Abstract
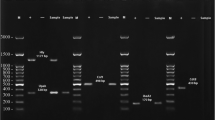
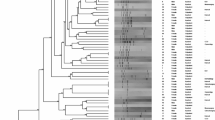
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are one of the most frequent infections in elderly people. The majority of infections is caused by uropathogenic E. coli. These strains contain a broad spectrum of virulence factors and are able to overcome defense barriers and colonize host organism. Population of elderly individuals has been growing globally and for that reason it is possible to expect a rise of UTIs among them. The aim of this study was to determine the phylogenetic group (A, B1, B2 and D) of urinary strains of E. coli isolated from elderly patients and evaluate the presence of 14 virulence genes (hly, cnf1, cdt, sat, afa, sfa, pap, aer, upaH, cah, pic, neuC, kpsMT II and traT) in these strains. We have carried out a phylogenetic analysis and virulence genes identification of 75 urinary E. coli isolates. Among our 75 E. coli strains, phylogenetic group B2 (64%) was the most dominant followed by groups D (16%), B1 (10.7%) and A (9.3%). The genes kpsMT II (65.3%), traT (61.3%), upaH (58.6%) and aer (52.0%) were found to be the most prevalent. We identified from 5 to 10 virulence genes in 44% strains belonging to B2 phylogroup. E. coli urinary strains examined in this study belonged mainly to phylogenetic group B2. We have also found that the majority of examined virulence genes, which are crucial for the establishment and maintenance of infection, were present in these strains.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- UPEC:
-
uropathogenic Escherichia coli
- UTI:
-
urinary tract infection
References
Abdi H.A. & Rashki A. 2014. Comparison of virulence factors distribution in uropathogenic E. coli isolates from phylogenetic groups B2 and D. Int. J. Enteric. Pathog. 2: e21725.
Agarwal J., Mishra B., Srivastava S., Srivastava R. & Pandey A. 2014. Virulence determinants in Escherichia coli associated with recurrent cystitis in sexually active women. Microb. Pathog. 74: 38–41.
Allsopp L.P., Totsika M., Tree J.J., Ulett G.C., Mabbett A.N., Wells J.T., Kobe B., Beatson S.A. & Schembri M.A. 2010. upah is a newly identified autotransporter protein that contributes to biofilm formation and bladder colonization by uropathogenic Escherichia coli CFT073. Infect. Immun. 78: 1659–1669.
Bashir S., Haque A., Sarwar Y., Aamir A. & Anwar M. I. 2012. Virulence profile of different phylogenetic groups of locally isolated community acquired uropathogenic E. coli from Faisalabad region of Pakistan. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 11: 23.
Biscola F.T., Abe M.C. & Guth B.E.C. 2011. Determination of adhesin gene sequences in, and biofilm formation by, O157 and non-O157 shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains isolated from different sources. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77: 2201–2208.
Boisen N., Ruiz-Perez F., Scheutz F., Krogfelt K.A. & Nataro J. P. 2009. Short report: high prevalence of serine protease autotransporter cytotoxins among strains of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 80: 294–301.
Clermont O., Bonacorsi S. & Bingen E. 2000. Rapid and simple determination of the Escherichia coli phylogenetic group. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66: 4555–4558.
Čurová K., Kmeťová M. & Siegfried L. 2014. CDT toxíny. Epidemiol. Mikrobiol. Imunol. 63: 134–139.
Dubois D., Delmas J., Cady A., Robin F., Sivignon A., Oswald E. & Bonnet R. 2010. Cyclomodulins in urosepsis strains of Escherichia coli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 48: 2122–2129.
Ejrnæs K. 2011. Bacterial characteristics of importance for recurrent urinary tract infections caused by Escherichia coli. Dan. Med. Bull. 58: B4187.
Ejrnæs K., Stegger M., Reisner A., Ferry S., Monsen T., Holm S.E., Lundgren B. & Frimodt-Mřller N. 2011. Characteristic of Escherichia coli causing persistence or relapse of urinary tract infections: phylogenetic groups, virulence factors and biofilm formation. Virulence 2: 528–537.
Farshad S. & Emamghorashi F. 2009. The prevalence of virulence genes of E. coli strains isolated from children with urinary tract infection. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 20: 613–617.
Fattahi S., Kafil H.S., Nahai M.R., Asgharzadeh M., Nori R. & Aghazadeh M. 2015. Relationship of biofilm formation and different virulence genes in uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolates from Northwest Iran. GMS Hyg. Infect. Control. 10: 1–7.
Ferreira D., Seca A.M.L., Pinto D.C.G.A. & Silva A.M.S. 2016. Targeting human pathogenic bacteria by siderophores: a proteomics review. J. Proteomics 145: 153–166.
Firoozeh F., Saffari M., Neamati F. & Zibaei M. 2014. Detection of virulence genes in Escherichia coli isolates from patients with cystitis and pyelonephritis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 29: 219–222.
Foxman B. 2010. The epidemiology of urinary tract infection. Nat. Rev. Urol. 7: 653–660.
Garcia E.C., Brumbaugh A.R. & Mobley H.L.T. 2011. Redundancy and specificity of Escherichia coli iron acquisition systems during urinary tract infection. Infect. Immun. 79: 1225–1235.
Guyer D.M., Gunther N.W. & Mobley H.L.T. 2001. Secreted proteins and other features specific to uropathogenic Escherichia coli. J. Infect. Dis. 183: 32–35.
Guyer D.M., Radulovic S., Jones F.E. & Mobley H.L.T. 2002. Sat, the secreted autotransporter toxin of uropathogenic Escherichia coli, is a vacuolating cytotoxin for bladder and kidney epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 70: 4539–4546.
Heywood W., Henderson B. & Nair S.P. 2005. Cytolethal distending toxin: creating a gap in the cell cycle. J. Med. Microbiol. 54: 207–216.
Janka A., Bielaszewska M., Dobrindt U., Greune L., Schmidt M.A. & Karch H. 2003. cytolethal distending toxin gene cluster in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H- an O157:H7: characterization and evolutionary consideration. Infect. Immun. 71: 3634–3638.
Johnson J.R. 1991. Virulence factors in Escherichia coli urinary tract infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 4: 80–128.
Johnson J.R., Kuskowski M.A., Gajewski A., Soto S., Horcajada J.P., Jimeney de Anta M.T. & Vila J. 2005. Extended virulence genotypes and phylogenetic background of Escherichia coli isolates from patients with cystitis, pyelonephritis, or prostatitis. J. Infect. Dis. 191: 46–50.
Johnson J.R. & Stell A.L. 2000. Extended virulence genotypes of Escherichia coli strains from patients with urosepsis in relation to phylogeny and host compromise. J. Infect. Dis. 181: 261–72.
Kadhum H.J., Finlay D., Rowe M.T., Wilson I.G. & Ball H.J. 2008. Occurrence and characteristics of cytotoxic necrotizing factors, cytolethal distending toxins and other virulence factors in Escherichia coli from human blood and faecal samples. Epidemiol. Infect. 136: 752–760.
Karimian A., Momtaz H. & Madani M. 2012. Detection of uropathogenic Escherichia coli virulence factors in patients with urinary tract infections in Iran. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 6: 6811–6816.
Katouli M. 2010. Population structure of gut Escherichia coli and its role in development of extra-intestinal infections. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2: 59–72.
Kline K.A. & Bowdish D.M.E. 2016. Infections in an aging population. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 29: 63–67.
Kmeťová M., Kendrovská E., Takáčová V., Sabol M. & Siegfried L. 2012. Virulentný profil a rezistencia Escherichia coli izolovaných od imunokompromitovaných pacientov pri urosepse. Urol. List 10: 37–40.
Koga V.L., Tomazetto G., Cyoia P.S., Neves M.S., Vidotto M.C., Nakazato G. & Kobayashi R.K.T. 2014. Molecular screening of virulence genes in extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli isolates from human blood culture in Brasil. BioMed Res. Int. 2014: 465054.
López-Banda D.A., Carrillo-Casas E.M., Leyva-Leyva M., Oroz-co-Hoyuela G., Manjarrez-Hernández A.H., Arroyo-Escalante S., Moncada-Barrón D., Villanueva-Recillas S., Xicohtencatl-Cortes J. & Hernández-Castro R. 2014. Identification of virulence factors genes in Escherichia coli isolates from women with urinary tract infection in Mexico. BioMed. Res. Int. 2014: 959206.
Maroncle N.M., Sivick K.E., Brady R., Stokes F.E. & Mobley H.L.T. 2006. Protease activity, secretion, cell entry, cytotoxicity, and cellular targets of secreted autotransporter toxin of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 74: 6124–6134.
Miajlovic H. & Smith S.G. 2014. Bacterial self-defence: how Escherichia coli evades serum killing. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 345: 1–9.
Mohajeri P., Khademi H., Ebrahimi R., Farhani A. & Rezaei M. 2014. Frequency distribution of virulence factors in uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from Kermanshah in 2011–2012. Int. J. Appl. Basic. Med. Res. 4: 111–116.
Moulin-Schouleur M., Schouler C., Tailliez P., Kao M.R., Brée A., Germon P., Oswald E., Mainil J., Blanco M. & Blanco J. 2006. Common virulence factors and genetic relationships between O18:k1:h7 Escherichia coli isolates of human and avian origin. J. Clin. Microbiol. 44: 3484–3492.
Mulvey M.A., Schilling J.D., Martinez J.J. & Hultgren S.J. 2000. Bad bugs and beleaguered bladders: interplay between uropathogenic Escherichia coli and innate hots defences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 8829–8835.
Navarro-Garcia F., Gutierrez-Jimenez J., Garcia-Tovar C., Castro L.A., Salazar-Gonzalez H. & Cordova V. 2010. Pic, an autotransporter protein secreted by different pathogens in the Enterobacteriaceae family, is a potent mucus secretagogue. Infect. Immun. 78: 4101–4109.
Naves P., del Prado G., Huelves L., Gracia M., Ruiz V., Blanco J., Dahbi G., Blanco M., del Carmen Ponte M. & Soriano F. 2008. Correlation between virulence factors and in vitro biofilm formation by Escherichia coli strains. Microb. Pathog. 45: 86–91.
Orth D., Grif K., Dierich M.P. & Würzner R. 2006. Cytolethal distending toxin in Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli: alleles, serotype distribution and biological effects. J. Med. Microbiol. 55: 1487–1492.
Restieri C., Garriss G., Locas M.C. & Dozois C.M. 2007. Autotransporter-encoding sequence are phylogenetically distributed among Escherichia coli clinical isolates and reference strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73: 1553–1562.
Ruiz J., Simon K., Horcajada J.P., Velasco M., Barranco M., Roig G., Moreno-Martínez A., Martínez J.A., Jiménez de Anta T., Mensa J. & Vila J. 2002. Difference in virulence factors among clinical isolates of Escherichia coli causing cystitis and pyelonephritis in women and prostatitis in men. J. Clin. Microbiol. 40: 4445–4449.
Sarkar S., Ulett G.C., Totsika M., Phan M.D., Schembri M.A. 2014. Role of capsule and O antigen in the virulence of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. PloS One 9: e94786.
Spurbeck R.R. & Mobley H.L.T. 2013. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli, pp. 499–521. In: Donnenberg M.S. (ed.) Escherichica coli. Pathotypes and Principles of Pathogenesis. Elsevier, ISBN 978-0-12-397048-0.
Stamm W.E. 2002. Scientific and clinical challenges in the management of urinary tract infections. Am. J. Med. 113: 1–4.
Subashchandrabose S. & Mobley H.L.T. 2015. Virulence and fitness determinants of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Spectr. 3: DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.UTI-0015-2012.
Torres A., Perna N.T., Burland V., Ruknudin A., Blattner F.R. & Kaper J.B. 2002. Characterization of Cah, a calcium-binding and heat extractable autotransporter protein of enterohaem-orrhagic Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 45: 951–966.
Tóth I., Hérault F., Beutin L. & Oswald E. 2003. Production of cytolethal distending toxin by pathogenic Escherichia coli strains isolated from human and animal sources: establishment of the existence of a new cdt variant (Type IV). J. Clin. Microbiol. 41: 4285–4291.
Usein C.R., Damian M., Tatu-Chitoiu D., Capusa C., Fagaras R., Tudorache D., Nica M. & Le Bouguénec C. 2001. Prevalence of virulence genes in Escherichia coli strains isolated from Romanian adult urinary tract infection cases. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 5: 303–310.
Vollmerhausen T.L. & Katouli M. 2014. Molecular characterisation of Escherichia coli isolates from hospitalised children and adults with urinary tract infections. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 33: 975–982.
Welch R.A. 2016. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli-associated exotoxins. Microbiol. Spectr. 4: DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.UTI-0011-2012.
Wiles J.T., Kulesus R.R. & Mulvey M.A. 2008. Origins and virulence mechanisms of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 85: 11–19.
Yamamoto S., Terai A., Yuri K., Kurazono H., Takeda Y. & Yoshida O. 1995. Detection of virulence factors in Escherichia coli by multiplex polymerase chain reaction. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 12: 85–90.
Yun K.W., Kim H.Y., Park H.K., Kim W. & Lim S.I. 2014. Virulence factors of uropathogenic Escherichia coli of urinary tract infection and asymptomatic bacteriuria in children. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 47: 455–461.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vargová, R., Kmeťová, M., Čurová, K. et al. Virulence genes in Escherichia coli strains isolated from urine of elderly patients. Biologia 72, 259–266 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1515/biolog-2017-0037
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/biolog-2017-0037