mainly on the Drucker-Prager model and a free-volume theory. The primary emphasis of this theory is on volume dilatation and its consequences on mechanical responses in metallic glasses that have been known from studies in both experiments and atomistic simulations. We also implemented the constitutive theory in a finite element modeling scheme and conducted numerical modeling of deformation of a metallic glass under plane-strain tension and compression. In particular, we focused our attention on the deviation of the shear band inclination angle, a commonly observed phenomenon for metallic glasses. We found very good qualitative agreement with available experimental data on shear band inclination angle and stress-strain relation. We also give a detailed discussion on different constitutive models, in particular the Coulomb-Mohr model, in the context of predicting the shear band inclination angle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.A. Davis and Y.T. Yeow: Flow and fracture of a Ni-Fe metallic-glass. J. Mater. Sci. 15, 230 (1980).
P.E. Donovan: Compressive deformation of amorphous Pd40Ni40P20. Mater. Sci. Eng. 98, 487 (1988).
P.E. Donovan: A yield criterion for Pd40Ni40P20 metallic-glass. Acta Metall. 37, 445 (1989).
C.T. Liu, L. Heatherly, D.S. Easton, C.A. Carmichael, J.H. Schneibel, C.H. Chen, J.L. Wright, M.H. Yoo, J.A. Horton, and A. Inoue: Test environments and mechanical properties of Zr-base bulk amorphous alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 29, 1811 (1998).
P. Lowhaphandu, S.L. Montgomery, and J.J. Lewandowski: Effects of superimposed hydrostatic pressure on flow and fracture of a Zr-Ti-Ni-Cu-Be bulk amorphous alloy. Scr. Mater. 41, 19 (1999).
K.M. Flores and R.H. Dauskardt: Mean stress effects on flow localization and failure in a bulk metallic glass. Acta Mater. 49, 2527 (2001).
K.M. Flores and R.H. Dauskardt: Crack-tip plasticity in bulk metallic glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 319, 511 (2001).
R. Vaidyanathan, M. Dao, G. Ravichandran, and S. Suresh: Study of mechanical deformation in bulk metallic glass through instrumented indentation. Acta Mater. 49, 3781 (2001).
W.J. Wright, R. Saha, and W.D. Nix: Deformation mechanisms of the Zr40Ti14Ni10Cu12Be24 bulk metallic glass. Mater. Trans. 42, 642 (2001).
M. Li, J. Eckert, L. Kecskes, and J. Lewandowski: Mechanical properties of metallic glasses and applications—Introduction. J. Mater. Res. 22, 255 (2007).
A.C. Lund and C.A. Schuh: The Mohr-Coulomb criterion from unit shear processes in metallic glass. Intermetallics 12, 1159 (2004).
A.C. Lund and C.A. Schuh: Yield surface of a simulated metallic glass. Acta Mater. 51, 5399 (2003).
Z.F. Zhang, G. He, J. Eckert, and L. Schultz: Fracture mechanisms in bulk metallic glassy materials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 045505 (2003).
M. Zhao and M. Li: Unpublished results.
L. Anand and C. Su: A theory for amorphous viscoplastic materials undergoing finite deformations, with application to metallic glasses. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 53, 1362 (2005).
P. Tandaiya, R. Narasimhan, and U. Ramamurty: Mode I crack tip fields in amorphous materials with application to metallic glasses. Acta Mater. 55, 6541 (2007).
Q.K. Li and M. Li: Atomic scale characterization of shear bands in an amorphous metal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 241903 (2006).
Q.K. Li and M. Li: Free volume evolution in metallic glasses subjected to mechanical deformation. Mater. Trans. 48, 1816 (2007).
M. Wakeda, Y. Shibutani, S. Ogata, and J. Park: Relationship between local geometrical factors and mechanical properties for Cu-Zr amorphous alloys. Intermetallics 15, 139 (2007).
A.R. Yavari, A. Le Moulec, A. Inoue, N. Nishiyama, N. Lupu, E. Matsubara, W.J. Botta, G. Vaughan, M. Di Michiel, and A. Kvick: Excess free volume in metallic glasses measured by x-ray diffraction. Acta Mater. 53, 1611 (2005).
K.M. Flores, D. Suh, R.H. Dauskardt, P. Asoka-Kumar, P.A. Sterne, and R.H. Howell: Characterization of free volume in a bulk metallic glass using positron annihilation spectroscopy. J. Mater. Res. 17, 1153 (2002).
M. Heggen, F. Spaepen, and M. Feuerbacher: Creation and annihilation of free volume during homogeneous flow of a metallic glass. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 033506 (2005).
R.S. Vallery, M. Liu, D.W. Gidley, M.E. Launey, and J.J. Kruzic: Characterization of fatigue-induced free volume changes in a bulk metallic glass using positron annihilation spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 261908 (2007).
H. Eyring: Viscosity, plasticity, and diffusion as examples of absolute reaction rates. J. Chem. Phys. 4, 283 (1936).
F. Spaepen: Microscopic mechanism for steady-state inhomoge-neous flow in metallic glasses. Acta Metall. 25, 407 (1977).
Q.K. Li and M. Li: Atomistic simulations of correlations between volumetric change and shear softening in amorphous metals. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 75, 094101 (2007).
M. Zhao and M. Li: Interpreting the change in shear band inclination angle in metallic glasses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 241906 (2008).
D.C. Drucker and W. Prager: Soil mechanics and plastic analysis or limit design. Q. Appl. Math. 10, 157 (1952).
P.S. Steif, F. Spaepen, and J.W. Hutchinson: Strain localization in amorphous metals. Acta Metall. 30, 447 (1982).
R. Huang, Z. Suo, J.H. Prevost, and W.D. Nix: Inhomogeneous deformation in metallic glasses. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 50, 1011 (2002).
Y.F. Gao: An implicit finite element method for simulating inho-mogeneous deformation and shear bands of amorphous alloys based on the free-volume model. Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 14, 1329 (2006).
J.D. Eshelby: The continuum theory of lattice defects, in Solid State Physics, edited by F. Seitz and D. Turnbull (Academic Press, Inc., New York, 1956), p. 79.
W.F. Chen: Plasticity in Reinforced Concrete (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1982), p. 216.
P.B. Bowden and J.A. Jukes: Plastic-flow of isotropic polymers. J. Mater. Sci. 7, 52 (1972).
R. Hill: On discontinuous plastic states, with special reference to localized necking in thin sheets. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1, 19 (1952).
Y.Z. Guo and M. Li: Unpublished results.
Q.K. Li and M. Li: Assessing the critical sizes for shear band formation in metallic glasses from molecular dynamics simulation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 231905 (2007).
L.A. Davis: Plastic instability in a metallic glass. Scr. Metall. 9, 339 (1975).
H. Kimura and T. Masumoto: Deformation and fracture of an amorphous Pd-Cu-Si alloy in V-notch bending tests. 1. Model mechanics of inhomogeneous plastic-flow in non-strain hardening solid. Acta Metall. 28, 1663 (1980).
H.J. Leamy, H.S. Chen, and T.T. Wang: Plastic-flow and fracture of metallic glass. Metall. Trans. 3, 699 (1972).
C.A. Pampillo and D.E. Polk: Strength and fracture characteristics of Fe, Ni-Fe and Ni-base glasses at various temperatures. Acta Metall. 22, 741 (1974).
L.A. Davis and S. Kavesh: Deformation and fracture of an amorphous metallic alloy at high-pressure. J. Mater. Sci. 10, 453 (1975).
R.D. Conner, A.J. Rosakis, W.L. Johnson, and D.M. Owen: Fracture toughness determination for a beryllium-bearing bulk metallic glass. Scr. Mater. 37, 1373 (1997).
H.A. Bruck, T. Christman, A.J. Rosakis, and W.L. Johnson: Quasi-static constitutive behavior of Zr41.25Ti13.75Ni10Cu12.5Be22.5 bulk amorphous-alloys. Scr. Metall. Mater. 30, 429 (1994).
T.W. Webb, X.H. Zhu, and E.C. Aifantis: A simple method for calculating shear band angles for pressure sensitive plastic materials. Mech. Res. Commun. 24, 69 (1997).
C.A. Schuh, T.C. Hufnagel, and U. Ramamurty: Overview No. 144—Mechanical behavior of amorphous alloys. Acta Mater. 55, 4067 (2007).
C.H. Hsueh, H. Bei, C.T. Liu, P.F. Becher, and E.P. George: Shear fracture of bulk metallic glasses with controlled applied normal stresses. Scr. Mater. 59, 111 (2008).
M. Kuroda and T. Kuwabara: Shear-band development in polycrystal-line metal with strength-differential effect and plastic volume expansion. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 458, 2243 (2002).
P. Thamburaja and R. Ekambaram: Coupled thermo-mechanical modelling of bulk-metallic glasses: Theory, finite-element simulations and experimental verification. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 55, 1236 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, M., Li, M. A constitutive theory and modeling on deviation of shear band inclination angles in bulk metallic glasses. Journal of Materials Research 24, 2688–2696 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0306
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0306