Abstract
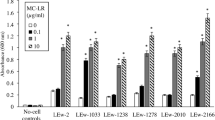
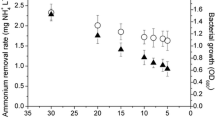
A microcystin-LR (MC-LR)-degrading bacterium was isolated from Lake Chaohu, a eutrophic freshwater lake containing toxic cyanobacterial blooms. Based on the analysis of 16S rDNA gene sequence and physiobiochemical characteristics, the isolated strain, most likely belongs to the genus Bacillus with the highest sequence similarity value with Bacillus nanhaiencis strain K-W39 (JQ799091.1), was named B. nanhaiencis strain JZ-2013. The strain JZ-2013 could grow on mineral salt medium supplied with MC-LR as sole carbon and nitrogen sources. The optimal temperature and pH for strain JZ-2013 growth and MC-LR biodegradation were 30°C and 8.0, respectively. The MC-LR with the initial concentration of 15 mg/L could be consumed 80 % by strain JZ-2013 within 9 days. The existence of exogenous carbon and nitrogen sources could significantly increase the removal efficiency of MC-LR. The strain JZ-2013 can efficiently removed MC-LR of low concentration in real water sample.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alamri SA (2012) Biodegradation of microcystin-RR by Bacillus flexus isolated from a Saudi freshwater lake. Saudi J Biol Sci 19:435–440
Bourne DG, Jones GJ, Blakeley RL, Jones A, Negri AP, Riddles P (1996) Enzymatic pathway for the bacterial degradation of the cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin LR. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:4086–4094
Bourne DG, Riddles P, Jones GJ, Smith W, Blakeley RL (2001) Characterisation of a gene cluster involved in bacterial degradation of the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin LR. Environ Toxicol 16:523–534
Bourne DG, Blakeley RL, Riddles P, Jones GJ (2006) Biodegradation of the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin LR in natural water and biologically active slow sand filters. Water Res 40:1294–1302
Campos A, Vasconcelos V (2010) Molecular mechanisms of microcystin toxicity in animal cells. Int J Mol Sci 11:268–287
Chen J, Hu LB, Zhou W, Yan SH, Yang JD, Xue YF, Shi ZQ (2010) Degradation of microcystin-LR and RR by a Stenotrophomonas sp. strain EMS isolated from Lake Taihu, China. Int J Mol Sci 11:896–911
Eleuterio L, Batista JR (2010) Biodegradation studies and sequencing of microcystin-LR degrading bacteria isolated from a drinking water biofilter and a fresh water lake. Toxicon 55:1434–1442
Falconer IR (1991) Tumor promotion and liver injury caused by oral consumption of cyanobacteria. Environ Toxicol 6:177–184
Gągała I, Mankiewicz-Boczek J (2012) The natural degradation of microcystins (Cyanobacterial Hepatotoxins) in fresh water-the future of modern treatment systems and water quality improvement. Pol J Environ Stud 21:1125–1139
Harada K, Imanishi S, Kato H, Mizuno M, Ito E, Tsuji K (2004) Isolation of Adda from microcystin-LR by microbial degradation. Toxicon 44:107–109
Hu LB, Yang JD, Zhou W, Yin YF, Chen J, Shi ZQ (2009) Isolation of a Methylobacillus sp. that degrades microcystin toxins associated with cyanobacteria. New Biotechnol 26:205–211
Jiang Y, Shao J, Wu X, Xu Y, Li R (2011) Active and silent members in the mlr gene cluster of a microcystin-degrading bacterium isolated from Lake Taihu, China. FEMS Microbiol Lett 322:108–114
Kumar S, Nei M, Dudley J, Tamura K (2008) MEGA: a biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Brief Bioinform 9:299–306
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Lemes GA, Kersanach R, Pinto LS, Dellagostin OA, Yunes JS, Matthiensen A (2008) Biodegradation of microcystins by aquatic Burkholderia sp. from a South Brazilian coastal lagoon. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 69:358–365
Manage PM, Edwards C, Singh BK, Lawton LA (2009) Isolation and identification of novel microcystin-degrading bacteria. Appl Environ Microb 75:6924–6928
Maruyama T, Park HD, Ozawa K, Tanaka Y, Sumino T, Hamana K, Hiraishi A, Kato K (2006) Sphingosinicella microcystinivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., a microcystin-degrading bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:85–89
Merel S, Clément M, Thomas O (2010) State of the art on cyanotoxins in water and their behaviour towards chlorine. Toxicon 55:677–691
Nishikawa-Matsushima R, Ohta T, Nishiwaki S, Suganuma M, Kohyama K, Ishikawa T, Carmichael WW, Fujiki H (1992) Liver tumor promotion by the cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin-LR. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 118:420–424
Pearson L, Mihali T, Moffitt M, Kellmann R, Neilan B (2010) On the chemistry, toxicology and genetics of the cyanobacterial toxins, microcystin, nodularin, saxitoxin and cylindrospermopsin. Mar Drugs 8:1650–1680
Ramani A, Rein K, Shetty KG, Jayachandran K (2012) Microbial degradation of microcystin in Florida’s freshwaters. Biodegradation 23:35–45
Rapala J, Berg KA, Lyra C, Niemi RM, Manz W, Suomalainen S, Paulin L, Lahti K (2005) Paucibacter toxinivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., a bacterium that degrades cyclic cyanobacterial hepatotoxins microcystins and nodularin. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1563–1568
Takenaka S, Watanabe MF (1997) Microcystin LR degradation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa alkaline protease. Chemosphere 34:749–757
Tsuji K, Naito S, Kondo F, Ishikawa N, Watanabe MF, Suzuki M, Harada K (1994) Stability of microcystins from cyanobacteria: effect of light on decomposition and isomerization. Environ Sci Technol 28:173–177
Ueno Y, Nagata S, Tsutsumi T, Hasegawa A, Watanabe MF, Park H-D, Chen G-C, Chen G, Yu S-Z (1996) Detection of microcystins, a blue-green algal hepatotoxin, in drinking water sampled in Haimen and Fusui, endemic areas of primary liver cancer in China, by highly sensitive immunoassay. Carcinogenesis 17:1317–1321
Valério E, Chaves S, Tenreiro R (2010) Diversity and impact of prokaryotic toxins on aquatic environments: a review. Toxins 2:2359–2410
Yan H, Pan G, Zou H, Li X, Chen H (2004) Effective removal of microcystins using carbon nanotubes embedded with bacteria. Chin Sci Bull 49:1694–1698
Zhang M, Pan G, Yan H (2010) Microbial biodegradation of microcystin-RR by bacterium Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05. J Environ Sci 22:168–175
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Specialized Research Fund for Doctoral Program of Higher Education from Chinese Ministry of Education (No. 20123424110004), the Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. 1208085MC42), the Key Laboratory of Bioresource Protection and Utilization of Anhui Province, the Key Laboratory of Biotic Environment and Ecological Safety of Anhui Province, and the Program for Innovative Research Team at Anhui Normal University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Shi, H., Liu, A. et al. Identification of a New Microcystin-Degrading Bacterium Isolated from Lake Chaohu, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 94, 661–666 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1531-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1531-7