Abstract
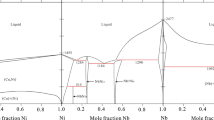
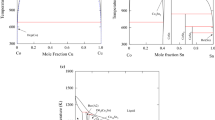
Cu–Zn is an important binary alloy system. In the interested temperature range from 300 to 1500 K, there are eight phases, liquid, Cu, β, β′, γ, δ, ϵ, and Zn phases. The thermodynamic descriptions of the Cu–Zn system are reassessed using the CALPHAD method. A new description of liquid phase and simplified description of body-centered cubic (bcc) phase are proposed. Good agreement has been found among the calculated thermodynamic properties, phase diagram, and the experimental information.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.L. Hoyt: On the copper-rich kalchoids. J. Inst. Met. 10(2), 235 1904
W. Campbell: A note on the constitution of certain tin-bearing brasses. ASTM Proc., 105, (1920).
D.J. Strawbridge, W. Hume-Rothery, A.T. Little: The constitution of aluminum–copper–magnesium–zinc alloys. at 460 °C. J. Inst. Met. 74, 191 1948
Registration Record of International Alloys Designations and Chemical Composition Limits for Wrought Aluminum and Wrought Aluminum Alloys The Aluminum Association Washington, DC 1987
C-Y. Chou, S-W. Chen: Phase equilibria of the Sn–Zn–Cu ternary system. Acta Mater 54(9), 2393 2006
C-Y. Chou, S-W. Chen, Y-S. Chang: Interfacial reactions in the Sn–9Zn–(xCu)Cu and Sn–9Zn–(xCu)Ni couples. J. Mater. Res. 21(7), 1849 2006
K. Fitzner, D. Jendrzejczyk, W. Gierlotka: Ninth Seminar Diffusion and Thermodynamics of Materials 2006 Brno, Czech Republic, Sept 13–15 2006
O. Bauer, M. Hansen: Der aufbau der kupfer–zinklegierungen. Z. Metallkd 19, 423 1927 in German
R. Ruer, K. Kremers: Über die Bestimmung der Temperatur des Endes der Erstarrung bei Mischkristallreihen mit Hilfe von Erhitzungskurven. Z. Anorg. Chem 184, 193 1929 in German
J. Shramm: An equilibrium study in the Cu–Zn system. Metallwirtschaft 14, 995–1001 1047–1050 1935
M. Hansen: Handbook of Binary Alloys Springer-Verlag Berlin 1936 652–672
G.V. Raynor: Annotated Equilibrium Diagram Series, No. 3 (The Institute of Metals, London, 1944)
T.B. Massalski, J.L. Murray, L.H. Bennet, H. Baker: Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, edited by T.B. Massalski American Society for Metals Materials Park, OH 1986
G. Shinoda, Y. Amano: The eutectoid transformation of the β′ phase in Cu–Zn alloys. Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met. 1, 54 1960
S.S. Rao, T.R. Anantharaman: Constitution of brasses below 500 °C. Z. Metallkd. 60, 312 1969
K. Parameswaran, G. Healy: A calorimetric investigation of the copper–zinc system. Met. Trans. B 9B, 657 1978
H-O. von Samson-Himmelstjerna: Heat capacity and heat of formation of molten alloys. Z. Metallkd. 28, 197 1936
O.J. Kleppa, R.C. King: Heat of formation of the solid solution of zinc, gallium and germanium in copper. Acta Metall. 10, 1183 1962
R.L. Orr, B.B. Argent: Heats of formation of the α-brasses. Trans. Faraday Soc. 61, 2126 1965
F. Korber, W. Oelsen: On the thermochemistry of alloys, III—Heat of formation of binary cast alloys of iron–antimony, cobalt–antimony, nickel–antimony, cobalt–tin, nickel–tin, copper–tin and copper–zinc. Mitt. K. W. I. Fur Eisenforschung. 19, 202 1937
Z. Weibke: On the heat of formation in the copper–zinc system. Z. Anorg. Chem. 323, 289 1937
G.R. Blair, D.B. Downie: A calorimetric study of silver–zinc and copper–zinc alloys. Met. Sci. J. 4, 1 1979
A. Schneider, H. Schmid: Vapour pressure of zinc and cadmium over their binary liquid alloys with copper, silver and gold. Z. Electrochem. 48, 627 1942
L.H. Everett, P.W.M. Jacobs, J.A. Kitchner: The activity of zinc in liquid copper–zinc alloys. Acta Metall. 5, 281 1957
D.B. Downie: Thermodynamic and structural properties of liquid zinc/copper alloys. Acta Metall. 12, 875 1964
T. Azakami, A. Yazawa: Activities of ink and cadmium in liquid copper base alloys. J. Min. Met. Inst. Jpn. 84, 1663 1968
S.L. Solovev, M.V. Knyazev, Y.I. Ivanov, A.V. Vanyukov: Mass spectrometric study of the partial characteristics of zinc in copper–zinc system. Zavod. Lab. 45, 841 1979
S. Sugino, H. Hagiwara: Activity of zinc in molten copper and copper–gold alloys. Nippon Kinzoku Gakaishi 50, 186 1986
W. Leitgebel: Evaporation of metals and alloys under atmospheric pressure. Z. Angor. Chem. 202, 305 1931
E.H. Baker: Vapour pressure and thermodynamic behaviour of liquid zinc–copper alloys at 1150 °C. Trans. Inst. Min. Metall. C 79, C1 1970
O.J. Kleppa, C.E. Thalmayer: An E.M.F. investigation of binary liquid alloys rich in zinc. J. Phys. Chem. 63, 1953 1959
U. Gerling, B. Predel: On the thermodynamic properties of liquid copper–zinc alloys. Z. Metallkd. 71, 158 1980
B.B. Argent, D.W. Wakeman: Thermodynamic properties of solid solutions, Part I—Copper + zinc solid solution. Trans. Faraday Soc. 54, 799 1958
D.B. Masson, J. Sheu: Variation in the composition dependence of the activity coefficient terminal solid solution of Ag–Zn, Ag–Cd and Cu–Zn. Metall. Trans. 1, 3005 1970
W. Seith, W. Krauss: The diffusion and vapour pressure in zinc in brasses. Z. Electrochem. 44, 98 1938
R. Hargreaves: The vapour pressure of zinc in brasses. J. Inst. Met. 64, 115 1939
J.P. Pemsler, E.J. Rapperport: Thermodynamic activity measurements using atomic absorption: copper–zinc. Trans. AIME 245, 1395 1969
A. Olander: An electrochemical investigation of brasses. Z. Phys. Chem. 164, 428 1933.9
PURE 4.4 SGTE Pure Elements (Unary) Database (Scientific Group Thermodata Europe, 1991–2006)
P.J. Spencer: A thermodynamic evaluation of the Cu–Zn system. Calphad 10, 175 1986
M. Kowalski, P.J. Spencer: Thermodynamic reevaluation of the Cu–Zn system. J. Phase Equilibria 14, 432 1993
ThermoCalc v. R., (Foundation of Computational Thermodynamics, Stockholm, Sweden, 2006).
Pandat, CompuTherm LLC, 437 S. Yellowstone Dr., Suite 217, Madison, WI 5371 9
T. Jantzen, P.J. Spencer: Thermodynamic assessments of the Cu–Pb–Zn and Cu–Sb–Zn systems. Calphad 22, 417 1998
P.W. Atkins, J. de Paula: Atkins’ Physical Chemistry, 7th ed. (Oxford University Press, 2001)
Acknowledgment
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the National Science Council of Taiwan (NSC95-2221-E-007-205).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gierlotka, W., Chen, Sw. Thermodynamic descriptions of the Cu–Zn system. Journal of Materials Research 23, 258–263 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2008.0035
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2008.0035