Abstract
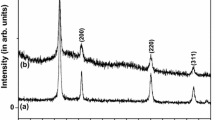
Nanocrystalline CeO2 powder was synthesized by a citrate-nitrate autoignition process and characterized by thermal analysis, x-ray diffraction, and impedance spectroscopy measurements. Nanocrystalline (20–40 nm) ceria powder with fluorite structure had formed in situ during the citrate-nitrate autoignition process. The powder prepared could be sintered to density more than 98% of theoretical density at 1450 °C. The nanocrystalline CeO2 exhibited an increase in conductivity in Ar and H2 than air above 600 °C, suggesting a possible electronic contribution to the conductivity at low oxygen partial pressures. Impedance measurements on the sintered samples unequivocally established the potential of this process in developing phase pure ceria compositions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Inaba and H. Tagawa: Ceria based solid electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 83, 1 (1996).
M. Mogensen, N.M. Sammes, and G.A. Tompsett: Physical, chemical and electrochemical properties of pure and doped ceria. Solid State Ionics 129, 63 (2000).
T.S. Stefanik and H.L. Tuller: Ceria-based gas sensors. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 21, 1967 (2001).
J.R. Jurado: Present several items on ceria-based ceramic electrolytes: Synthesis, additive effects, reactivity and electrochemical behaviour. J. Mater. Sci. 36, 1133 (1993).
V.V. Kharton, F.M. Figueiredo, L. Navarro, E.N. Navmovich, A.V. Kovalevsky, A.A. Varemshnko, A.P. Viskup, A. Carnieiro, F.M.B. Marques, and J.R. Frade: Ceria-based materials for solid oxide fuel cells. J. Mater. Sci. 36, 1105 (2001).
H.L. Tuller: Ionic conduction in nano crystalline materials. Solid State Ionics 131, 143 (2000).
Y.M. Chiang, E.B. Lavik, I. Kosacki, H.L. Tuller, and J.Y. Ying: Defect and transport properties of nanocrystalline CeO2−x. Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 185 (1996).
A. Tschope, J.Y. Ying, and H.L. Tuller: Catalytic redox activity and electrical conductivity of nanocrystalline non-stoichiometric cerium oxide. Sens. Actuators B 31, 111 (1996).
Y.C. Zhou and M.N. Rahaman: Hydrothermal synthesis and sintering of ultrafine CeO2 powders. J. Mater. Res. 8, 1680 (1993).
M. Hirano and E. Kato: The hydrothermal synthesis of ultrafine cerium (IV) oxide ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 15, 1249 (1996).
J.G. Li, T. Ikegami, J.H. Lee, and T. Mori: Characterization and sintering of nanocrystalline CeO2 powders synthesized by a mimic alkoxide method. Acta Mater. 49, 419 (2001).
J. Zhang, X. Ju, Z.Y. Wu, T. Liu, T.D. Hu, Y.N. Xie, and Z.L. Zhang: Structural characterization of cerium oxide nanocrystals prepared by the micro emulsion method. Chem. Mater. 13, 4192 (2001).
X. Chu, W. Chung, and L.D. Schmidt: Sintering of sol-gel prepared submicrometer particles studied by transmission electron microscopy. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 76, 2115 (1993).
P.L. Chen and I.W. Chen: Reactive cerium IV oxide powders by the homogeneous precipitation method. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 76, 1577 (1993).
R.D. Purohit, B.P. Sharma, K.T. Pillai, and A.K. Tyagi: Ultrafine ceria powders via glycine-nitrate combustion. Mater. Res. Bull. 36, 2711 (2001).
S.T. Arun and K.C. Patil: Combustion synthesis and properties of nanostructured ceria-zirconia solid solutions. Nanostruct. Mater. 10, 955 (1998).
S. Nakane, T. Tachi, M. Yoshinaka, K. Hirota, and O. Yamaguchi: Characterization and sintering of reactive cerium IV oxide powders prepared by the hydrazine method. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80, 3221 (1997).
H. Xu, L. Gao, H. Gu, and D. Yan: Synthesis of solid, spherical CeO2 particles prepared by the spray pyrolysis reaction method. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 85, 139 (2002).
Y.C. Zhou, R.J. Philips, and J.A. Switzer: Electrochemical synthesis and sintering of nanocrystalline cerium (IV) oxide powders. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 78, 981 (1995).
P.S. Devi and H.S. Maiti: A novel auto-ignited combustion process for the synthesis of Bi-Pb-Sr-Ca-Cu-O superconductor with a Tc (o) of 125K. J. Solid State Chem. 109, 35 (1994).
P.S. Devi and H.S. Maiti: A modified citrate gel route for the synthesis of phase pure Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8 superconductor. J. Mater. Res. 9, 1357 (1994).
A. Chakraborty, P.S. Devi, S. Roy, and H.S. Maiti: Lowtemperature synthesis of ultrafine La0.84Sr0.16MnO3 powder by an auto-ignition process. J. Mater. Res. 9, 986 (1994).
A. Chakraborty, P.S. Devi, and H.S. Maiti: Preparation of La1-xSrxMnO3 (0<x< 0.6) powder by auto ignition of carboxylate-nitrate gels. Mater. Lett. 20, 63 (1994).
A. Chakraborty, P.S. Devi, and H.S. Maiti: Low-temperature synthesis and some physical properties of barium substituted lanthanum manganite (La1-xBaxMnO3). J. Mater. Res. 10, 918 (1995).
N. Chakrabarti and H.S. Maiti: Chemical synthesis of barium zirconate titanate powder by an autocombustion technique. J. Mater. Chem. 6, 1169 (1996).
P.S. Devi, Y. Lee, J. Margolis, J.B. Parise, S. Sampath, H. Herman, and J.C. Hanson: Comparison of citrate-nitrate gel combustion and precursor plasma spray process for the synthesis of yittrium aluminum garnet. J. Mater. Res. 17, 2846 (2002).
Impedance Spectroscopy Emphasizing Solid Materials and Systems, edited by J.R. MacDonald (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1987).
J.C.C. Abrantes, J.A. Labrincha, and J.R. Frade: Representations of impedance spectra of ceramics. Part I. Simulated study cases. Mater. Res. Bull. 35, 955 (2000).
Z. Zhan, T. Wen, H. Tu, and Z. Lu: AC impedance investigation of samarium-doped ceria. J. Electrochem. Soc. 148, A427 (2001).
K. Huang, M. Feng, and J.B. Goodenough: Synthesis and electrical properties of dense Ce0.9Gd0.1O1.95 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 81, 357 (1998).
I.R. Gibson, G.P. Dransfield, and J.T.S. Irvine: Sinterability of commercial 8 mol% yttria-stabilized zirconia powders and the effect of sintered density on the ionic conductivity. J. Mater. Sci. 33, 4297 (1998).
D.Y. Wang and A.S. Nowick: The grain boundary effect in doped ceria solid electrolytes. J. Solid State Chem. 35, 325 (1980).
A. Tschope, E. Sommer, and R. Birringer: Grain size dependent electrical conductivity of polycrystalline cerium oxide: I. Experiments. Solid State Ionics 139, 257 (2001).
N. Bonanos and E.P. Butler: Ionic conductivity of monoclinic and tetragonal ytria-zirconia single crystals. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 4, 561 (1985).
R.K. Slotwinski, N. Bonanos, and E.P. Butler: Electrical properties of MgO+Y2O3 and CaO+Y2O3 partially stabilized zirconias. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 4, 641 (1985).
C. Tian and S. Chan: Ionic conductivities, sintering temperatures and microstructures of bulk ceramics CeO2 doped with Y2O3. Solid State Ionics 134, 89 (2000).
Y.M. Chiang, E.B. Lavik, and D.A. Blom: Defect thermodynamics and electrical properties of nanocrystalline oxides: Pure and doped CeO2. Nanostruct. Mater. 9, 633 (1997).
R. Gerhardt and A.S. Nowick: Grain-boundary effect in ceria doped trivalent cations: II. Microstructure and microanalysis. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 69, 641 (1986).
G. Chiodelli, G. Flor, and M. Scagliotti: Electrical properties of the ZrO2-CeO2 system. Solid State Ionics 91, 109 1996).
A. Arulraj, F. Goutenoire, M. Tabellout, O. Bohnke, and P. Lacorre: Synthesis and characterization of the anionic conductor system La2MO2O9-0.5xFx (x=0.02–0.30). Chem. Mater. 14, 2492 (2002).
S.P.S. Badwal, F.T. Ciacchi, and J. Drennan: Investigation of the stability of ceria-gadolinia electrolytes in solid oxide fuel cell environments. Solid State Ionics 121, 253 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basu, S., Devi, P.S. & Maiti, H.S. Synthesis and properties of nanocrystalline ceria powders. Journal of Materials Research 19, 3162–3171 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2004.0442
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2004.0442