Abstract
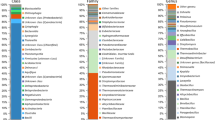
Two bacterial communities (NO92 and GBS) capable of degrading carbon tetrachloride (CT) were enriched from in-house CT-contaminated water. These communities are able to degrade CT in the presence of toluene. To characterize the community structure and diversity, one enrichment (NO92) was subjected to 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene-based molecular analysis. The 16S rRNA genes were amplified from the bulk genomic community DNA and cloned into plasmid vectors. Unique 16S rRNA gene clones, i.e., phylotypes, were detected by four tetrameric restriction enzymes. Together, 123 16S rRNA gene clones were obtained; thirty-one showed different restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) patterns. About 73% of the clones belong to two dominant RFLP patterns. Phylogenetic analysis based on the partial 16S rRNA gene sequences of 10 major phylotypes showed that all the phylotypes that were sequenced were affiliated with the high G+C Gram-positive bacteria. Whereas seven of the phylotypes (∼80% of the clones) were closely related to Rhodococcus, the other three (∼5% of the clones) were related to Curtobacterium. These results suggest that this CT-degrading community is diverse but is predominated by closely related bacterial groups.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sherwood, J. L., Petersen, J. N., Skeen, R. S., and Hooker, B. S. (1995), in Bioremediation of Chlorinated Solvents, Hinchee, R. E., Leeson, A., and Semprini, L., eds., Battle Press, Columbus, OH, pp. 85–89.
van Eekert, M. H. A., Veiga, M. C., Field, J. A., Stams, A. J. M., and Schraa, G. (1995), in Bioremediation of Chlorinated Solvents, Hinchee, R. E., Leeson, A., and Semprini, L., eds., Battle Press, Columbus, OH, pp. 139–146.
Weathers, L. J. and Parkin, G. F. (1995), in Bioremediation of Chlorinated Solvents, Hinchee, R. E., Leeson, A., and Semprini, L., eds., Battle Press, Columbus, OH, pp. 117–122.
Freedman, D. L., Lasecki, M., Hashsham, S., and Scholze, R. (1995), in Bioremediation of Chlorinated Solvents, Hinchee, R. E., Leeson, A., and Semprini, L., eds., Battle Press, Columbus, OH, pp. 45–52.
Petrovskis, E. A., Vogel, T. M., Saffarini, D. A., Nealson, K. H., and Andriaens, P. (1995), in Bioremediation of Chlorinated Solvents, Hinchee, R. E., Leeson, A., and Semprini, L., eds., Battle Press, Columbus, OH, pp. 61–67.
Sittig, M. (1985), Handbook of Toxic and Hazardous Chemicals and Carcinogens, 2nd ed. Noyes Publications, New York.
Criddle, C. S., DeWitt, J. T., Grbi-Gali, D., and McCarty, P. L. (1990), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56, 3240–3246.
Bowden, S. (1996), MS thesis, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville.
Strong-Gunderson, J. and Palumbo, A. V. (1994), J. Ind. Microbiol. 13, 361–366.
Little, C. D., Palumbo, A. V., Herbes, S. E., Lindstrom, M. E., Tyndall, R. L., and Gilmer, P. J. (1988), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54, 951–956.
Zhou, J.-Z., Bruns, M. A., and Tiedje, J. M. (1996), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62, 461–468.
Zhou, J.-Z., Fries, M. R., Chee-Sanford, J., and Tiedje, J. M. (1995), Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 45, 500–506.
Weisburg, W. W., Barns, S. M., Pelletier, D. A., and Lane, D. J. (1991), J. Bacteriol. 173, 697–703.
Kwok, S. and Higuchi, R. (1989), Nature 339, 237, 238.
Zhou, J.-Z., Davey, M. E., Figueras, J. B., Rivkina, E., Glichinsky, D., and Tiedje, J. M. (1997), Phylogenetic diversity of the bacterial community from a tundra soil sample. Microbiology 143, 3913–3919.
Figueras, J. B., Zhou, J.-Z., Abella, C. A., and Tiedje, J. M. (1996), Structure of the anoxygenic phototrophic bacterial community in Wintergreen Lake (MI, USA) by analysis of 16S rRNA genes. unpublished.
Moyer, C. L., Dobbs, F. C., and Karl, D. M. (1994), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60, 871–879.
Moyer, C. L., Dobbs, F. C., and Karl, D. M. (1995), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61, 1551–1562.
Tipper, J. C. (1979), Paleobiology 5, 423–434.
Devereaux, J., Haeberli, P., and Smithies, O. (1984), Nucleic Acids Res. 12, 387–395.
Larsen, N., Olsen, G. J., Maidak, B. L., McCaughey, M. J., Overbeek, R., Macke, T. J., Marsh, T. L., and Woese, C. R. (1993), Nucleic Acids Res. 21(Suppl.), 3021–3023.
Felsenstein, J. (1989), Cladistics 5, 164–166.
Kimura, M. (1980), J. Mol. Evol. 16, 111–120.
Liu, W.-T., Marsh, T. L., Cheng, H., and Forney, L. J. (1997), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63, 4516–4522.
Sneath, P. H. A., Mair, N. S., and Sharpe, M. E. (1984), Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, vol. 2, Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Palumbo, A.V. & Strong, J.M. Phylogenetic characterization of a mixed microbial community capable of degrading carbon tetrachloride. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 80, 243–253 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:80:3:243
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:80:3:243