Abstract
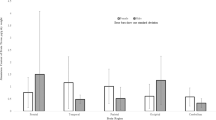
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and parkinsonism-dementia complex (PDC) are neurodegenerative disorders that occurred with extremely high frequency among the native population on Guam, especially in the 1950s and 1960s, but have substantially declined over the last half-century. The etiology of these diseases is unknown, but the most plausible hypothesis centers on imbalances in essential and toxic metals. We have determined the concentrations of Cd, Co, Cu, Fe, Mn, Rb, V, and Zn in formalin-fixed brain tissue collected during the period 1979–1983 from eight Guamanian patients with ALS, four with PDC, and five control subjects using high-resolution inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. The concentrations of Cd are markedly and significantly elevated both in gray and white matter in ALS, but not in PDC patients. The concentrations of Zn are elevated for both patient groups, in both gray and white matter, but only the difference in gray matter for PDC is significant. For the other metals, no significant differences are found.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. T. Kurland and D. W. Mulder, Epidemiologic investigations of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 1. Preliminary report on geographic distribution, with special reference to the Mariana Islands, including clinical and pathologic observations, Neurology 4, 355–378, 438–448 (1954).
A. Hirano, L. T. Kurland, R. S. Krooth, and S. Lessell, Parkinsonism-dementia complex, an endemic disease on the island of Guam. I. Clinical features, Brain 84, 642–661 (1961).
J. A. Brody and L. T. Kurland, Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism-dementia in Guam, in Tropical Neurology, J. D. Spillane, ed., Oxford University Press, New York, pp. 355–375 (1973).
D. C. Gajdusek, Motor-neuron disease in natives of New Guinea, N. Engl. J. Med. 268, 474–476 (1963).
K. Kimura, Y. Yase, Y. Higashi, et al., Epidemiological and geomedical studies on amytrophic lateral sclerosis, Dis. Nerv. Syst. 24, 155–159 (1963).
A. Hirano, N. Malamud, and L. T. Kurland, Parkinsonism-dementia complex, an endemic disease on the island of Guam. II. Pathological features, Brain 84, 662–679 (1961).
V. Buée-Scherrer, L. Buée, P. R. Hof, et al., Neurofibrillary degeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/parkinsonism-dementia complex of Guam: immunochemical characterization of tau proteins, Am. J. Pathol. 146, 924–932 (1995).
M. Mawal-Dewan, M. L. Schmidt, B. Balin, D. P. Perl, V. M.-Y. Lee, and J. Q. Trojanowski, Identification of phosphorylation sites in PHF-TAU from patients with Guam amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/parkinsonism-dementia complex, J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 55, 1051–1059 (1996).
R. M. Garruto, Pacific paradigms of environmentally induced neurological disorders: clinical, epidemiological and molecular perspectives, Neurotoxicology 12, 347–377 (1991).
J. E. Bailey-Wilson, C. C. Plato, R. C. Elston, and R. M. Garruto, Potential role of an additive genetic component in the cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism-dementia in the western Pacific, Am. J. Med. Genet. 45, 68–76 (1993).
P. Poorkaj, D. Tsuang, E. Wijsman, et al., TAU as a susceptibility gene for amyotropic lateral sclerosis-parkinsonism dementia complex of Guam, Arch. Neurol. 58, 1871–1878 (2001).
C. C. Plato, D. Galasko, R. M. Garruto, et al., ALS and PDC of Guam: forty-year follow-up, Neurology 58, 765–773 (2002).
R. M. Garruto, R. Yanagihara, and D. C. Gajdusek, Disappearance of high-incidence amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism-dementia on Guam, Neurology 35, 193–198 (1985).
P. Rodgers-Johnson, R. M. Garruto, R. Yanagihara, K.-M. Chen, D. C. Gajdusek, and C. J. Gibbs, Jr., Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism-dementia on Guam: a 30-year evaluation of clinical and neuropathologic trends, Neurology 36, 7–13 (1986).
D. Galasko, D. P. Salmon, U.-K. Craig, L. J. Thal, G. Schellenberg, and W. Wiederholt, Clinical features and changing patterns of neurodegenerative disorders on Guam, 1997–2000, Neurology 58, 90–97 (2002).
C. C. Plato, R. M. Garruto, D. Galasko, et al., Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism-dementia complex of Guam: Changing incidence rates during the past 60 years, Am. J. Epidemiol. 157, 149–157 (2003).
P. S. Spencer, P. B. Nunn, J. Hugon, et al., Guam amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-parkinsonism-dementia linked to a plant excitant neurotoxin, Science 237, 517–522 (1987).
D. C. Gajdusek, Cycad toxicity not the cause of high-incidence amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/parkinsonism-dementia on Guam, Kii peninsula of Japan, or in West New Guinea, in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Concepts in Pathogenesis and Etiology, A. J. Hudson, ed., University of Toronto Press, Toronto, pp. 317–325 (1990).
M. W. Duncan, J. C. Steele, I. J. Kopin, and S. P. Markey, 2-Amino-3(methylamino)-propanoic acid (BMAA) in cycad flour: An unlikely cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism dementia of Guam, Neurology 40, 767–772 (1990).
F. Esclaire, G. Kisby, P. Spencer, J. Milne, M. Lesort, and J. Hugon, The Guam cycad toxin methylazoxymethanol damages neuronal DNA and modulates tau mRNA expression and excitotoxicity, Exp. Neurol. 155, 11–21 (1999).
I. Khabazian, J. S. Bains, D. E. Williams, et al., Isolation of various forms of sterol β-d-glucoside from the seed of Cycas circinalis: neurotoxicity and implications for ALS-parkinsonism dementia complex, J. Neurochem. 82, 516–528 (2002).
D. C. Crapper McLachlan, C. D. McLachlan, B. Krishnan, S. S. Krishnan, A. J. Dalton, and J. C. Steele, Aluminium and calcium in soil and food from Guam, Palau and Jamaica: implications for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism-dementia syndromes of Guam, Environ. Geochem. Health 11, 45–53 (1989).
Y. Yase, The pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Lancet 2, 292–296 (1972).
F. Yoshimasu, M. Yasui, Y. Yase, et al., Studies on amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by neutron activation analysis. 2. Comparative study of analytical results on Guam PD, Japanese ALS and Alzheimer disease cases, Folia Psychiatr. Neurol. Jpn. 34, 75–82 (1980).
F. Yoshimasu, M. Yasui, Y. Yase, et al., Studies on amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by neutron activation analysis. 3. Systematic analysis of metals on Guamanian ALS and PD cases, Folia Psychiatr. Neurol. Jpn. 36, 173–180 (1982).
R. D. Traub, T. C. Rains, R. M. Garruto, D. C. Gajdusek, and C. J. Gibbs, Jr., Brain destruction alone does not elevate brain aluminum, Neurology 31, 986–990 (1981).
M. Yasui, K. Ota, and R. M. Garruto, Concentrations of zinc and iron in the brains of Guamanian patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism-dementia, Neurotoxicology 14, 445–450 (1993).
F. Yoshimasu, Y. Uebayashi, Y. Yase, S. Iwata, and K. Sasajima, Studies on amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by neutron activation analysis, Folia Psychiatr. Neurol. Jpn. 30, 49–55 (1976).
M. Yasui, Y. Yase, K. Ota, and R. M. Garruto, Aluminum deposition in the central nervous system of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from the Kii peninsula of Japan, Neurotoxicology 12, 615–620 (1991).
M. Yasui, Y. Yase, T. Kihira, K. Adachi, and Y. Suzuki, Magnesium and calcium contents in CNS tissues of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients from the Kii peninsula, Japan, Eur. Neurol. 32, 95–98 (1992).
H. Vanhoe, A review of the capabilities of ICP-MS for trace element analysis in body fluids and tissues, J. Trace Elements Electrolytes Health Dis. 7, 131–139 (1993).
J. Begerow, M. Turfeld, and L. Dunemann, New horizons in human biomonitoring of environmentally and occupationally relevant metals—sector-field ICP-MS versus electrothermal AAS, J. Anal. Atomic Spectrom. 15, 347–352 (2000).
M. Yasui, M. J. Strong, K. Ota, and M. A. Verity, eds., Mineral and Metal Neurotoxicology, CRC, Boca Raton, FL (1997).
F. H. Anderson, E. P. Richardson, Jr., H. Okazaki, and J. A. Brody, Neurofibrillary degeneration on Guam: frequency in Chamorros and non-Chamorros with no known neurological disease, Brain 102, 65–77 (1979).
V. J. Bush, T. P. Moyer, K. P. Batts, and J. E. Parisi, Essential and toxic element concentrations in fresh and formalin-fixed human autopsy tissues, Clin. Chem. 41, 284–294 (1995).
R. D. Meldrum, Erroneous aluminum and cobalt tissue concentrations from using formalin, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 57, 59–62 (2001).
M. T. Rajan, K. S. J. Rao, B. M. Mamatha, et al., Quantification of trace elements in normal human brain by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry, J. Neurol. Sci. 146, 153–166 (1997).
L. Zecca, R. Pietra, C. Goj, C. Mecacci, D. Radice, and E. Sabbioni, Iron and other metals in neuromelanin, substantia nigra, and putamen of human brain, J. Neurochem. 62, 1097–1101 (1994).
A. E. Panayi, N. M. Spyrou, B. S. Iversen, M. A. White, and P. Part, Determination of cadmium and zinc in Alzheimer’s brain tissue using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, J. Neurol. Sci. 195, 1–10 (2002).
J. E. Ahlskog, S. C. Waring, L. T. Kurland, et al., Guamanian neurodegenerative disease: investigation of the calcium metabolism/heavy metal hypothesis, Neurology 45, 1340–1344 (1995).
N. M. Spyrou and J. D. Stedman, Cadmium concentrations in the brains of Alzheimer cases, Trans. Am. Nucl. Soc. 74, 6–7 (1996).
R. Pamphlett, R. McQuilty, and K. Zarkos, Blood levels of toxic and essential metals in motor neuron disease, Neurotoxicology 22, 401–410 (2001).
M. Vinceti, D. Guidetti, M. Bergomi, et al., Lead, cadmium, and selenium in the blood of patients with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Ital. J. Neurol. Sci. 18, 87–92 (1997).
P. A. E. S. Smitt, H. van Beek, A.-J. Baars, et al., Increased metallothionein in the liver and kidney of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Arch. Neurol. 49, 721–724 (1992).
B. Arvidson, A review of axonal transport of metals, Toxicology 88, 1–14 (1994).
W. R. Markesbery, W. D. Ehmann, J. M. Candy, et al., Neutron activation analysis of trace elements in motor neuron disease spinal cord, Neurodegeneration 4, 383–390 (1995).
Z. X. Zhang, D. W. Anderson, N. Mantel, and G. C. Román, Motor neuron disease on Guam: geographic and familial occurrence, 1956–85, Acta Neurol. Scand. 94, 51–59 (1996).
J. D. Mitchell, I. A. Harris, B. W. East, and B. Pantland, Trace elements in cerebrospinal fluid in motor neurone disease, Br. Med. J. 288, 1791–1792 (1984).
J. D. Mitchell, B. W. East, I. A. Harris, and B. Pentland, Manganese, selenium and other trace elements in spinal cord, liver and bone in motor neurone disease, Eur. Neurol. 31, 7–11 (1991).
S. E. Arnold and A. Kumar, Reversible dementias, Med. Clin. North Am. 77, 215–230 (1993).
R. J. Uitti, A. H. Rajput, B. Rozdilsky, and W. K. Yuen, Regional distribution of metals in human brain, Clin. Invest. Med. 10, 10–13 (1987).
M. A. Deibel, W. D. Ehmann, and W. R. Markesbery, Copper, iron, and zinc imbalances in severely degenerated brain regions in Alzheimer’s disease: possible relation to oxidative stress, J. Neurol. Sci. 143, 137–142 (1996).
C. R. Cornett, W. R. Markesbery, and W. D. Ehmann, Imbalances of trace elements related to oxidative damage in Alzheimer’s disease brain, Neurotoxicology 19, 339–345 (1998).
R. J. Uitti, A. H. Rajput, B. Rozdilsky, M. Bickis, T. Wollin, and W. K. Yuen, Regional metal concentrations in Parkinson’s disease, other chronic neurological diseases, and control brains, Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 16, 310–314 (1989).
D. Berg, M. Gerlach, M. B. H. Youdim, et al., Brain iron pathways and their relevance to Parkinson’s disease, J. Neurochem. 79, 225–236 (2001).
K. J. Thompson, S. Shoham, and J. R. Connor, Iron and neurodegenerative disorders, Brain Res. Bull. 55, 155–164 (2001).
J. D. Mitchell, Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: toxins and environment, Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Other Motor Neuron Disord. 1, 235–250 (2000).
I. Mena, O. Marin, S. Fuenzalida, and G. C. Cotzias, Chronic manganese poisoning: clinical picture and manganese turnover, Neurology 17, 128–136 (1967).
D. B. Calne, N.-S. Chu, C.-C. Huang, C.-S. Lu, and W. Olanow, Manganism and idiopathic parkinsonism: Similarities and differences, Neurology 44, 1583–1586 (1994).
R. A. K. Srivastava and J. C. Jain, Scavenger receptor class B type I expression and elemental analysis in cerebellum and parietal cortex regions of the Alzheimer’s disease brain, J. Nuerol. Sci. 196, 45–52 (2002).
M. Yukawa, M. Suzuki-Yasumoto, K. Amano, and M. Terai, Distribution of trace elements in the human body determined by neutron activation analysis, Arch. Environ. Health 35, 36–44 (1980).
S. Yoshida, Y. Yase, S. Iwata, Y. Mizumoto, K.-M. Chen, and D. C. Gajdusek, Comparative trace-elemental study on amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and parkinsonism-dementia (PD) in the Kii peninsula of Japan and Guam, Wakayama Med. Rep. 30, 41–53 (1988).
D. T. Dexter, P. Jenner, A. H. V. Schapira, and C. D. Marsden, Alterations in levels of iron, ferritin, and other trace metals in neurodegenerative diseases affecting the basal ganglia, Ann. Neurol. 32, S94–S100 (1992).
D. Wenstrup, W. D. Ehmann, and W. R. Markesbery, Trace element imbalances in isolated subcellular fractions of Alzheimer’s disease brains, Brain Res. 533, 125–131 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gellein, K., Garruto, R.M., Syversen, T. et al. Concentrations of Cd, Co, Cu, Fe, Mn, Rb, V, and Zn in formalin-fixed brain tissue in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism-dementia complex of guam determined by high-resolution ICP-MS. Biol Trace Elem Res 96, 39–60 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:96:1-3:39
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:96:1-3:39