Abstract
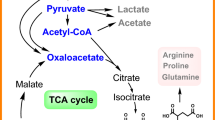
Itaconic acid is a value-added organic acid that is widely applied in industrial production. It can be converted from citric acid by some microorganisms including Aspergillus terreus and Aspergillus niger. Because of high citric acid production (more than 200 g/L), A. niger strains may be developed into powerful itaconic acid-producing microbial cell factories. In this study, industrial citric acid-producing strain A. niger YX-1217, capable of producing 180.0–200.0 g/L, was modified to produce itaconic acid by metabolic engineering. A key gene cadA encoding aconitase was expressed in A. niger YX-1217 under the control of three different promoters. Analyses showed that the PglaA promoter resulted in higher levels of gene expression than the PpkiA and PgpdA promoters. Moreover, the synthesis pathway of itaconic acid was extended by introducing the acoA gene, and the cadA gene, encoding aconitate decarboxylase, into A. niger YX-1217 under the function of the two rigid short-peptide linkers L1 or L2. The resulting recombinant strains L-1 and L-2 were induced to produce itaconic acid in fed-batch fermentations under three-stage control of agitation speed. After fermentation for 104 h, itaconic acid concentrations in the recombinant strain L-2 culture reached 7.2 g/L, which represented a 71.4% increase in itaconic acid concentration compared with strain Z-17 that only expresses cadA. Therefore, co-expression of acoA and cadA resulted in an extension of the citric acid metabolic pathway to the itaconic acid metabolic pathway, thereby increasing the production of itaconic acid by A. niger.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen MR, Salazar MP, Schaap PJ et al (2011) Comparative genomics of citric acid-producing Aspergillus niger ATCC 1015 versus enzyme-producing CBS 513.88. Genome Res 21:885–897. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.112169.11
Blazeck J, Hill A, Jamoussi M, Pan A, Miller J, Alper HS (2015) Metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica for itaconic acid production. Metab Eng 32:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2015.09.005
Blumhoff M, Steiger MG, Marx H, Mattanovich D, Sauer M (2013) Six novel constitutive promoters for metabolic engineering of aspergillus niger. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:259–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4207-9
Elenshasy H, Hellmuth K, Rinas U (2001) Gpda-promoter-controlled production of glucose oxidase by recombinant aspergillus niger using nonglucose carbon sources. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 90:57–66. https://doi.org/10.1385/abab:90:1:57
Fang W, Yang X, Zhang Y, Pei Y (2002) Rapid extraction of DNA and RNA from fungi. Chin J Appl Environ Biol 8:305–307. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1006-687X.2002.03.018
Ganzlin M, Rinas U (2008) In-depth analysis of the Aspergillus niger glucoamylase (glaA) promoter performance using high throughput screening and controlled bioreactor cultivation techniques. J Biotechnol 135:266–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2008.04.005
Gao X, Ni K, Zhao C et al (2014a) Enhancement of the activity of enzyme immobilized on polydopamine-coated iron oxide nanoparticles by rational orientation of formate dehydrogenase. J Biotechnol 188:36–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.07.443
Gao X, Yang S, Zhao C et al (2014b) Artificial multienzyme supramolecular device: highly ordered self-assembly of oligomeric enzymes in vitro and in vivo. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 126:14027–14030. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201405016
Gao X, Zhao C, Yu T et al (2015) Construction of a reusable multi-enzyme supramolecular device via disulfide bond locking. Chem Commun 51:10131–10133. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CC02544
Geiser E, Przybilla SK, Friedrich A, Buchel W, Wierckx N, Blank LM, Bölker M (2015) Ustilago maydis produces itaconic acid via the unusual intermediate trans-aconitate. Microb Biotechnol 9:116–126. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12329
Graaff LD, Broeck HVD, Visser J (1992) Isolation and characterization of the Aspergillus niger pyruvate kinase gene. Curr Genet 22:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00351737
Hossain AH, An L, Brickwedde A et al (2016) Rewiring a secondary metabolite pathway towards itaconic acid production in aspergillus niger. Microb Cell Fact 15:130. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-016-0527-2
Kanamasa S, Dwiarti L, Okabe M, Park E (2008) Cloning and functional characterization of the cisaconitic acid decarboxylase (CAD) gene from Aspergillus terreus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80:223–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1523-1
Kennedy J, Auclair K, Kendrew SG, Park C, Vederas JC, Hutchinson CR (1999) Modulation of polyketide synthase activity by accessory proteins during lovastatin biosynthesis. Science 284:1368–1372. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.284.5418.1368
Kim J, Seo HM, Bhatia SK et al (2017) Production of itaconate by whole-cell bioconversion of citrate mediated by expression of multiple cis-aconitate decarboxylase (cada) genes in Escherichia coli. Sci Rep 7:39768. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep39768
Kuenz A, Gallenmüller Y, Willke T, Vorlop KD (2012) Microbial production of itaconic acid: developing a stable platform for high product concentrations. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96:1209–1216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4221-y
Li A, Luijk NV, Beek MT, Caspers M, Punt P, Werf MVD (2011) A clone-based transcriptomics approach for the identification of genes relevant for itaconic acid production in Aspergillus. Fungal Genet Biol 48:602–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2011.01.013
Li A, Pfelzer N, Zuijderwijk R, Punt P (2012) Enhanced itaconic acid production in aspergillus niger, using genetic modification and medium optimization. BMC Biotechnol 12:57. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6750-12-57
Li A, Pfelzer N, Zuijderwijk R, Brickwedde A, Van ZC, Punt P (2013a) Reduced by-product formation and modified oxygen availability improve itaconic acid production in aspergillus niger. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:3901–3911. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4684-x
Li M, Zhou L, Liu M, Huang Y, Sun X, Lu F (2013b) Construction of an engineering strain producing high yields of α-transglucosidase via agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Asperillus niger. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 77:1860–1866. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.130281
Lin L, Wang F, Wei D (2011) Chlorimuron ethyl as a new selectable marker for disrupting genes in the insect-pathogenic fungus Metarhizium robertsii. J Microbiol Methods 87:241–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2011.07.018
Magnuson J, Lasure L (2004) Advances in fungal biotechnology for industry, agriculture and medicine. Organic acid production by filamentous fungi. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, pp 307–340
Mao Y, Yin Y, Zhang L, Alias SA, Gao B, Wei D (2015) Development of a novel aspergillus, uracil deficient expression system and its application in expressing a cold-adapted α-amylase gene from antarctic fungi Geomyces pannorum. Process Biochem 50:1581–1590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2015.06.016
Mattern IE, Van Noort JM, Van DBP, Archer DB, Roberts IN, van den Hondel CA (1992) Isolation and characterization of mutants of Aspergillus niger deficient in extracellular proteases. Mol Gen Genet 234:332–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00283855
Okabe M, Lies D, Kanamasa S, Park EY (2009) Biotechnological production of itaconic acid and its biosynthesis in Aspergillus terreus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84:597–606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2132-3
Otten A, Brocker M, Bott M (2015) Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for the production of itaconate. Metab Eng 30:156–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2015.06.003
Punt PJ, Dingemanse MA, Kuyvenhoven A, Soede RDM, Pouwels PH, van den Hondel CAMJJ (1990) Functional elements in the promoter region of the Aspergillus nidulans gpda gene encoding glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Gene 93:101–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1119(90)90142-E
Punt PJ, Schuren FHJ, Lehmbeck J, Christensen T, Hjort C, van den Hondel CA (2008) Characterization of the Aspergillus niger prtT, a unique regulator of extracellular protease encoding genes. Fungal Genet Biol 45:1591–1599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2008.09.007
Ruijter GJG, van de Vondervoort PJ, Visser J (1999) Oxalic acid production by Aspergillus niger: an oxalate-non-producing mutant produces citric acid at pH 5 and in the presence of manganese. Microbiology 145:2569–2576. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-145-9-2569
Steiger MG, Mach RL, Mach-Aigner AR (2009) An accurate normalizationstrategy for RT-qPCR in Hypocrea jecorina (Trichoderma reesei). J Biotechnol 145:30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2009.10.012
Steiger MG, Punt PJ, Ram AF, Mattanovich D, Sauer M (2016) Characterizing mtta as a mitochondrial cis-aconitic acid transporter by metabolic engineering. Metab Eng 35:95–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2016.02.003
Storms R, Zheng Y, Li H, Sillaots S, Martinez-Perez A, Tsang A (2005) Plasmid vectors for protein production, gene expression and molecular manipulations in Aspergillus niger. Plasmid 53:191–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plasmid.2004.10.001
Straat LVD, Vernooij M, Lammers M, Berg WVD, Schonewille T, Cordewener J, Meer IVD, Koops A, Graaff LHD (2014) Expression of the aspergillus terreus itaconic acid biosynthesis cluster in Aspergillus niger. Microb Cell Fact 13:11. https://doi.org/10.4161/bioe.29936
Van DSL, Vernooij M, Lammers M et al (2014) Expression of the aspergillus terreus itaconic acid biosynthesis cluster in aspergillus niger. Microb Cell Fact 13:11. https://doi.org/10.4161/bioe.29936
Willke T, Vorlop KD (2001) Biotechnological production of itaconic acid. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:289–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530100685
Xie H, Ma Q, Wei DZ, Wang FQ (2018) Transcriptomic analysis of Aspergillus niger, strains reveals the mechanism underlying high citric acid productivity. Bioresour Bioprocess 5:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-018-0208-6
Yang Z, Gao X, Xie H, Wang F, Ren Y, Wei D (2016) Enhanced itaconic acid production by self-assembly of two biosynthetic enzymes in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 114:457. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26081
Yin X, Shin HD, Li J, Du G, Liu L, Chen J (2017) Pgas, a low-pH-induced promoter, as a tool for dynamic control of gene expression for metabolic engineering of Aspergillus niger. Appl Environ Microbiol 83:e03222-16. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03222-16
Zhao C, Chen S, Fang H (2018) Consolidated bioprocessing of lignocellulosic biomass to itaconic acid by metabolically engineering neurospora crassa. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:9577–9584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9362-1
Zhao C, Cui Z, Zhao X, Zhang J, Liu J (2019) Enhanced itaconic acid production in Yarrowia lipolytica via heterologous expression of a mitochondrial transporter mtt. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:2181–2192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09627-z
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Shan Dong Weifang Ensign Industry Co., Ltd. (Weifang, China) for donating the industrial strain of A. niger YX-1217. We thank Kate Fox, DPhil, from Liwen Bianji, Edanz Group China (www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
The National Special Fund for State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering supported this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HX and FQW designed the experiments. QYM supplied A. niger YX-1217. HX performed the experiments and analyzed the data. FQW and DZW provided reagents and materials. HX wrote the manuscript. FQW revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, H., Ma, Q., Wei, D. et al. Metabolic engineering of an industrial Aspergillus niger strain for itaconic acid production. 3 Biotech 10, 113 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-2080-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-2080-2