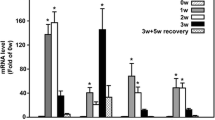
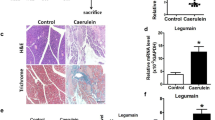
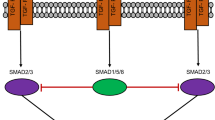
Abstract
The biological cause of fibrosis is the accumulation of excessive amounts of extracellular matrix (ECM) which leads to tissue dysfunction and organ failure. A strong correlation can be found between pancreatic diseases and fibrotic processes, in particular chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. There is growing evidence that pancreatic fibrosis represents a dysregulation of the normal repair processes after injury. This concept is based on the findings that fibrosis and tissue repair involve similar biological reactions regulated by the same group of molecules. The best characterized example for these regulatory molecules are the members of the transforming growth factor beta family (TGFβ). TGFβ1 represents the prototype of this family of highly similar growth factors, with the unique ability to stimulate the expression and deposition of extracellular matrix and to inhibit its degradation. Growth factor-induced fibrotic events are targeted by a myofibroblast-like cell called pancreatic stellate cell (PSC). These cells show enhanced expression of all-important ECM proteins after TGFβ stimulation including collagen, fibronectin and proteoglycans. At the same time TGFβ inhibits the degradation of ECM by blocking the secretion of proteases and stimulating the production of naturally occurring protease inhibitors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hay ED. Extracellular matrix alters epithelial differentiation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1993;5:1029–1035.
Hay ED. Biogenesis and organization of extracellular matrix. FASEB J 1999; 13 Suppl 2:S281-S283.
Basque JR, Chailler P, Menard D. Laminins and TGF-beta maintain cell polarity and functionality of human gastric glandular epithelium. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2002;282:C873-C884.
Verrecchia F, Mauviel A. Transforming Growth Factor-beta Signaling Through the Smad Pathway: Role in Extracellular Matrix Gene Expression and Regulation. J Invest Dermatol 2002;118:211–215.
Eickelberg O. Endless healing: TGF-beta, SMADs, and fibrosis. FEBS Lett 2001;506:11–14.
Riesle E, Friess H, Zhao L, et al. Increased expression of transforming growth factor beta s after acute oedematous pancreatitis in rats suggests a role in pancreatic repair. Gut 1997;40:73–79.
Santana A, Saxena B, Noble NA, Gold LI, Marshall BC. Increased expression of transforming growth factor beta isoforms (beta 1, beta 2, beta 3) in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1995;13:34–44.
Nakao A, Fujii M, Matsumura R, et al. Transient gene transfer and expression of Smad7 prevents bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice. J Clin Invest 1999;104:5–11.
Friess H, Lu Z, Riesle E, Uhl W, Brundler AM, Horvath L, Gold LI, Korc M, Büchler MW. Enhanced expression of TGF-betas and their receptors in human acute pancreatitis. Ann Surg 1998;227:95–104.
O’Kane S, Ferguson MW. Transforming growth factor beta’s and wound healing. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 1997;29:63–78.
Böttinger EP, Jakubczak JL, Roberts IS, et al. Expression of a dominant-negative mutant TGF-beta type II receptor in transgenic mice reveals essential roles for TGF-beta in regulation of growth and differentiation in the exocrine pancreas. EMBO J 1997;16:2621–2633.
van Laethem JL, Deviere J, Resibois A, et al. Localization of transforming growth factor beta 1 and its latent binding protein in human chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 1995;108:1873–1881.
Gress TM, Müller-Pillasch F, Elsasser HP, et al. Enhancement of transforming growth factor beta 1 expression in the rat pancreas during regeneration from caerulein-induced pancreatitis. Eur J Clin Invest 1994;24:679–685.
Menke A, Yamaguchi H, Gress TM, Adler G. Extracellular matrix is reduced by inhibition of transforming growth factor β1 in pancreatitis in the rat. Gastroenterology 1997;113:295–303.
Kennedy RH, Bockman DE, Uscanga L, Choux R, Grimaud JA, Sarles H. Pancreatic extracellular matrix alterations in chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas 1987;2:61–72.
Kasuga H, Ito Y, Sakamoto S, et al. Effects of anti-TGF-beta type II receptor antibody on experimental glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 2001;60:1745–1755.
Isaka Y, Brees DK, Ikegaya K, et al. Gene therapy by skeletal muscle expression of decorin prevents fibrotic disease in rat kidney. Nat Med 1996;2:418–423.
Border WA, Noble NA, Yamamoto T, et al. Natural inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta protects against scarring in experimental kidney disease. Nature 1992;360:361–364.
Kopp JB, Factor VM, Mozes M, et al. Transgenic mice with increased plasma levels of TGF-beta 1 develop progressive renal disease. Lab Invest 1996;74:991–1003.
Sanvito F, Nichols A, Herrera PL, et al. TGF-beta 1 over-expression in murine pancreas induces chronic pancreatitis and together with TNF-alpha, triggers insulin-dependent diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1995;217:1279–1286.
Vogelmann R, Ruf D, Wagner M, et al. Development of pancreatic fibrosis in a TGFβ transgenic mouse. Gastroenterology 1999;116:1174–1175.
Sanvito F, Herrera PL, Huarte J, et al. TGF-beta 1 influences the relative development of the exocrine and endocrine pancreas in vitro. Development 1994;120:3451–3462.
Vogelmann R, Ruf D, Wagner M, Adler G, Menke A. Effects of fibrogenic mediators on the development of pancreatic fibrosis in a TGF-beta1 transgenic mouse model. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2001;280:G164-G172.
Alexander CM, Werb Z. Proteinases and extracellular matrix remodeling. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1989;1:974–982.
Müller-Pillasch F, Gress TM, Yamaguchi H, Geng M, Adler G, Menke A. The influence of transforming growth factor β1 on the expression of genes coding for extracellular matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases during regeneration from caerulein-induced pancreatitis. Pancreas 1997;15:168–175.
Matrisian LM. Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in matrix remodeling. TIG 1990;6:121–125.
Edwards DR, Murphy G, Reynolds JJ, et al. Transforming growth factor beta modulates the expression of collagenase and metalloproteinase inhibitor. EMBO J 1987;6:1899–1904.
Kerr LD, Miller DB, Matrisian LM. TGF-β1 inhibition of transin/stromelysin gene expression is mediated through as fos binding sequence. Cell 1990;61:267–278.
Massague J. The transforming growth factor-beta family. Annu Rev Cell Biol 1990;6:597–641.
Roberts AB, Flanders KC, Heine UI, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta: multifunctional regulator of differentiation and development. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 1990;327:145–154.
Miyazono K, Heldin CH. The mechanism of action of transforming growth factor-beta. Gastroenterol Jpn 1993;28:Suppl 4:81–85.
Moustakas A, Souchelnytskyi S, Heldin CH. Smad regulation in TGF-β signal transduction. J Cell Sci 2001;114:4359–4369.
Yue J, Mulder KM. Transforming growth factor-beta signal transduction in epithelial cells. Pharmacol Ther 2001;91:1–34.
Piek E, Heldin CH, Ten DP. Specificity, diversity, and regulation in TGF-beta superfamily signaling. FASEB J 1999;13:2105–2124.
Inagaki Y, Truter S, Ramirez F. Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates alpha 2(I) collagen gene expression through a cis-acting element that contains an Sp1-binding site. J Biol Chem 1994;269:14,828–14,834.
Ritzenthaler JD, Goldstein RH, Fine A, Lichtler A, Rowe DW, Smith BD. Transforming-growth-factor-beta activation elements in the distal promoter regions of the rat alpha 1 type I collagen gene. Biochem J 1991;280:157–162.
Roberts AB, Heine UI, Flanders KC, Sporn MB. Transforming growth factor-beta. Major role in regulation of extracellular matrix. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1990;580:225–232.
Wenger C, Ellenrieder V, Alber B, et al. Expression and differential regulation of connective tissue growth factor in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene 1999;18:1073–1080.
Schuppan D, Strobel D, Hahn EG. Hepatic fibrosis—therapeutic strategies. Digestion 1998;59:385–390.
Grotendorst GR, Okochi H, Hayashi N. A novel transforming growth factor beta response element controls the expression of the connective tissue growth factor gene. Cell Growth Differ 1996;7:469–480.
Kato Y, Inoue H, Fujiyama Y, Bamba T. Morphological identification of and collagen synthesis by periacinar fibroblastoid cells cultured from isolated rat pancreatic acini. J Gastroenterol 1996;31:565–571.
Bachem MG, Schneider E, Gross H, et al. Identification, culture, and characterization of pancreatic stellate cells in rats and humans. Gastroenterology 1998;115:421–432.
Gressner AM. The cell biology of liver fibrogenesis—an imbalance of proliferation, growth arrest and apoptosis of myofibroblasts. Cell Tissue Res 1998;292:447–452.
Bachem MG, Schmid-Kotsas A, Gross H-J, et al. Pancreatic stellate cells and their role in human pancreatic fibrogenesis, in Chronic Pancreatitis: Novel Concepts in Biology and Therapy, Büchler MW, Friess H, Uhl W, Malfertheiner P, eds., Blackwell Science, Berlin: 2001;134–147.
Schneider E, Schmid-Kotsas A, Zhao J, et al. Identification of mediators stimulating proliferation and matrix synthesis of rat pancreatic stellate cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2001;281:C532-C543.
Luttenberger T, Schmid-Kotsas A, Menke A, et al. Platelet-derived growth factors stimulate proliferation and extracellular matrix synthesis of pancreatic stellate cells: implications in pathogenesis of pancreas fibrosis. Lab Invest 2000;80:47–55.
Gress TM, Müller-Pillasch F, Lerch MM, Friess H, Büchler M, Adler G. Expression and in-situ localization of genes coding for extracellular matrix proteins and extracellular matrix degrading proteases in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer 1995;62:407–413.
Klöppel G. Pathology of nonendocrine pancreatic tumors, in The Pancreas: Biology, Pathobiology, and Diseases, Go VLW, DiMagno EP, Gardner JD, Lebenthal E, Reber HA, Scheele GA, eds., Raven Press, New York: 1993;871–897.
Friess H, Yamanaka Y, Büchler M, et al. Enhanced expression of transforming growth factor beta isoforms in pancreatic cancer correlates with decreased survival. Gastroenterology 1993;105:1846–1856.
Ellenrieder V, Hendler S, Ruhland S, Boeck W, Adler G, Gress TM. TGF-β-induced invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells is mediated by matrix metalloproteinase-2 and urokinase plasminogen activator system. Int J Cancer 2001;93:204–211.
Menke A, Philippi C, Vogelmann R, et al. Down-regulation of E-cadherin gene expression by collagen Type I and Type III in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 2001;61:3508–3517.
Border WA, Noble NA. TGF-beta in kidney fibrosis: a target for gene therapy. Kidney Int 1997;51:1388–1396.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Menke, A., Adler, G. TGFβ-induced fibrogenesis of the pancreas. Int J Gastrointest Canc 31, 41–46 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1385/IJGC:31:1-3:41
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/IJGC:31:1-3:41