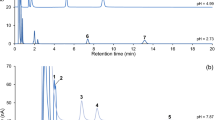
Abstract
A liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry method has been developed to perform the determination of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), norepinephrine (NE), dopamine (DA) and their metabolites, i.e., 5-hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid (5-HIAA), 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenylglycol (MHPG) sulfate, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) and homovanillic acid (HVA) in rat brain tissue. Analytes were separated on a Thermo C18 column (4.6 mm × 250 mm, 5 μm, SN: 1245575T, Thermo electron corporation, USA) with a mobile phase of 0.05% formic acid/acetonitrile (92:8 for ESI+, 82:18 for ESI−, v/v) at the flow-rate of 0.8 mL min−1. The LC system was coupled to a Waters Micromass Quattro Premier XE tandem quadruple mass spectrometer. MS acquisition of 5-HT, NE and DA was performed in positive electrospray ionization multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode, while negative electrospray ionization MRM mode was used to monitor their metabolites. The calibration curves were linear within the concentration range of 4–4,450 ng mL−1 for 5-HT, 4–4,110 ng mL−1 for NE and 4–4,100 ng mL−1 for DA (r ≥ 0.999). The limit of quantitation was 4 ng mL−1. 5-HIAA, MHPG, DOPAC and HVA have good linearity within the range of 12–1,000 ng mL−1(r ≥ 0.998) and the limit of quantitation was 12 ng mL−1. The intra- and inter-day RSD were lower than 8.45%. The method is sensitive, fast, accurate and usable for quantity determination of monoamine neurotransmitters and their metabolites in neuropsychiatric diseases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jacob 3rd P, Wilson M, Yu L, Mendelson J, Jones RT (2002) Anal Chem 74:5290–5296. doi:10.1021/ac020101a
Manini P, Andreoli R, Cavazzini S, Bergamaschi E, Mutti A, Niessen WM (2000) J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 744:423–431. doi:10.1016/S0378-4347(00)00285-1
Hows MEP, Lacroix L, Heidbreder C, Organ AJ, Shah AJ (2004) J Neurosci Methods 138:123–132. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2004.03.021
Jernej B, Banović M, Cicin-Sain L, Hranilović D, Balija M, Oresković D et al (2000) Psychiatry Res 94:153–162. doi:10.1016/S0165-1781(00)00129-3
Guan Z, Miao L, Zhang W (1997) Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi 13:185–188
Piletz JE, Halaris A (1989) Clin Chim Acta 185:165–176. doi:10.1016/0009-8981(89)90039-9
Fauler G, Leis HJ, Huber E, Schellauf C, Kerbl R, Urban C et al (1997) J Mass Spectrom 32:507–514. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9888(199705)32:5<507::AID-JMS503>3.0.CO;2-9
Lunte SM, O’Shea TJ (1994) Electrophoresis 15:79–86. doi:10.1002/elps.1150150112
Kele M, Ohmacht R (1996) J Chromatogr A 730:59–62. doi:10.1016/0021-9673(95)01186-2
Lakshmana MK, Raju TR (1997) Anal Biochem 246:166–170. doi:10.1006/abio.1996.9997
Mashige F, Ohkubo A, Matsushima Y, Takano M, Tsuchiya E, Kanazawa H et al (1994) J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 658:63–68. doi:10.1016/0378-4347(94)00227-4
Wang Y, Fice DS, Yeung PK (1999) J Pharm Biomed Anal 21:519–525. doi:10.1016/S0731-7085(99)00117-X
Chan EC, Ho PC (2000) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 14:1959–1964. doi:10.1002/1097-0231(20001115)14:21<1959::AID-RCM117>3.0.CO;2-T
Fuh MR, Tai YL, Pan WH (2001) J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 752:107–114. doi:10.1016/S0378-4347(00)00531-4
Magera MJ, Stoor AL, Helgeson JK, Matern D, Rinaldo P (2001) Clin Chim Acta 306:35–41. doi:10.1016/S0009-8981(01)00397-7
Kushnir MM, Urry FM, Frank EL, Roberts WL, Shushan B (2002) Clin Chem 48:323–331
Törnkvist A, Sjöberg PJR, Markides KE, Bergquist J (2004) J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 801:323–329. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2003.11.036
Li W, Rossi DT, Fountain ST (2000) J Pharm Biomed Anal 24:325–333. doi:10.1016/S0731-7085(00)00422-2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, F., Wang, F., Zhu, R. et al. Determination of 5-Hydroxytryptamine, Norepinephrine, Dopamine and Their Metabolites in Rat Brain Tissue by LC–ESI–MS–MS. Chroma 69, 207–213 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-008-0879-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-008-0879-9