Abstract
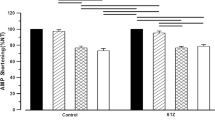
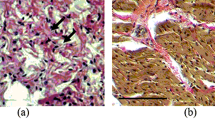
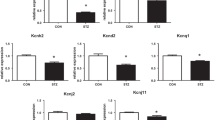
Diabetes mellitus is complicated with the development of cardiac contractile dysfunction and electrical instability, which contributes to high morbidity and mortality in diabetic patients. This study examined the possible roles of enhanced endothelin-1 (ET-1) on diabetes-induced alterations in ventricular myocyte electrophysiology. Type 1 diabetic rats were induced by single dose injection of streptozotocin (STZ) and treated with or without ET-1 receptor antagonist bosentan for 8 wk before myocyte isolation. Action potential, outward K+ currents, and inward Ca2+ currents in ventricular myocytes were recorded using whole-cell patch clamp technique. STZ-injected rats exhibited hyperglycemia, reduced body weight gain, and elevated plasma ET-1 concentration, indicative of diabetes induction. Ventricular myocytes isolated from diabetic rats exhibited prolonged action potential and reduced all three types of outward K+ currents. Resting membrane potential, height of action potential, and L-type Ca2+ current were not altered in diabetic myocytes. In vivo chronic treatment of diabetic rats with bosentan significantly augmented K+ currents and reversed action potential prolongation in ventricular myocytes. On the other hand, bosentan treatment had no detectable effect on the electrophysiological properties in control myocytes. In addition, bosentan had no effect on L-type Ca2+ currents in both control and diabetic myocytes. Our data suggest that altered electrophysiological properties in ventricular myocytes were largely resulted from augmented ET-1 system in diabetic animals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hileeto, D., Cukiernik, M., Mukherjee, S., et al. (2002). Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 18, 386–394.
Chen, S., Evans, T., Mukherjee, K., Karmazyn, M., and Chakrabarti, S. (2000). J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 32, 1621–1629.
Malhotra, A., Penpargkul, S., Fein, F. S., Sonnenblick, E. H., and Scheuer, J. (1981). Circ. Res. 49, 1243–1250.
Zhang, X., Ye, G., Duan, J., Chen, A. F., and Ren, J. (2003). Endocr. Res. 29, 227–236.
Casis, O., Gallego, M., Iriarte, M., and Sanchez-Chapula, J. A. (2000). Diabetologia 43, 101–109.
Nobe, S., Aomine, M., Arita, M., Ito, S., and Takaki, R. (1990). Cardiovasc. Res. 24, 381–389.
Jourdon, P. and Feuvray, D. (1993). J. Physiol. 470, 411–429.
Shimoni, Y., Hunt, D., Chuang, M., Chen, K. Y., Kargacin, G., and Severson, D. L. (2005). J. Physiol. 567, 177–190.
Pacher, P., Ungvari, Z., Nanasi, P. P., and Kecskemeti, V. (1999). Acta Physiol. Scand. 166, 7–13.
Robillon, J. F., Sadoul, J. L., Benmerabet, S., Joly-Lemoine, L., Fredenrich, A., and Canivet, B. (1999). Diabetes Metab. 25, 419–423.
Magyar, J., Iost, N., Kortvely, A., et al. (2000). Pflugers Arch. 441, 144–149.
Shimoni, Y., Severson, D., and Giles, W. (1995). J. Physiol. 488, 673–688.
Chen, S., Evans, T., Mukherjee, K., Karmazyn, M., and Chakrabarti, S. (2000). J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 32, 1621–1629.
Erbas, T., Erbas, B., Kabakci, G., Aksoyek, S., Koray, Z., and Gedik, O. (2000). Clin. Cardiol. 23, 259–263.
Makino, A. and Kamata, K. (1998). Br. J. Pharmacol. 123, 1065–1072.
Verma, S., Arikawa, E., and McNeill, J. H. (2001). Am. J. Hypertens. 14, 679–687.
Ding, Y., Zou, R., Judd, R. L., Schwartz, D. D., and Zhong, J. (2006). J. Cardiothora-Ren. Res. 1, 23–32.
Nerbonne, J. M. and Kass, R. S. (2005). Physiol. Rev. 85, 1205–1253.
Rana, B. S., Band, M. M., Ogston, S., Morris, A. D., Pringle, S. D., and Struthers, A. D. (2002). Am. J. Cardiol. 90, 483–487.
Landstedt-Hallin, L., Englund, A., Adamson, U., and Lins, P. E. (1999). J. Intern. Med. 246, 299–307.
El-Atat, F. A., McFarlane, S. I., Sowers, J. R., and Bigger, J. T. (2004). Curr. Diab. Rep. 4, 187–193.
Xu, Z., Patel, K. P., Lou, M. F., and Rozanski, G. J. (2002). Cardiovasc. Res. 53, 80–88.
Wang, D. W., Kiyosue, T., Shigematsu, S., and Arita, M. (1995). Am. J. Physiol. 269, H1288-H1296.
Shimoni, Y. and Liu, X. F. (2003). J. Physiol. 550, 401–412.
Pierce, G. N. and Russell, J. C. (1997). Cardiovasc. Res. 34, 41–47.
Nishiyama, A., Ishii, D. N., Backx, P. H., Pulford, B. E., Birks, B. R., and Tamkun, M. M. (2001). Am. J. Physiol. 281, H1800-H1807.
Takahashi, K., Ghatei, M. A., Lam, H. C., O'Halloran, D. J., and Bloom, S. R. (1990). Diabetologia 33, 306–310.
Hopfner, R. L., McNeill, J. R., and Gopalakrishnan, V. (1999). Eur. J. Pharmacol. 374, 221–227.
Evans, T., Deng, D. X., Chen, S., and Chakrabarti, S. (2000). Diabetes 49, 662–666.
Chen, S., Evans, T., Deng, D., Cukiernik, M., and Chakrabarti, S. (2002). Nephron 90, 86–94.
Szokodi, I., Horkay, F., Merkely, B., et al. (1998). Cardiovasc. Res. 38, 356–364.
Gross, M. L., Heiss, N., Weckbach, M., et al. (2004). Diabetologia 47, 316–324.
Kahler, J., Mendel, S., Weckmuller, J., et al. (2000). J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 32, 1429–1437.
Washizuka, T., Horie, M., Watanuki, M., and Sasayama, S. (1997). Circ. Res. 81, 211–218.
Hagiwara, K., Nunoki, K., Ishii, K., Abe, T., and Yanagisawa, T. (2003). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 310, 634–640.
Ding, Y., Zou, R., Judd, R. L., and Zhong, J. (2006). Endocrine 29, 135–141.
Zhong, J., Hwang, T. C., Adams, H. R., and Rubin, L. J. (1997). Am. J. Physiol. 273, H2312-H2324.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Y., Zou, R., Judd, R.L. et al. Endothelin-1 receptor blockade prevented the electrophysiological dysfunction in cardiac myocytes of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Endocr 30, 121–127 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:30:1:121
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:30:1:121