Abstract
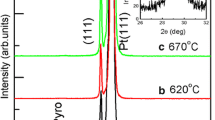
Modified lead titanate of 0.9PbTiO3 −0.1Pb(Mg0.5 W0.5)O3 thin films have been deposited onto Pt-coated Si substrates by pulsed laser deposition. Films were crystallized in situ during deposition or by post-depositional heat treatment (post-annealing). Compositional and structural characterization showed that the phase formation and microstructure of the films were highly sensitive to deposition conditions. Perovskite single phase films were formed in situ at 650 °C, PO2 = 40 Pa as well as by post-annealing amorphous films at 650 °C. In the post-annealing process, the amorphous as-deposited phase was crystallized to perovskite and/or pyrochlore, and the ratio of perovskite to pyrochlore was found to be influenced by the depositional PO2. Depending on the deposition temperature, the grain structures of the crystallized films were columnar or equiaxed. A relatively homogeneous surface morphology was obtained by deposition at a lower pressure (PO2 = 13 Pa). The in situ crystallized films showed variable crystallographic orientation. The more (111) oriented films had the lowest remanent polarizations and the highest coercive fields. A method for preparing randomly oriented films, via a two-step deposition process with intermediate annealing, is believed to give the most consistent results and the best ferroelectric properties at the present level of development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. A. Paz de Araujo, L. D. McMillan, B. M. Melnick, J. D. Cuchiaro, and J. F. Scott, Ferroelectrics 104, 241–256 (1990).
M. Okuyama and Y. Hamakawa, Ferroelectrics 63, 243–252 (1985).
W. A. Geideman, IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelec. Freq. Contr. 38, 704–711 (1991).
K. S. Grabowski, J. S. Horwitz, and D. B. Chrisey, Ferroelectrics 116, 19–33 (1991).
S. K. Dey and R. Zuleeg, Ferroelectrics 108, 37–46 (1990).
K. L. Saenger, R. A. Roy, K. F. Etzold, and J. J. Cuomo, in Ferroelectric Thin Films, edited by E. R. Myers and A. I. Kingon (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 200, Pittsburgh, PA, 1990), pp. 115–120.
G. A. Petersen, Jr. and J. R. McNeil, Thin Solid Films 220, 87–91 (1992).
S. Otsubo, T. Maeda, T. Minamikawa, Y. Yonezawa, A. Mori-moto, and T. Shimizu, Jpn. Appl. Phys. 29 (1), L133–L136 (1990).
R. W. Schwartz, B. A. Tuttle, D. H. Doughty, C. E. Land, D. C. Goodnow, C. L. Hernandez, T. J. Zender, and S. L. Martinez, IEEE Trans. Ultras. Ferroelec. Freq. Contr. 38 6, 677–682 (1991).
N. N. Krainik and A. I. Agranovskaya, Sov. Phys.-Solid State 2, 63–65 (1960).
K. Uchino, M. Aizawa, and S. Nomura, Ferroelectrics 64, 199–208 (1985).
B. W. Lee, H. M. Lee, L. P. Cook, P. K. Schenck, A. Paul, W. Wong-Ng, C. K. Chiang, P. S. Brody, B. J. Rod, and K. W. Bennett, in Laser Ablation in Materials Processing, edited by B. Braren, J. J. Dubowski, and D. Norton (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 285, Pittsburgh, PA, 1992), pp. 403–407.
K. Iijima, Y. Tomita, R. Takayama, and I. Ueda, J. Appl. Phys. 60 1, 361–367 (1986).
M. Ishida, H. Matsunami, and T. Tanaka, J. Appl. Phys. 48 3, 951–953 (1977).
A. H. Carim, B. A. Tuttle, D. H. Doughty, and S. L. Martinez, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 74 6, 1455–1458 (1991).
C. V. R. Vasant Kumar, R. Pascual, and M. Sayer, J. Appl. Phys. 71 2, 864–874 (1992).
L. P. Cook, M. D. Vaudin, P. K. Schenck, W. Wong-Ng, C. K. Chiang, and P. S. Brody, in Evolution of Thin-Film and Surface Microstructure, edited by C. V. Thompson, J. Y. Tsao, and D. J. Srolovitz (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 202, Pittsburgh, PA, 1991), pp. 241–246.
E. Kinsbron, M. Sternheim, and R. Knoell, Appl. Phys. Lett. 42 9, 835–837 (1983).
A. I. Zaslavskii and M. F. Bryzhina, Sov. Phys.-Crystallography 7 5, 577–583 (1963).
G. Arlt, D. Hennings, and G. de With, J. Appl. Phys. 58 4, 1619–1625 (1985).
B. G. Demczyk, R. S. Rai, and G. Thomas, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 73 3, 615–620 (1990).
B. G. Demczyk, A. G. Khachaturyan, and G. Thomas, Scripta Metall. 21 7, 967–969 (1989).
O. Eryu, K. Murakami, K. Masuda, A. Kasuya, and Y. Nishina, Appl. Phys. Lett. 54 26, 2716–2718 (1989).
T. Ogawa, A. Senda, and T. Kasanami, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 30 (9B), 2145–2148 (1991).
B. Jaffe, W. R. Cook, and H. Jaffe, Piezoelectric Ceramics (Academic Press, New York, 1971), pp. 77–80.
J. M. Herbert, Ferroelectric Ceramics (Gordon and Breach Sci. Pub., New York, 1985), pp. 137–145.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, B.W., Cook, L.P., Schenck, P.K. et al. Processing and characterization of compositionally modified PbTiO3 thin films prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Journal of Materials Research 12, 509–517 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1997.0073
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1997.0073