Abstract
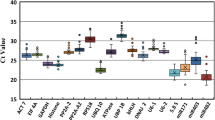
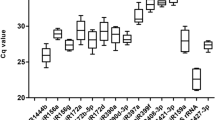
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play key roles in plant responses to biotic and abiotic stresses by modulating their own expression and a wide array of target mRNAs. Reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR is a sensitive and widely used method to study miRNA expression profile. Accurate analysis and interpretation of results require the selection of an appropriate reference gene. Reference genes selected should have a constant expression level under different stress conditions. Six reference candidates, including two miRNAs (miRNA 156 and miRNA 172), an rRNA (5S rRNA), a snRNA (U6) and two protein coding genes (actin and protein phosphatase 2A), were selected for normalization of miRNA expression in Lablab purpureus. The expression stability of candidate reference genes was investigated in ten samples and analysed using NormFinder, BestKeeper and hkgFinder softwares. The analyses suggested that miRNA 156 is the appropriate reference gene, as it had better expression stability than protein-coding genes, and other non-coding RNAs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Cq:
-
quantification cycle
- miRNA:
-
microRNA
- PP2A:
-
protein phosphatase 2A
- RT-qPCR:
-
reverse transcription quantitative PCR
- SD:
-
standard deviation
References
Andersen C.L., Jensen J.L. & Orntoft T.F. 2004. Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res. 64: 5245–5250.
Borowski J.M., Galli V., Messias R.S., Perin E.C., Buss J.H., dos Anjos e Silva S.D. & Rombaldi C.V. 2014. Selection of candidate reference genes for real-time PCR studies in lettuce under abiotic stresses. Planta 239: 1187–1200.
Brunner A.M., Yakovlev I.A. & Strauss S.H. 2004. Validating internal controls for quantitative plant gene expression studies. BMC Plant Biol. 4: 14.
Bustin S.A. 2002. Quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR): trends and problems, J. Mol. Endocrinol. 29: 23–39.
Bustin S.A., Benes V., Garson J.A., Hellemans J., Huggett J., Kubista M., Mueller R., Nolan T., Pfaffl M.W., Shipley G.L., Vandesompele J. & Wittwer C.T. 2009. The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 55: 611–622.
Chen C., Ridzon D.A., Broomer A.J., Zhou Z., Lee D.H., Nguyen J.T., Barbisin M., Xu N.L., Mahuvakar V.R., Andersen M.R., Lao K.Q., Livak K.J. & Guegler K.J. 2005. Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 33: e179.
Chen X., Zhang Z., Liu D., Zhang K., Li A. & Mao L. 2010. SQUAMOSA promoter-binding protein-like transcription factors: star players for plant growth and development. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 52: 946–951.
Cushman J.C. & Bohnert H.J. 2000. Genomic approaches to plant stress tolerance. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 3: 117–124.
Czechowski T., Stitt M., Altmann T., Udvardi M.K. & Scheible W.R. 2005. Genome-wide identification and testing of superior reference genes for transcript normalization in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 139: 5–17.
D’Souza M.R. & Devaraj V.R. 2010. Biochemical responses of hyacinth bean (Lablab purpureus) to salinity stress. Acta Physiol. Plant. 32: 341–353.
D’Souza M.R. & Devaraj V.R. 2011. Specific and non-specific responses of hyacinth bean (Dolichos lablab) to drought stress. Indian J. Biotechnol. 10: 130–139.
Feng H., Huang X., Zhang Q., Wei G., Wang X. & Kang Z. 2012. Selection of suitable inner reference genes for relative quantification expression of microRNA in wheat. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 51: 116–122.
Fuller D.Q. 2003. African crops in prehistoric South Asia: a critical review, pp. 239–271. In: Neumann K., Butler A. & Kahlheber S. (eds), Food, Fuel and Fields; Progress in Africa Archaeobotany. Heinrich-Barth-Institut, Cologne.
Gutierrez L., Mauriat M., Guenin S., Pelloux J., Lefebvre J.F., Louvet R., Rusterucci C., Moritz T., Guerineau F., Bellini C. & Wuytswinkel O.V. 2008. The lack of a systematic validation of reference genes: a serious pitfall undervalued in reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis in plants. Plant Biotechnol. 6: 609–618.
Guenin S., Mauriat M., Pelloux J., Wuytswinkel O.V., Bellini C. & Gutierrez L. 2009 Normalization of qRT-PCR data: the necessity of adopting a systematic, experimental conditionsspecific, validation of references. J. Exp. Bot. 60: 487–493.
Kokila S. 2015. Molecular characterization of transcripts induced under drought and salt stress from Lablab purpureus (hyacinth bean). PhD Thesis, Department of Biochemistry, Central College Campus, Bangalore University, Bangalore, India.
Kong W., Zhao J.J., He L. & Cheng J.Q. 2009. Strategies for profiling microRNA expression. J. Cell. Physiol. 218: 22–25.
Kou S.J., Wu X.M., Liu Z., Liu Y.L., Xu Q. & Guo W.W. 2012. Selection and validation of suitable reference genes for miRNA expression normalization by quantitative RT-PCR in citrus somatic embryogenic and adult tissues. Plant Cell Rep. 31: 2151–2163.
Kulcheski F.R., Marcelino-Guimaraes F.C., Nepomuceno A.L., Abdelnoor R.V. & Margis R. 2010. The use of microRNAs as reference genes for quantitative polymerase chain reaction in soybean. Anal. Biochem. 406: 185–192.
Li Q.Q., Skinner J. & Bennett J.E. 2012. Evaluation of reference genes for real-time quantitative PCR studies in Candida glabrata following azole treatment. BMC Mol. Biol. 13: 22.
Libault M., Thibivilliers S., Bilgin D., Radwan O., Benitez M., Clough S.J. & Stacey G. 2008. Identification of four soybean reference genes for gene expression normalization. Plant Genome 1: 44–54.
Lin Y.L. & Lai Z.X. 2013. Evaluation of suitable reference genes for normalization of microRNA expression by real-time reverse transcription PCR analysis during longan somatic embryogenesis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 66: 20–25.
Livak K.J. & Schmittgen T.D. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-δδCT method. Methods 25: 402–408.
Luo X., Shi T., Sun H., Song J., Ni Z. & Gao Z. 2014. Selection of suitable inner reference genes for normalisation of microRNA expression response to abiotic stresses by RT-qPCR in leaves, flowers and young stems of peach. Scientia Horticulturae 165: 281–287.
Maass B.L., Knox M.R., Venkatesha S.C., Angessa T.T., Ramme S. & Pengelly B.C. 2010. Lablab purpureus — a crop lost for Africa? Tropical Plant Biol. 3: 123–135.
Peltier H.J. & Latham G.J. 2008. Normalization of microRNA expression levels in quantitative RT-PCR assays: identification of suitable reference RNA targets in normal and cancerous human solid tissues. RNA 14: 844–852.
Devaraj Pfaffl M.W., Tichopad A., Prgomet C. & Neuvians T.P. 2004. Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper-Excelbased tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnol. Lett. 26: 509–515.
Rodriguez M., Canales E. & Borras-Hidalgo O. 2005. Molecular aspects of abiotic stress in plants. Biotecnologia Aplicada 22: 1–10.
Schmittgen T.D. & Zakrajsek B.A. 2000. Effect of experimental treatment on housekeeping gene expression: validation by real-time, quantitative RT-PCR. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 46: 69–81.
Selvey S., Thompson E.W., Matthaei K., Lea R.A., Irving M.G. & Griffiths L.R. 2001. ß-Actin — an unsuitable internal control for RT-PCR. Mol. Cell. Probes 15: 307–311.
Shi R. & Chiang V.L. 2005. Facile means for quantifying microRNA expression by real-time PCR. Biotechniques 39: 519–525.
Sunkar R., Chinnusamy V., Zhu J. & Zhu J.K. 2007. Small RNAs as big players in plant abiotic stress responses and nutrient deprivation. Trends Plant Sci. 12: 301–309.
Thellin O., Zorzi W., Lakaye B., Borman B.D., Coumans B., Hennen G., Grisar T., Igout A. & Heinen E. 1999. Housekeeping genes as internal standards: use and limits. J. Biotechnol. 75: 291–295.
Udvardi M.K., Czechowski T. & Scheible W.R. 2008. Eleven golden rules of quantitative RT-PCR. Plant Cell 20: 1736–1737.
Varkonyi-Gasic E., Wu R., Wood M., Walton E.F. & Hellens R.P. 2007. Protocol: a highly sensitive RT-PCR method for detection and quantification of microRNAs. Plant Methods 3: 12.
Yao L.M., Wang B., Cheng L.J. & Wu T.L. 2013. Identification of key drought stress-related genes in the hyacinth bean. PLoS One 8: e58108.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thilagavathy, A., Devaraj, V.R. Evaluation of appropriate reference gene for normalization of microRNA expression by real-time PCR in Lablab purpureus under abiotic stress conditions. Biologia 71, 660–668 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1515/biolog-2016-0091
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/biolog-2016-0091