Abstract
Our investigations of human C-reactive protein (CRP) and CRP transgenic mice have produced novel data that firmly establish this protein as an important host defense molecule. For example, we have learned that depending on the disease model, the beneficial effect of CRP can be direct, depend on the protein's ability to engage complement and Fcγreceptors, or rely on its ability to bridge innate and adaptive immunity. In addition, the degree of protection correlates with acute phase expression, but more important, also with the amount of CRP expressed constitutively. Furthermore, differences in baseline levels of CRP among healthy individuals and among patients can be attributed to a CRP gene polymorphism. In this article, we discuss these and other observations we have made during the last 5 yr and summarize our ongoing studies and future plans related to CRP biology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abernathy TJ, Avery OT: The occurrence duringacute infections of a protein not normally present in the blood. I. Distribution of the reactive protein in patient's sera and the effect of calcium on the flocculation reaction with C-polysaccharide of pneumococcus. J Exp Med 1941;73:173–182.
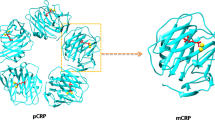
Shrive AK, Cheetham GMT, Holden D, Myles DAA, Turnell WG, Volanakis JE, Pepys MB, Bloomer AC, Greenhough TJ: Three dimensional structure of human C-reactive protein. Nat Struct Biol 1996;3:346–354.
Anderson JK, Stroud RM, Volanakis JE: Studies on the binding specificity of human C-reactive protein for phosphorylcholine. Fed Proc 1978;37:1495.
Szalai AJ, Agrawal A, Greenhough TJ, Volanakis JE. C-reactive protein: structural biology, gene expression, and host-defense function. Immunol Res 1997;16:127–136.
Szalai AJ, Agrawal A, Greenhough TJ, Volanakis JE: C-reactive protein: structural biology and host-defense function. Clin Chem Lab Med 1999;37:265–270.
Szalai AJ: Thean timicrobial activity of C-reactive protein. Microb Infect 2001;4:201–205.
Agrawal A, Volanakis JE: Probing the C1q-binding site on human C-reactive protein by site-directed mutagenesis. J Immunol 1994;152: 5404–5410.
Marnell LL, Mold C, Volzer MA, Burlingame RW, DuClos TW: C-reactive protein binds to Fc7R1 in transfected COS cells. J Immunol 1995;155:2185–2193.
Bharadwaj D, Stein M-P, Volzer M, Mold C, DuClos TW: The major receptor for C-reactive protein on leukocytes is Fc7 receptor II. J Exp Med 1999;190:585–590.
Mold C, Gewurz H, Du Clos TW: Regulation of complement activation by C-reactive protein. Immuno pharmacology 1999;422:23–30.
Pepys MB, Baltz ML, Gomer K, Davies AJS, Doenhoff M: Serum amyloid P component is an acutephase reactantin the mouse. Nature 1979;278:259–261.
Ciliberto G, Arcone R, Wagner EF, Rüther U: Inducible and tissuespecific expression of human C-reactive protein in transgenic mice. EMBO J 1987;6:4017–4022.
Murphy C, Beckers J, Rüther U: Regulation of the humanC-reactive protein gene in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 1995;270: 704–708.
Szalai AJ, Briles DE, Volanakis JE: Human C-reactive protein is protective against fatal Streptococcus pneumoniae infection in transgenic mice. J Immunol 1995;155: 2557–2563.
Yamada S, Gotoh T, Nakashima Y, Kayaba K, Ishikawa S, Nago N, Nakamura Y, Itoh Y, Kajii E: Distribution of serum C-reactive protein and its association with atherosclerosis risk factors in a Japanese population. Am J Epidemiol 2001;153:1183–1190.
Szalai AJ, van Ginkel FW, Wang Y, McGhee JR, Volanakis JE: Complement-dependent acute-phase expression of C-reactive protein and serum amy loid P-component. J Immunol 2000;165:1030–1035.
Szalai AJ, Van Cott JL, McGhee JR, Volanakis JE, Benjamin WH Jr: Human C-reactive protein is protective against fatal Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium infection in transgenic mice. Infect Immun 2000;68:5652–5656.
Burlingame RW, Volzer MA, Harris J, Du Clos TW: The effects of acute phase proteins on clearance of chromatin from the circulation of normal mice. J Immunol 1996;156:4783–4788.
Du Clos TW, Zlock LT, Hicks PS, Mold C: Decreased autoantibody levels and enhanced survival of (NZB XNZW)F, mice treated with C-reactive protein. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 1994;70: 22–27.
Gershoy D, Kim S, Brot N, Elkon KB: C-reactive protein binds to apoptotic cells, protects the cells from assembly of the terminal complement components, and sustains an antiinflammatory innate immune response: implications for systemicautoimmunity. J Exp Med 2000;192:1353–1363.
Szalai AJ, Marion TN, Weaver CT, Volanakis JE: Human C-reactive protein(CRP) is protective against murine SLE in NZB/W F1 mice. Clin Exp Rheum 1998;16: 201.
Szalai AJ, Nataf S, Hu X-Z, Bamum SR: Experimentalallergic encephalomyelitis is inhibited in transgenic mice expressing human c-reactive protein. J Immunol 2002;168:in press.
Ridker PM, Cushman M, Stampfer MJ, Tracy RP, Hennekens CH: Inflammation, aspirin, and the risk of cardiovascular disease inapparently healthy men. N Engl J Med 1997;336:973–979.
Westhuyzen J, Healy H: Review: biology and relevance of C-reactive protein in cardiovascular and renal disease. Ann Clin Lab Sci 2000; 30:133–143.
Lei K-J, Liu T, Zon G, Soravia E, Liu T-Y, Goldman ND: Genomic DNA sequence for human C-reactive protein. J Biol Chem 1985; 260:13,377–13,383.
Woo P, Korenberg JR, Whitehead AS: Characterization of genomic and complem entary DNA sequence of human C-reactive protein, and comparison with the complementary sequence of serum amyloid P component. J Biol Chem 1985; 260:13,384–13,388.
Weber JL, Kwitek AE, May PE: Dinucleotide repeatpolymorphism at the CRP locus. Nucl Acid Res 1990;18:4635.
Szalai AJ, McCrory A, Cooper GS, Wu J, Kimberly RP: Association between baseline levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) andadin-ucleotide repeat polymorphism in the intron of the CRP gene. Gene Immun 2002;3:14–19.
Adler AJ, Scheller A, Robins DM: The stringency and magnitude of androgen-specific gene activation are combina torial functions of receptor and nonreceptor binding site sequences. Mol Cell Biol 1993; 13:6326–6335.
Lutgens E, Daemen M, Kockx M, Doevendans P, Hofker M, Havekes L, Wellens H, de Muinck ED: Atherosc lerosis in APOE*3-Leiden transgenicmice: from proliferative to a the romato usstage. Circulation 1999;99:276–283.
Van Molle W, Denecker G, Rodriguez I, Brouckaert P, Vandenabeele P, Libert C: Activation of caspases in lethal experimental hepatitis and prevention by acute phase proteins. J Immunol 1999; 163:5235–5241.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szalai, A.J., McCrory, M.A. Varied biologic functions of c-reactive protein. Immunol Res 26, 279–287 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1385/IR:26:1-3:279
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/IR:26:1-3:279