Abstract
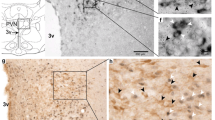
Dopamine (DA) secreted by tubero infundibular dopaminergic (TIDA) neurons in the hypothalamus is the major inhibitory factor controlling prolactin (PRL) secretion from the anterior pituitary. Endogenous opioid peptides (EOPs), mainly the neuropeptide β-endorphin, have a stimulatory influence on PRL secretion. During the first half of pregnancy in rats, PRL secretion is characterized by two daily surges, the nocturnal surge and the diurnal surge. We tested the hypothesis that EOPs are critical stimulatory factors in regulating the nocturnal PRL surge, possibly via inhibition of TIDA neuronal activity. Naloxone (NAL), an opioid antagonist, was continuously infused (0.2 mg/10 μL/min iv) during the expected time of the nocturnal PRL surge in day 8 pregnant rats. Radioimmunoassay (RIA) was used to measure plasma PRL levels, and the immunocytochemical (ICC) staining of Fos/FRA was performed to detect changes in transcriptional activity of neurons in the hypothalamus. ICC of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), the rate-limiting enzyme for DA synthesis, was performed to visualize TIDA neurons in the arcuate nucleus. The results showed that the nocturnal surge of PRL was markedly delayed and dampened in NAL-treated rats (p<0.01). The numbers of both Fos/FRA and (Fos/FRA)/TH dual-staining neurons increased in the arcuate nucleus following NAL treatment (p<0.05 for both comparisons).
These data indicate that EOPs are critical stimulatory factors for the nocturnal PRL surge and that the actions of EOPs are partially mediated via decreasing TIDA neuronal activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Butcher, R. L., Fugo, N. W., and Collins, W. E. (1972) Endocrinology 90, 1125–1127.
Gala, R. R. and Haisenleder, D. J. (1984) Life Sci. 34, 179–185.
Morishige, W. K. and Rothchild, I. (1974) Endocrinology 95, 260–274.
Ben-Jonathan, N. (1985) Endocr. Reviews 6(4), 564–589.
Bjorklund, A., Moore, R. Y., Nobin, A., and Stenevi, U. (1973) Brain Res. 51, 171–191.
Rivier, C., Vale, W., Ling, N., Brown, M., and Guillemin, R. (1977) Endocrinology 100, 238–241.
Ferland, L., Kledzik, G. S., Cusan, L., and Labrie, F. (1978) Mol. Cell Endocrinology 12, 267–272.
Ieiri, T., Chen, H. T., Campbell, G. A., and Meites, J. (1980) Endocrinology 106, 1568–1570.
Callahan, P., Baumann, M. H. and Rabii, J. (1996) J. Neuroendocrinology 8, 771–776.
Selmanoff, M. and Gregerson, K. A. (1986) Neuroendocrinology 42, 255–259.
Brown, B., Deffmar, P. W., Dobson, P. R., Lynn, A. G., Metcalf, G., and Morgan B. A. (1978) J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 30, 644–645.
Mezey, E., Kiss, J. Z., Mueller, G. P., Eskay, R., O'Donohue, T. L., and Palkovits, M. (1985) Brain Res. 328, 341–347.
Moore, K. E. and Lookingland, K. J. (1995) In: Psychopharmacology: The Fifth Generation of Progress. Bloom, F. E., Kupfer, D. J. (eds.), Raven Press, New York.
Horvath, T. L., Naftolin, F., and Leranth, C. (1992) Endocrinology 131(3), 1547–1555.
Morel, G. and Pelletier, G. (1986) Peptides 7, 1197–1199.
Mansour, A., Fox, C. A., Akil, H., and Watson, S. J. (1995) Trends Neurosci. 18, 22–29.
Van Loon, G. R., Ho, D., and Kim, C. (1980) Endocrinology 106, 76–80.
Gudelsky, G. A. and Porter, J. C. (1979) Life Sci. 25, 1697–1702.
Arita, J. and Kimura, F. (1988) Endocrinology 123, 694–699.
Sagrillo, C. A. and Voogt, J. L. (1991) Endocrinology 129(2), 925–930.
Wang, H. J., Hoffman, G. E., and Smith, M. S. (1993) Endocrinology 133(4), 1657–1663.
Pape, J. R., Hiofi, P., and Tramu, G. (1996) J. Neuroendocrinology 8, 375–386.
Erskine, M. S. (1995) Endocrine Review 16(4), 508–528.
Neill, J. D. and Nagy, G. M. (1994) In: The Physiology of Reproduction. 2nd ed. Knobil, E. and Neill, J. D. (eds.), Raven Press, New York.
Janik, J., Callahan, P., and Rabii, J. (1996) J. Neuroendocrinology 4(6), 701–708.
James, I. F. and Goldstein, A. (1984) Mol. Pharmacol. 25, 337–342.
Vale, W., Rivier, C., and Brown, M. (1977) Annu. Rev. Physiol. 39, 473.
Arey, B. J. and Freeman, M. E. (1990) Endocrinology 126, 279–284.
Arey, B. J. and Freeman, M. E. (1990) Endocrinology 130(1), 126–132.
Fitzsimmons, M. D., Olschowka, J. A., Wiegand, S. J., and Hoffman, G. E. (1992) Brain Res. 581, 10–18.
Paxinos, G. and Watson, G. (eds.) (1997) In: The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. Academic Press, New York.
Lerant, A., Herman, M. E., and Freeman, M. E. (1996) Endocrinology 137(9), 3621–3628.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, Y., Voogt, J.L. Effects of naloxone infusion on nocturnal prolactin secretion and Fos/FRA expression in pregnant rats. Endocr 10, 145–152 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:10:2:145
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:10:2:145