Abstract
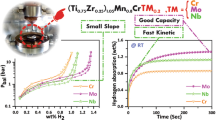
The electrochemical capacity, hydrogen absorbed/desorbed activation properties of alloy Zr(Mn0.1V0.3Ni0.6)2 were improved after Ti substitution for the Zr. The microstructure of Zr1xTix (Mn0.1V0.3Ni0.6)2 (x = 0, 0.5) alloys was analyzed by x-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and energy dispersive spectrum (EDS) analysis. A systematic structural analysis shows that there are two phases in the Ti-substituted alloy of Zr0.5Ti0.5(Mn0.1V0.3Ni0.6)2: C14 Laves phase and Ti-containing “premartensite” R phase of Ti0.8Zr0.2Ni. The improvement of electrochemical properties of alloy Zr(Mn0.1V0.3Ni0.6)2 after Ti substitution can be attributed to the Ti substitution for Zr sites in C14 Laves phase, the formation of Ti0.8Zr0.2Ni R-phase, and disappearance of Zr–Ni binaries.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Piotrowska, Electron. Technol. 24, 3 (1991).
B. L. Sharma, Semiconductors and Semimetals 15, 1 (1981).
V. L. Rideout, Solid State Electron. 18, 541 (1975).
N. E. Lumpkin, W. D. King, and T. L. Tansley, J. Mater. Res. 11, 1238 (1996).
N. E. Lumpkin, G. R. Lumpkin, and K. S. A. Butcher, J. Mater. Res. 11, 1244 (1996).
C. R. M. Grovenor, Properties of Gallium Arsenide (The Institution of Electrical Engineers, New York, 1986), p. 17.4.
J. B. Gunn, IBM J. Res. Develop. 8, 141 (1964).
M. Hansen and K. Andeko, Constitution of Binary Alloys (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1958), 206 pp.
T. Kim and D. D. L. Chung, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 4, 762 (1986).
P. Auvray, A. Guivarc’h, H. L’Haridon, and J.P. Mercier, Thin Solid Films 127, 39 (1985).
G. S. Marlow, M. B. Das, and L. Tongson, Solid State Electron. 26, 259 (1983).
A. A. Lakhani, R. C. Potter, and D. M. Beyea, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 3, 605 (1988).
N. Braslau, J. B. Gunn, and J. L. Staples, Solid State Electron. 10, 381 (1967).
J. L. Staples, U.S. Patent 3,386,867 (1968).
J. B. Gunn, IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 23, 705 (1976).
C. R. M. Grovenor, Properties of Gallium Arsenide, 2nd ed. (Inspec EMIS Datareviews Series no. 2, 1989), 403 pp.
A. Piotrowska and E. Kaminska, Thin Solid Films 193/194, 511 (1990).
Y. Robinson, Solid State Electron. 18, 331 (1976).
M. Wittemer, R. Pretorius, J.W. Mayer, and M-A. Nicolet, Solid State Electron. 20, 433 (1977).
L. Weiss and H. L. Hartnagel, Electron. Lett. 11, 263 (1975).
J. S. Harris, Y. Nannichi, G. L. Pearson, and G. F. Davis, J. Appl. Phys. 40, 4575 (1969).
M. Andrews and N. Holonyak, Solid State Electron. 15, 601 (1972).
M. Otsubo, H. Kumabe, and H. Miki, Solid State Electron. 20, 617 (1977).
W. T. Anderson, A. Christou, and J. Davey, IEEE J. Solid State Circ. SC-13, 4, 430 (1978).
N. Braslau, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 19 (3), 803 (1981).
W. Patrick, W. S. Mackie, S. P. Beaumont, and C. D. W. Wilkenson, Appl. Phys. Lett. 48, 986 (1986).
D. Sigurd, G. Ottaviani, V. Marrello, J. W. Mayer, and J. O. McCaldin, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 12, 135 (1975).
M. N. Yoder, Solid State Electron. 23, 117 (1980).
P. O’Connor, A. Dori, M. Feuer, and R. Vounckx, IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 34, 765 (1987).
T. S. Kuan, P. E. Batson, T. N. Jackson, H. Rupprecht, and E. L. Wilkie, J. Appl. Phys. 54, 6952 (1983).
T. C. Shen, G. B. Gao, and H. Morkoc, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 10 (5), 2113 (1992).
R. E. Williams, Gallium Arsenide Processing Techniques (Artech House, Inc., Dedham, MA, 1984), 406 pp.
C. R. M. Grovenor, Thin Solid Films (Switzerland) 104, 409 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, X., Zhang, Z., Zhang, X. et al. Effect of Ti Substitution on the Microstructure and Properties of Zr–Mn–V–Ni AB2 Type Hydride Electrode Alloys. Journal of Materials Research 14, 12 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1999.0174
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1999.0174