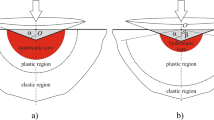
Abstract
In our previous paper [Feng et al., Acta Mater. 55, 2929 (2007)], an analytical model is proposed to estimate the stress field around an elastoplastic indentation/contact, matching nicely with the finite element analysis. The model is related to an embedded center of dilatation (ECD) in a half-space. In this paper, we focus on determining the ECD strength B* and the ECD depth ξ. By matching an expanding cavity model and the ECD model, we find that B* ≈ Yc3/6 and ξ ≈ 0.4c, where Y is the yield strength and c is the plastic zone radius. We provide a method to predict Y, c, and thereby B* as well as ξ through nanoindentation data, and we also demonstrate that pileup is the physical reason for the existence of the upper limit for the ratio of hardness to Y. Thus, our ECD model is completed by combining our previous paper (the analytical expression) and this paper (the essential parameters).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Tangand and A.H.W. Ngan: Nanoindentation measurement of mechanical properties of soft solid covered by a thin liquid film. Soft Materials 5, 169 (2007).
G. Feng and A.H.W. Ngan: Creep and strain burst in indium and aluminium during nanoindentation. Scr. Mater. 45, 971 (2001).
G. Feng and W.D. Nix: Indentation size effect in MgO. Scr. Mater. 51, 599 (2004).
K.L. Johnson: Contact Mechanics (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, New York, 1987).
A.K. Bhattacharya and W.D. Nix: Finite-element simulation of indentation experiments. Int. J. Solids Struct. 24, 881 (1988).
A.C. Fischer Cripps: Elastic-plastic behaviour in materials loaded with a spherical indenter. J. Mater. Sci. 32, 727 (1997).
S.S. Chiang, D.B. Marshall, and A.G. Evans: The response of solids to elastic plastic indentation. 1. Stresses and residual-stresses. J. Appl. Phys. 53, 298 (1982).
S. Biwa and B. Storakers: An analysis of fully plastic Brinell indentation. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 43, 1303 (1995).
B. Storakers, S. Biwa, and P.L. Larsson: Similarity analysis of inelastic contact. Int. J. Solids Struct. 34, 3061 (1997).
B. Storakers and P.L. Larsson: On Brinell and Boussinesq indentation of creeping solids. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 42, 307 (1994).
E.H. Yoffe: Elastic stress-fields caused by indenting brittle materials. Philos. Mag. A 46, 617 (1982).
G. Feng, S. Qu, Y. Huang, and W.D. Nix: An analytical expression for the stress field around an elastoplastic indentation/contact. Acta Mater. 55, 2929 (2007).
B. Noble and D.A. Spence: Formulation of Two-Dimensional and Axisymmetric Problems for an Elastic Half-Space (Mathematics Research Center, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, 1971).
R. Hill: The Mathematical Theory of Plasticity (Clarendon Press, Oxford, UK, 1983).
D. Tabor: The Hardness of Metals (Clarendon Press, Oxford, UK, 1951).
F.J. Lockett: Indentation of rigid/plastic material by conical indenter. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 11, 345 (1963).
T.O. Mulhearn: Deformation of metals by Vickers-type pyramidal indenters. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 7, 85 (1959).
L.E. Samuels and T.O. Mulhearn: An experimental investigation of the deformed zone associated with indentation hardness impressions. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 5, 125 (1957).
A.E.H. Love: A Treatise on the Mathematical Theory of Elasticity, 4th ed. (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1927).
R.F. Cook and G.M. Pharr: Direct observation and analysis of indentation cracking in glasses and ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 73, 787 (1990).
D.J. Morris and R.F. Cook: Radial fracture during indentation by acute probes: I, Description by an indentation wedging model. Int. J. Fract. 136, 237 (2005).
X.N. Jing, S. Maiti, and G. Subhash: A new analytical model for estimation of scratch-induced damage in brittle solids. J. Am. Cerarti. Soc. 90, 885 (2007).
D. Tabor: Indentation hardness and its measurements: Some cautionary comments, in Microindentation Techniques in Materials Science and Engineering: A Symposium Sponsored by ASTM Committee E-4 on Metallography and by the International Metallographic Society, 15–18 July 1984 (International Metallographic Society, Philadelphia, PA, 1986), p. 129.
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic-modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992).
R.D. Mindlin and D.H. Cheng: Thermoelastic stress in semi-infinite solid. J. Appl. Phys. 21, 931 (1950).
D. Kramer, H. Huang, M. Kriese, J. Robach, J. Nelson, A. Wright, D. Bahr, and W.W. Gerberich: Yield strength predictions from the plastic zone around nanocontacts. Acta Mater. 47, 333 (1998).
G.M. Pharr and A. Bolshakov: Understanding nanoindentation unloading curves. J. Mater. Res. 17, 2660 (2002).
A.K. Ghosal and S.K. Biswas: Examination of stress-fields in elastic plastic indentation. Philos. Mag. B 67, 371 (1993).
M.S. Bobji and S.K. Biswas: Determination and study of the strength of the blister field generated by conical indentation. Philos. Mag. A 73, 399 (1996).
A. Mukhopadhyay and S.K. Biswas: Indentation of sintered alumina clay composite—An experimental discussion of a combined Boussinesq and blister stress-field approach. Philos. Mag. Lett. 64, 77 (1991).
W.P. Yu and J.P. Blanchard: An elastic-plastic indentation model and its solutions. J. Mater. Res. 11, 2358 (1996).
Y.T. Cheng and C.M. Cheng: Scaling relationships in conical indentation of elastic perfectly plastic solids. Int. J. Solids Struct. 36, 1231 (1999).
I.N. Sneddon: Fourier Transforms (McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1951).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, G., Qu, S., Huang, Y. et al. A quantitative analysis for the stress field around an elastoplastic indentation/contact. Journal of Materials Research 24, 704–718 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0097
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0097