Abstract
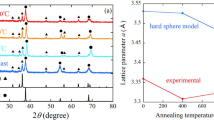
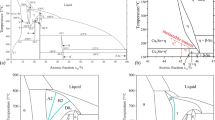
The kinetics of intermetallic compound (IMC) layer and Cu dissolution at Sn1.5Cu/Cu interface under high magnetic field was experimentally examined. It is found that the IMC layer growth is controlled by flux-driven ripening process. The high magnetic field promotes the growth of IMC layer, retards the dissolution of Cu substrate, and decreases the content of Cu solute at the liquid–IMC interface front. Based on the experimental results, it is considered that the magnetization induced by magnetic field promotes the ripening process for IMC layer growth. The Lorentz force dampening the convection and magnetization decreasing the Cu solubility limit can retard the Cu dissolution and change the solute distribution at the liquid–IMC interface front.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J-W Yoon, J-H Lim, H-J Lee, J. Joo, S-B Jung, W-C Moon Interfacial reactions and joint strength of Sn–37Pb and Sn–3.5Ag solders with immersion Ag-plated Cu substrate during aging at 150 °C. J. Mater. Res. 21, 3196 (2006)
J. Zhao, C-Q Cheng, L. Qi, C-Y Chi Kinetics of intermetallic compound layers and shear strength in Bi-bearing SnAgCu/Cu soldering couples. J. Alloys Compd. 473, 382 (2009)
Z-F Li, J. Dong, X-Q Zeng, C. Lu, W-J Ding, Z-M Ren Influence of strong static magnetic field on intermediate phase growth in Mg–Al diffusion couple. J. Alloys Compd. 440, 132 (2007)
X. Ren, G-Q Chen, W-L Zhou, C-W Wu, J-S Zhang Effect of high magnetic field on intermetallic phase growth in Ni–Al diffusion couples. J. Alloys Compd. 472, 525 (2009)
Q. Wang, D-G Li, K. Wang, Z-Y Wang, J-C He Effects of high uniform magnetic fields on diffusion behavior at the Cu/Al solid/liquid interface. Scr. Mater. 56, 485 (2007)
D-G Li, Q. Wang, T. Liu, G-J Li, J-C He Growth of diffusion layers at liquid Al–solid Cu interface under uniform and gradient high magnetic field conditions. Mater. Chem. Phys. 117, 504 (2009)
D-G Li, Q. Wang, G-J Li, T. Liu, J-C He High magnetic field controlled interdiffusion behavior at Bi–Bi0.4Sb0.6 liquid/solid interface. J. Mater. Sci. 44, 1918 (2009)
J. Zhao, P. Yang, F. Zhu, C-Q Cheng The effect of high magnetic field on the growth behavior of Sn–3Ag–0.5Cu/Cu IMC layer. Scr. Mater. 54, 1077 (2006)
C-Q Cheng, J. Zhao, Y. Xu Effect of high magnetic field on the morphology of (Cu, Ni)6Sn5 at Sn0.3Ni/Cu interface. Mater. Lett. 63, 1478 (2009)
T. Laurila, V. Vuorinen, J-K Kivilahti Interfacial reactions between lead-free solders and common base materials. Mater. Sci. Eng., R 49, 1 (2005)
A-M Gusak, K-N Tu Kinetic theory of flux-driven ripening. Phys. Rev. B 66, 115403 (2002)
M-L Huang, T. Loeher, A. Ostman, H. Reichl Role of Cu in dissolution kinetics of Cu metallization in molten Sn-based solders. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 181908 (2005)
V.I. Dybkov Growth Kinetics of Chemical Compound Layers 1st ed (Cambridge International Science Publishing, Cambridge, England 1998) 135–138
Y-Y Khine, R-M Banish, Alexander J-I-D. Convective contamination in self-diffusivity experiments with an applied magnetic field. J. Cryst. Growth 250, 274 (2003)
G-M Oreper, J. Szekely The effect of a magnetic field on transport phenomena in a Bridgman–Stockbarger crystal growth. J. Cryst. Growth 67, 405 (1984)
J. Eckert, J-C Holzer, C-E Krill III, W-L Johnson Mechanically driven alloying and grain-size changes in nanocrystalline Fe–Cu powders. J. Appl. Phys. 73, 2794 (1993)
D-A Porter, K-E Easterling, M-Y Sherif Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloys 3rd ed (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, London 2008) 39
J-K Choi, H. Ohtsuka, Y. Xu, W-Y Choo Effects of a strong magnetic field on the phase stability of plain carbon steels. Scr. Mater. 43, 221 (2000)
H. Matsushima, D. Kiuchi, Y. Fukunaka Measurement of dissolved hydrogen supersaturation during water electrolysis in a magnetic field. Electrochim. Acta 54, 5858 (2009)
X. Li, Y. Fautrelle, Z-M Ren, A. Gagnoud, R. Moreau, Y-D Zhang, C. Esling Effect of a high magnetic field on the morphological instability and irregularity of the interface of a binary alloy during directional solidification. Acta Mater. 57, 1689 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Cq., Zhao, J. & Xu, Y. Kinetics of intermetallic compound layers and Cu dissolution at Sn1.5Cu/Cu interface under high magnetic field. Journal of Materials Research 25, 359–367 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2010.0055
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2010.0055