Abstract
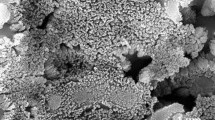
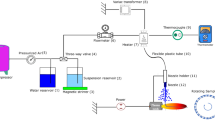
Suspension plasma spraying was used to synthesize Y2O3 nanoparticles. The Y2O3 starting material was first dispersed in a solvent to form a suspension and then injected axially into the plume of an inductive radio frequency plasma. It was found that the as-sprayed Y2O3 particles had a size distribution from nano to micron scale and various morphological features, which varied with processing conditions as well as solvent and plasma gas type. In comparison with water, organic solvents led to a higher productivity and smaller particle size, whereas water introduced impurities such as Y2O2C2, which is isotypic to La2O2C2. Introduction of oxygen as an auxiliary plasma gas was an effective way to eliminate this impurity. In addition, complete combustion of the organic solvent and recombination of oxygen atoms above 4000 K also elevated the heat treatment degree of Y2O3. As a result, application of O2 with an organic solvent resulted in an even smaller mean particle size and narrower size distribution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.R. Ronda, T. Jüstel, and H. Nikol: Rare earth phosphors: Fundamentals and applications. J. Alloys Compd. 275–277, 669 (1998).
O. Forlani and S. Rossini: Rare earths as catalysts for the oxidative coupling of methane to ethylene. Mater. Chem. Phys. 31, 155 (1992).
A.I.Y Tok, L.H. Luo, F.Y.C Boey, and S.H. Ng: Consolidation and properties of Gd0.1Ce0.9O1.95 nano-particles for SOFC electrolytes. J. Mater. Res. 21, 119 (2006).
H. Kishi, Y. Mizuno, and H. Chazono: Base-metal electrode-multilayer ceramic capacitors: Past, present and future perspectives. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 42, 1 (2003).
C.C. Koch: Nanostructured Materials—Processing, Properties and Potential Applications (William Andrew Publishing / Noyes, New York, 2002), p. 3.
Y.M. Miao, Q.L. Zhang, H. Yang, and H.P. Wang: Low-temperature synthesis of nano-crystalline magnesium titanate materials by the sol-gel method. Mater. Sci. Eng., B 128, 103 (2006).
F. Wang, X.P. Fan, D.B. Pi, and M.Q. Wang: Hydrothermal synthesis of Nd3+-doped orthoborate nanoparticles that emit in the near-infrared. J. Solid State Chem. 177, 3346 (2004).
R.B. Zhang and L. Gao: Preparation of nanosized titania by hydrolysis of alkoxide titanium in micelles. Mater. Res. Bull. 37, 1659 (2002).
G.F. Gaertner and P.F. Miquel: Particle generation by laser ablation from solid targets in gas flows. Nanostruct. Mater. 4, 559 (1993).
R. Jossen, R. Mueller, S.E. Pratsinis, M. Watson, and M.K. Akhtar: Morphology and composition of spray-flame-made yttria-stabilized zirconia nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 16, 609 (2005).
R. Kumar, P. Cheang, and K.A. Khor: Radio frequency (RF) suspension plasma sprayed ultra-fine hydroxyapatite (HA)/zirconia composite powders. Biomaterials 24, 2611 (2003).
T. Ishigaki, S.M. Oh, J.G. Li, and D.W. Park: Controlling the synthesis of TaC nanopowders by injecting liquid precursor into RF induction plasma. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 6, 111 (2005).
M. Sugasawa, N. Kikukawa, N. Ishikawa, N. Kayano, and T. Kimura: Synthesis of Y–Fe–O ultrafine particles using inductively coupled plasma. J. Aerosol Sci. 29, (5/6), 675 (1998).
F. Gitzhofer, E. Bouyer, and M.I. Boulos: Suspension plasma spray. U.S. Patent No. 5 609 921 (3 November 1997).
E. Bouyer, F. Gitzhofer, and M.I. Boulos: Suspension plasma spraying for hydroxyapatite powder preparation by RF plasma. IEEE T. Plasma Sci. 25, 1066 (1997).
M. Vardelle, A. Vardelle, P. Fauchais, K.I. Li, B. Dussoubs, and N.J. Themelis: Controlling particle injection behavior relationship in plasma spraying. J. Therm. Spray Tech. 10, 267 (2001).
National Institute of Standards & Technology, Standard Reference Material 660a, Certificate Issue Date: 13 September 2000.
R.W. Cheary and A.A. Coelho: A fundamental parameter approach to x-ray line profile fitting. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 25, 109 (1992).
R. Ye, P. Proulx, and M.I. Boulos: Turbulence phenomena in the radio frequency induction plasma torch. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 42, 1585 (1999).
PDF-2 Database, International Center of Diffraction Data, Release 1998.
A.D. Butherus and H.A. Eick: Preparation, characterization and some thermodynamic properties of lanthanum oxide carbide, La2O2C2. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 35, 1925 (1973).
R.L. Seiver and H.A. Eick: The crystal structure of dilanthanum dioxide dicarbide, La2O2C2. J. Less-Comm. Mater. 44, 1 (1976).
X.L. Sun, A.I.F Tok, R. Huebner, and F.Y.C Boey: Phase transformation of ultrafine rare earth oxide powders synthesized by radio frequency plasma spraying. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 27, 125 (2007).
M.T. Swihart: Vapor-phase synthesis of nanoparticles. Curr. Opin. Colloid In. 8, 127 (2003).
A.B. Murphy and C.J. Arundell: Transport coefficients of argon, nitrogen, oxygen, argon-nitrogen, and argon-oxygen plasmas. Plasma Chem. Plasma. 451, 14 (1994).
G. Baldinozzi, J.F. Berar, and G. Calvarin: Rietveld refinement of two-phase Zr-doped Y2O3. Mater. Sci. Forum 278, 680 (1998).
P. Fauchais: Understanding plasma spraying. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 37, 86 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, X.L., Tok, A.I.Y., Boey, F.Y.C. et al. Solvent and plasma gas influence on the synthesis of Y2O3 nanoparticles by suspension plasma spraying. Journal of Materials Research 22, 1306–1313 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2007.0161
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2007.0161