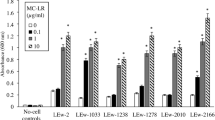
Abstract
The paper describes the isolation and characterization of a novel pelagic bacterial strain capable of hepatotoxic microcystin (MC) degradation. From a total of 24 bacterial strains isolated from water samples collected during the cyanobacteria blooming period in Jeziorsko reservoir, Poland, only the strain JEZ-8L was found to completely degrade microcystin-LR (MC-LR). The strain JEZ-8L was found to include the full mlrABCD gene cluster associated with the biological degradation of MC. To our knowledge, the strain JEZ-8L may represent the first report of an isolated bacterium to contain the full mlrABCD gene cluster in an aquatic ecosystem from central Europe. The nucleotide sequence analysis of each mlr gene and their translated amino acid sequences revealed a close similarity to other MC-degrading bacteria belonging to the Sphingomonadaceae family. Phylogenetic analysis using the bacterial gene marker 16S rRNA revealed 99% sequence similarity with nine strains from the Sphingosinicella genus. The nucleotide sequence similarity between the strain JEZ-8L and Sphingosinicella microcystinivorans Y2 was probably the most representative, since the strain Y2 is known to be a MC-degrading bacterium with confirmed detection from the full mlrABCD gene cluster. It is important to mention that our findings represent a preliminary study on the microbiota involved in MC degradation in water bodies from central Poland. The MC-degrading activity of the strain JEZ-8L could be promising for further research towards the elaboration of biotechnological solutions to reduce the harmful effects of MCs in water.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CyanoHABs:
-
cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms
- MC:
-
microcystin
References
Amalfitano S., Coci M., Corno G. & Luna G. 2015. A microbial perspective on biological invasions in aquatic ecosystems. Hydrobiologia 746: 13–22.
Balkwill J., Fredrickson J. & Romine F. 2006. Sphingomonas and related genera, pp. 605–629. In: Dworkin M., Falkow S., Rosenberg E., Schleifer K. & Stackenbrandt E. (eds), The Prokaryotes, a Handbook on the Biology of Bacteria. Springer, Berlin, Germany.
Bourne D., Jones G., Blakeley R., Jones A., Negri A. & Riddles P. 1996. Enzymatic pathway for the bacterial degradation of the cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin LR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62: 4086–4094.
Bourne D., Riddles G., Jones G., Smith W. & Blakeley R. 2001 Characterization of a gene cluster involved in bacterial degradation of the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin LR. Environ. Toxicol. 16: 523–534.
Christoffersen K., Lyck S., Winding A. & Winding A. 2002. Microbial activity and bacterial community structure during degradation of microcystins. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 27: 125–136.
De la Cruz A., Antoniou M., Hiskia A., Pelaez M., Song W., O’Shea K., He X. & Dionys-Iou D. 2011. Can we effectively degrade microcystins? — Implications on human health. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 11: 19–37.
Dziga D., Maksylewicz A., Maroszek M., Budzyńska A., Napior-kowska-Krzebietke A., Toporowska M., Grabowska M., Kozak A., Rosińska J. & Meriluoto J. 2017. The biodegradation of microcystins in temperate freshwater bodies with previous cyanobacterial history. Ecotoxol. Environ. Saf. 145: 420–430.
Dziga D., Wasylewski M., Wladyka B., Nybom S. & Meriluoto J. 2013. Microbial degradation of microcystins. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 26: 841–852.
Edwards C. & Lawton L.A. 2009. Bioremediation of cyanotoxins. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 67: 109–129.
Gągała I., Izydorczyk K., Jurczak T. & Mankiewicz-Boczek J. 2012. The key parameters and early warning methods to identify presence of toxigenic blooms dominated by Microcystis aeruginosa in the Jeziorsko reservoir (Central Poland). Fresen. Environ. Bull. 21: 295–303.
Gągała I. & Mankiewicz-Boczek J. 2012. The natural degradation of microcystins (cyanobacterial hepatotoxins) in fresh water — the future of modern treatment systems and water quality improvement. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 21: 1125–1139.
Geueke B., Busse H., Fleischmann T., Kampfer P. & Kohler H.P. 2007. Description of Sphingosinicella xenopeptidilytica sp. nov., a β-peptide-degrading species, and emended descriptions of the genus Sphingosinicella and the species Sphingosinicella microcystinivorans. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57: 107–113.
Geueke B., Namoto K., Seebach K., Kohler H.P. 2005. A novel β-peptidyl aminopeptidase (BapA) from strain 3-2W4 cleaves peptide bonds of synthetic β-tri- and β-dipeptides. J. Bacteriol. 187: 5910–5917.
Gillings M. & Hagan-Lawson E. 2014. The cost of living in the Anthropocene. Earth Perspectives 1: 1–11.
Ho L., Hoefel D., Saint C.P. & Newcombe G. 2007. Isolation and identification of a novel microcystin-degrading bacterium from a biological sand filter. Water Res. 41: 4685–4695.
Ho L., Sawade E. & Newcombe G. 2012. Biological treatment options for cyanobacteria metabolite removal: a review. Water Res. 46: 1536–1548.
Inoue K., Habe H., Yamane H., Omori T. & Nojiri H. 2005. Diversity of carbazole-degrading bacteria having the car gene cluster: Isolation of a novel gram-positive carbazole-degrading bacterium. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 245: 145–153.
Ishii H., Nishijima M. & Abe T. 2004. Characterization of degradation process of cyanobacterial hepatotoxins by a gramnegative aerobic bacterium. Water Res. 38: 2667–2676.
Jones G., Bourne D., Blakeley R. & Doelle H. 1994. Degradation of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxin microcystin by aquatic bacteria. Nat. Toxins 2: 228–235.
Jurczak T., Tarczyńska M., Izydorczyk K., Mankiewicz J., Zalewski M. & Meriluoto J. 2005. Elimination of microcystins by water treatment processes — examples from Sulejów Reservoir, Poland. Water Res. 39: 2394–2406.
Kobos J., Blaszczyk A., Hohlfeld N., Toruńska-Sitarz, Krakowiak A., Hebel A., Sutryk K., Grabowska M., Toporowska M., Kokociński M., Messyasz B., Rybak A., NapiówkowskaKrzebietke A., Nawrocka L., Pelechata A., Budzyńska A., Zagajewski P. & Mazur-Marzec H. 2013. Cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins in Polish freshwater bodies. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. St. 42: 358–378.
Kong Y., Xu X.Y., Zhu L., Xu J. & Lin H.Z. 2011. Microbial degradation of microcystins in water environment: a review. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 22: 1646–1652.
Kormas K. & Lymperopoulou D. 2013. Cyanobacterial toxin degrading bacteria: who are they? Biomed. Res. Int. 2013: 463894.
Lane D.J. 1991. 16S/23S rRNA sequencing, pp. 115–175. In: Stackebrandt E. & Goodfellow M. (eds) Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Lezcano M.A., Morón-López J., Agha R., López-Heras I., Nozal L., Quesada A. & El-Shehawy R. 2016. Presence or absence of mlr genes and nutrient concentration co-determine the microcystin biodegradation efficiency of a natural bacterial community. Toxins 8: 318.
Li J., Li R. & Li J. 2017. Current research scenario for microcystins biodegradation — a review on fundamental knowledge, application prospects and challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 595: 615–632.
Maeda R., Nagashima H., Widada J., Iwata K. & Omori T. 2008. Novel marine carbazole-degrading bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 292: 203–209.
Manage P., Edwards C., Singh B. & Lawton L. 2009. Isolation and identification of novel microcystin-degrading bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75: 6924–6928.
Mankiewicz-Boczek J., Gagala I., Jurczak T., Jaskulska A., Pawelczyk J. & Dziadek J. 2015. Bacteria homologous to Aeromonas capable of microcystin degradation. Open Life Sci. 10: 119–129.
Mankiewicz-Boczek J., Kobos J., Gagala J., Izydorczyk K. & Toruńska A. 2012. Poland: management and regulation of toxic cyanobacteria, pp. 109–114. In: Chorus I. (ed.), Current Approaches to Cyanotoxin Risk Assessment, Risk Management and Regulations in Different Countries. Federal Environmental Agency, Germany.
Mankiewicz-Boczek J., Palus J., Gagala I., Izydorczyk K., Jurczak T., Dziubaltowska E., Stepnik M., Arkusz J., Komorowska M. & Zalewski M. 2011. Effects of microcystinscontaining cyanobacteria from a temperate ecosystem on human lymphocytes culture and their potential for adverse human health effects. Harmful Algae 10: 356–365.
Maruyama T., Park H., Ozawa K., Tanaka Y., Sumino T., Hamana K., Hiraishi A. & Kato K. 2006. Sphingosinicella microcystinivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., a microcystin-degrading bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 56: 85–89.
Newcombe G., Chorus I., Falconer I. & Lin T. 2012. Cyanobacteria: impacts of climate change on occurrence, toxicity and water quality management. Water Res. 46: 1347–1348.
Paerl H.W., Hall N.S. & Calandrino E.S. 2011. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a world experiencing anthropogenic and climate-induced change. Sci. Total Environ. 409: 1739–1745.
Park H., Sasaki Y., Maruyama T., Yanagisawa E., Hiraishi A. & Kato A. 2001. Degradation of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxin microcystin by a new bacterium isolated from a hypertrophic lake. Environ. Toxicol. 16: 337–343.
Rapala J., Berg K., Lyra Ch., Niemi R., Manz W., Suomalainen S., Paulin L. & Lahti K. 2005. Paucibacter toxinivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., a bacterium that degrades cyclic cyanobacterial hepatotoxins microcystins and nodularin. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 55: 1563–1568.
Rivasseau C., Martins S. & Hennion M. 1998. Determination of some physicochemical parameters of microcystins (cyanobacterial toxins) and trace level analysis in environmental samples using liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 799: 155–169.
Saito T., Okano K., Park H., Itayama T., Inamori Y., Neilan B., Burns B. & Sugiura N. 2003 Detection and sequencing of the microcystin LR-degrading gene, mlrA, from new bacteria isolated from Japanese lakes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 229: 271–276.
Tsuji K., Asakawa M. & Anzai Y. 2006. Degradation of microcystins using immobilized microorganism isolated in an eutrophic lake. Chemosphere 65: 117–124.
Tsuji K., Naito S., Kondo F., Ishikawa N., Watanabe M., Suzuki M. & Harada K. 1994. Stability of microcystins from cyanobacteria — I. Effect of Llight on decomposition and isomerization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 28: 173–177.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
11756_2017_72121394_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
The online version of this article (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/biolog-2017-0172) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Font Nájera, A., Serwecińska, L.E., Gągała-Borowska, I. et al. The characterization of a novel bacterial strain capable of microcystin degradation from the Jeziorsko reservoir, Poland: a preliminary study. Biologia 72, 1394–1402 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1515/biolog-2017-0172
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/biolog-2017-0172