Abstract
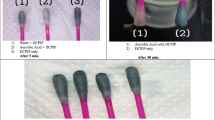
This study investigated the degradation of 4-chlorophenol (4-CP) by Caldariomyces fumago chloroperoxidase (CPO). Enzymatic oxidations were studied in reaction mixtures at pH 3.0, 4.0, and 6.0 in the presence and absence of Cl− containing 3.5 IU of CPO and 4-CP and hydrogen peroxide concentrations within the range of 0.5–50 and 0.005–50 mM, respectively. Distinct patterns of products regarding color, concentration, and solubility were observed. Reaction mixtures at pH 6.0 containing 3.5 IU of CPO and 5.0 mM 4-CP and H2O2 (1:1 stoichiometry) showed the highest 4-CP removal of 95% and the highest formation of a dark precipitate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kirby, P. (2000), The ISSO 14001 Approach to environmental management, Pollutec Environmental Limited, Oakville, Ontario, Canada.
NADCA Environmental Issues (1999), Phenols in Die Castings Wastestreams Clean Water Act, EPA North American Die Casting Association, Rosemont, IL.
Resolução CONAMA No. 20 inciso IX art. 7 (1994), classificação de águas doces, salobres e salinas do Brasil CONAMA Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente, Governo Federal, Brazil.
Sistema de Licenciamento de Atividates Poluidoras (1986), Criterios e Padrões para Lançamento de Efluentes Liquidos, CECA-SLAP-FEEMA, Governo Federal, Brasilia, Brazil.
Carmichael, R., Fedorak, M. P., and Pickard, M. A. (1985), Biochem. Lett. 7(4), 289–294.
Atlow, S. C., Bonadonna-Amparo, L., and Klibanov, A. M. (1983), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 26, 599–603.
Spiker, J. K., Crawford, D. L., and Thiel, E. C. (1992), Appl. Microbiol Biotechnol. 37, 518–523.
Rivas, J. F., Kolaczkowski, S. T., Beltran, F. J., and McLurgh, D. (1999) J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 74, 390–398.
Smith, J. M., Payne, G. F., Lumpkin, J. A., and Karns, J. S. (1991), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 39, 741–752.
Crecchio, C., Ruggiero, P., and Pizzigallo, D. R. (1995) Biotechnol. Bioeng 48, 581–585.
Wada, S., Ichikawa, H., and Tatsumi, K. (1994), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 45, 304–309.
Aitken, M. D., Massey, I. J., Chen, T., and Heck, P. E. (1993), Water Res. 28(9), 1879–1889.
Courteix, A. and Bergel, A. (1995) Enzyme Microb. Technol. 17, 1094–1100.
Courteix, A. and Bergel, A. (1995) Enzyme Microb. Technol. 17, 1087–1093.
Danner, D. J., Brignac, P. J., Arceneaux, D., and Patel, V. (1972), Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 156, 759–763.
Svitel, J. and Miertus, S. (1998) Environ. Sci. Technol. 32(6), 828–832.
Ortiz-León, M., Velasco, L., and Vazquez-Duhalt, R. (1995) Biochem. Biophys. Res. 215(3), 968–973.
Orser, C.S. and Lange, C.C. (1994), Biodegradation 5, 277–288.
Pickard, M. A. and Hashimoto, A. (1988), Can J. Microbiol. 34, 998–1002.
Pickard, M. A. (1981), Can. J. Microbiol. 27, 1298–1305.
Pickard, M. A., Kadima, T. A., and Carmichael, R. (1991), J. Ind. Microbiol. 7, 235–242.
Morris, D. R. and Hager, L. P. (1965), J. Biol. Chem. 241(8), 1763–1768.
Toyobo do Brazil (2000), Colorimetric Method for the Determination of Peroxidase Activity by the Oxidation of OAP, Campinas, SP, Brazil.
Hager, L. P., Morris, D. R., Drown, F. S., and Eberwein, H. (1965), J. Biol. Chem. 241(8), 1769–1777.
Merck (1972), Reactivos de Coloración para Cromatografía em Capa Fina y Papel, Primera Edición. E., Merck, Darmstadt, Germany.
Danner, J. D., Brignac, P. J., Arceneux, D., and Patel, V. (1973), Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 156, 759–763.
Woodburn, K. B., Delfino, J. J., and Rao, P. S. C. (1992), Chemosphere 24, 1037–1046.
Chin, Y. P., Peven, C. S., and Weber, W. J. Jr. (1988), Water Res. 22, 873–881.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
La Rotta H., C.E., P.S.Bon, E. 4-Chlorophenol degradation by chloroperoxidase from Caldariomyces fumago . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 98, 191–203 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:98-100:1-9:191
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:98-100:1-9:191