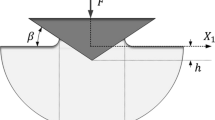
Abstract
Dimensional analysis and finite element modeling were conducted to examine conical indentation in homogeneous materials and in hard films on soft substrates. In this paper, the solid materials modeled follow the incremental theory of plasticity with a von-Mises yield surface. The validity of the Oliver–Pharr method was examined. It was found that, for hard films on soft substrates, the Oliver–Pharr method is applicable only when the indentation depth is less than 10% of the film thickness. A linear relationship between the ratio of hardness to reduced modulus and the ratio of reversible work to total work was observed for conical indentation in homogeneous materials and in hard films on soft substrates. This relationship can be used to analyze instrumented indentation experiments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Bückle: Use of hardness test to determine other material properties, in The Science of Hardness Testing and its Research Applications, edited by J.H. Westbrook and H. Conrad (American Society of Metals, Metals Park, OH, 1973), p. 453–487.
Z.H. Xu and D. Rowcliffe: Finite element analysis of substrate effects on indentation behavior of thin films, Thin Solid Films 447–448, 399 (2004).
B. Jonsson and S. Hogmark: Hardness measurement of thin films, Thin Solid Films 114, 257 (1984).
P.J. Burnett and D.S. Rickerby: Assessment of coating hardness, Surf. Eng. 3, 69 (1987).
A.M. Korsunsky, M.R. McGurk, S.J. Bull and T.F. Page: On the hardness of coated systems, Surf. Coat. Technol. 99, 171 (1998).
R.B. King: Elastic analysis of some punch problems for a layered medium, Int. J. Solids Struct. 23, 1657 (1987).
M.F. Doerner and W.D. Nix: A method for interpreting the data from depth sensing indentation instruments, J. Mater. Res. 1, 601 (1986).
A.K. Bhattacharya and W.D. Nix: Analysis of elastic and plastic deformation associated with indentation testing of thin films on substrates, Int. J. Solids Struct. 24, 1287 (1988).
H. Gao, C. Chu and J. Lee: Elastic contact versus indentation modeling of multi-layered materials, Int. J. Solids Struct. 29, 2471 (1992).
J. Mencik, D. Munz, E. Quandt, E.R. Weppelmann and M.V. Swain: Determination of elastic modulus of thin layers using nanoindentation, J. Mater. Res. 12, 2475 (1997).
R. Saha and W.D. Nix: Effects of the substrate on the determination of thin film mechanical properties by nanoindentation, Acta Mater. 50, 23 (2002).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments, J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: Advances in understanding and refinements to methodology, J. Mater. Res. 19, 3 (2004).
A. Bolshakov and G.M. Pharr: Influences of pileup on the measurement of mechanical properties by load and depth sensing indentation techniques, J. Mater. Res. 13, 1049 (1998).
T.-Y. Cheng and M.-C. Cheng: Effect of ‘sinking in’ and ‘piling up’ on estimating the contact area under load in indentation, Philos. Mag. Lett. 78, 115 (1998).
Y.Y. Lim, M.M. Chaudhri and Y. Enomota: Accurate determination of the mechanical properties of thin aluminum films deposited on sapphire flats using nanoindentations, J. Mater. Res. 14, 2314 (1999).
T.Y. Tsui and G.M. Pharr: Substrate effects on nanoindentation mechanical property measurement of soft films on hard substrates, J. Mater. Res. 14, 292 (1999).
K. Tunvisut, O’N.P. Dowd and E.P. Busso: Use of scaling functions to determine mechanical properties of thin coatings from microindentation tests, Int. J. Solids Struct. 38, 335 (2001).
T.-Y. Cheng and M.-C. Cheng: Relationships between hardness, elastic modulus, and the work of indentation, Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 614 (1998).
T.-Y. Cheng, Z.Y. Li and M.-C. Cheng: Scaling relationships for indentation measurements, Philos. Mag. 82, 1821 (2002).
B.R. Lawn and V.R. Howes: Elastic recovery at hardness indentations, J. Mater. Sci. 16, 2745 (1981).
M. Sakai: Energy principle of the indentation-induced inelastic surface deformation and hardness of brittle materials, Acta Metall. Mater. 41, 1751 (1993).
J. Menick and M.V. Swain: Micro-indentation tests with pointed indenters, Mater. Forum 18, 277 (1994).
A.E. Giannakopoulos and S. Suresh: Determination of elastoplastic properties by instrumented sharp indentation, Scripta Mater. 40, 1191 (1999).
M. Dao, N. Chollacoop, Van K.J. Vliet, T.A. Venkatesh and S. Suresh: Computational modeling of the forward and reverse problems in instrumented sharp indentation, Acta Mater. 49, 3899 (2001).
J. Malzbender and de G. With: Energy dissipation, fracture toughness and the indentation load-displacement curves of coated materials, Surf. Coat. Technol. 135, 60 (2000).
Z.H. Xu and D. Rowcliffe: Method to determine the plastic properties of bulk materials by nanoindentation, Philos. Mag. A 82, 1893 (2002).
W. Ni, T.-Y. Cheng, M.-C. Cheng and D.S. Grummon: An energy-based method for analyzing instrumented spherical indentation experiments, J. Mater. Res. 19, 149 (2004).
I.N. Sneddon: The relaxation between load and penetration in the axisymmetric boussinesq problem for a punch of arbitrary profile, Int. J. Eng. Sci. 3, 47 (1965).
N.M. Jennett, G. Aldrich-Smith and A.S. Maxwell: Validated measurement of Young’s modulus, Poisson ratio, and thickness for thin coatings by combining instrumented nanoindentation and acoustical measurements, J. Mater. Res. 19, 143 (2004).
D. Schneider, P. Siemroth, T. Schulke, J. Berthold, B. Schultrich, H.H. Schneider, R. Ohr and B. Petereit: Quality control of ultra-thin and super-hard coatings by laser-acoustics, Surf. Coat. Technol. 153, 252 (2002).
T. Chudoba, M. Griepentrog, A. Duck, D. Schneider and F. Richter: Young’s modulus measurements on ultra-thin coating, J. Mater. Res. 19, 301 (2004).
G.I. Barenblatt: Scaling, Self-similarity, and Intermediate Asymptotics (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U.K., 1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, W., Cheng, YT. Modeling conical indentation in homogeneous materials and in hard films on soft substrates. Journal of Materials Research 20, 521–528 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2005.0071
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2005.0071