Abstract
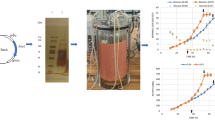
The gpdA-promoter-controlled exocellular production of glucose oxidase (GOD) by recombinant Aspergillus niger NRRL-3 (GOD3-18) during growth on glucose and nonglucose carbon sources was investigated. Screening of various carbon substrates in shake-flask cultures revealed that exocellular GOD activities were not only obtained on glucose but also during growth on mannose, fructose, and xylose. The performance of A. niger NRRL-3 (GOD3-18) using glucose, fructose, or xylose as carbon substrate was compared in more detail in bioreactor cultures. These studies revealed that gpdA-promoter-controlled GOD synthesis was strictly coupled to cell growth. The gpdA-promoter was most active during growth on glucose. However, the unfavorable rapid GOD-catalyzed transformation of glucose into gluconic acid, a carbon source not supporting further cell growth and GOD production, resulted in low biomass yields and, therefore, reduced the advantageous properties of glucose. The total (endo- and exocellular) specific GOD activities were lowest when growth occurred on fructose (only a third of the activity that was obtained on glucose), whereas utilization of xylose resulted in total specific GOD activities nearly as high as reached during growth on glucose. Also, the portion of GOD excreted into the culture fluid reached similar high levels (≅ 90%) by using either glucose or xylose as substrate, whereas growth on fructose resulted in a more pelleted morphology with more than half the total GOD activity retained in the fungal biomass. Finally, growth on xylose resulted in the highest biomass yield and, consequently, the highest total volumetric GOD activity. These results show that xylose is the most favorable carbon substrate for gpdA-promoter-controlled production of exocellular GOD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Visser, J., Bussink, H.-J., and Witteveen, C. (1994), in Gene Expression in Recombinant Microorganisms, Smith, A., ed., Marcel Dekker, New York, pp. 241–308.
Punt, P. J., Dingemanse, M. A., Kuyvenhoven, A., Soede, R. D. M., Pouwels, P. H., and van den Hondel, C. A. M. J. J. (1990), Gene 93, 101–109.
Punt, P. J., Zegers, N. D., Busscher, M., Powels, P. H., and van den Hondel, C. A. M. J. J. (1991), J. Biotechnol. 17, 19–34.
Gouka, R. J., Punt, P. J., and van den Hondel, C. A. M. J. J. (1997), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 47, 1–11.
Hellmuth, K., Pluschkell, S., Jung, J.-K., Ruttkowski, E., and Rinas, U. (1995), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 43, 978–984.
Pluschkell, S., Hellmuth, K., and Rinas, U. (1996), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 51, 215–220.
German standard methods for the examination of water, waste water and sludge. (1983), Anions (group D); determination of phosphorus compounds (D 11). VCH, Weinheim, New York.
El-Enshasy, H., Hellmuth, K., and Rinas, U. (1999), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 81, 1–11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Enshasy, H., Hellmuth, K. & Rinas, U. GpdA-promoter-controlled production of glucose oxidase by recombinant aspergillus niger using nonglucose carbon sources. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 90, 57–66 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:90:1:57
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:90:1:57