Abstract
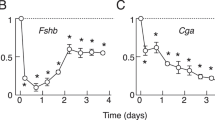
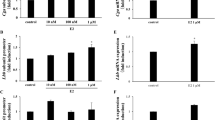
In a previous study, we clearly demonstrated that an application of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) to cultured rat pituitary cells increased the expression of GnRH receptor (GnRH-R) mRNA through transcriptional activation of GnRH-R gene rather than suppression of the turnover rate of GnRH-R mRNA. Along with GnRH, gonadal steroids seem to be an important regulator for GnRH-R expression in the pituitary gland. Recent in vivo studies reported that an application of gonadal steroids to gonadectomized animals modulated GnRH-R mRNA expression in the pituitary gland. However, it has not been clearly understood whether steroids may act directly at the pituitary or indirectly via modulation of hypothalamic GnRH release. Therefore, we assessed the effects of estrogen and progesterone on GnRH-R mRNA expression in primary cultured female rat pituitary cells. Neither estradiol nor progesterone modulates the basal expression of GnRH-R mRNA in primary cultured pituitary cells. When cultured pituitary cells were exposed to different doses of estradiol in combination with GnRH (0.2 nM), the GnRH-stimulated increment of GnRH-R mRNA expression was not significantly changed by estradiol at any given doses. However, when different doses of progesterone were added to primary cultured pituitary cells in combination with GnRH (0.2 nM), GnRH-induced increases in GnRH-R mRNA levels were reduced in a dose-related manner, showing a significant reduction at 100 nM progesterone. Furthermore, the addition of estradiol reinforced the suppressive effect of progesterone on the homologous upregulation of GnRH-R mRNA expression. Collectively, our results clearly demonstrated that progesterone directly attenuates the homologous upregulation of GnRH-R mRNA expression at the pituitary level, and that estradiol potentiates the effect of progesterone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clayton, R. N., Solano, A. R., Garcia-Vela, A., Dufau, M. L., and Catt, K. J. (1980). Endocrinology 107, 699–706.
Savoy-Moore, R. T., Schwartz, N. B., Duncan, J. A., and Marshall, J. C. (1980). Science 209, 942–944.
Bauer-Dantoin, A. C., Hollenberg, A. N., and Jameson, J. L. (1993). Endocrinology 133, 1911–1914.
Brooks, J., Taylor, P. L., Saunders, P. T., Eidne, K. A., Struthers, W. J., and McNeilly, A. S. (1994). Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 94, R23-R27.
Kakar, S. S., Grantham, K., Musgrove, L. C., Devor, D., Sellers, J. C., and Neill, J. D. (1994). Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 101, 151–157.
Padmanabhan, V., Dalkin, A., Yasin, M., Haisenleder, D. J., Marshall, J. C., and Landefeld, T. D. (1995). Biol. Reprod. 53, 263–269.
Bauer-Dantoin, A. C., Weiss, J., and Jameson, J. L. (1995). Endocrinology 136, 1014–1019.
Yasin, M., Dalkin, A. C., Haisenleder, D. J., Kerrigan, J. R., and Marshall, J. C. (1995). Endocrinology 136, 1559–1564.
Adams, B. M., Sakurai, H., and Adams, T. E. (1997). J. Reprod. Fertil. 111, 207–212.
Turzillo, A. M., Nolan, T. E., and Nett, T. M. (1998). Endocrinology 139, 4890–4894.
Turzillo, A. M., Clapper, J. A., Moss, G. E., and Nett, T. M. (1998). J. Reprod. Fertil. 113, 251–256.
Kaiser, U. B., Jakubowiak, A., Steinberger, A., and Chin, W. W. (1997). Endocrinology 138, 1224–1231.
Lin, X. and Conn, P. M. (1998). Endocrinology 139, 3896–3902.
Cheon, M., Park, D., Kim, K., Park, S. D., and Ryu, K. (1999). Endocrine 11, 49–55.
Cheon, M., Park, D., Park, Y., Kam, K., Park, S. D., and Ryu, K. (2000). Endocrine 13, 47–53.
Sakurai, H., Adams, B. M., and Adams, T. E. (1997). J. Endocrinol. 152, 91–98.
Wu, J. C., Sealfon, S. C., and Miller, W. L. (1994). Endocrinology 134, 1846–1850.
Park, D., Cheon, M., Kim, C., Kim, K., and Ryu, K. (1996). Eur. J. Endocrinol. 134, 236–242.
Evans, R. W., Sholiton, L. J., and Leavitt, W. W. (1978). Steroids 31, 69–81.
Rainbow, T. C., McGinnis, M. Y., Krey, L. C., and McEwen, B. S. (1982). Neuroendocrinology 34, 426–432.
Calderon, J. J., Muldoon, T. G., and Mahesh, V. B. (1987). Endocrinology 120, 2428–2435.
Karsch, F. J. (1987). Annu. Rev. Physiol. 49, 365–382.
Krey, L. C., Kamel, F., and MacLusky, N. J. (1990). Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 68, 95–103.
Wilfinger, W. W., Larsen, W. J., Downs, T. R., and Wilbur, D. L. (1984). Tissue Cell 16, 483–497.
Chomczynski, P. and Sacchi, N. (1987). Anal. Biochem. 162, 156–159.
Seong, J. Y., Kang, S. S., Kam, K., Han, Y. G., Kwon, H. B., Ryu, K., and Kim, K. (1998). Mol. Brain Res. 53, 226–235.
Kaiser, U. B., Zhao, D., Cardona, G. R., and Chin, W. W. (1992). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 189, 1645–1652.
Seong, J. Y. and Kim, K. (1996). Neurosci. Protocols 20, 1–17.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheon, M., Park, D., Park, Y. et al. Progesterone together with estrogen attenuates homologous upregulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor mRNA in primary cultured rat pituitary cells. Endocr 13, 379–384 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:13:3:379
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:13:3:379