Abstract
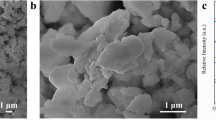
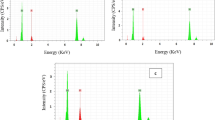
The corrosion characteristics of two Ni-Cr-Mo-B alloy powders sprayed by the high-velocity oxy-fuel (HVOF) process have been studied using potentiodynamic and potentiostatic corrosion analysis in 0.5 M H2SO4. The deposits were also microstructurally characterized using x-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (utilizing both secondary electron and backscattered electron modes), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Results from the microstructural examination of the two alloys have revealed a predominantly amorphous/nanocrystalline face centered cubic (fcc) matrix containing submicron boride precipitates as well as regions of martensitically transformed laths.
Apparent recrystallization of the amorphous matrix has also been observed in the form of cellular crystals with a fcc structure. The oxide stringers observed at splat boundaries were found to be columnar grained α-Cr2O3, though regions of the spinel oxide NiCr2O4 with a globular morphology were also observed. The coatings of the two alloys exhibited comparable resistance to corrosion in 0.5 M H2SO4, as revealed by potentiodynamic tests. They both had rest potentials approximately equal to −300 mV saturated calomel electrode (SCE) and passive region current densities of ∼1 mA/cm2. Microstructural examination of samples tested potentiostatically revealed the prevalence of degradation at splat boundaries, especially those where significant oxidation of the deposit occurred.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.E. Arvidsson, Comparison of Superalloy Coatings Sprayed with Plasma and HVOF, Thermal Spray Coatings: Properties, Processes and Applications, T.F. Bernecki, Ed., ASM International, 1991, p 295–301
H. Edris, D.G. McCartney, and A.J. Sturgeon, Microstructural Characterization of High Velocity Oxy-Fuel Sprayed Coatings of Inconel 625, J. Mater. Sci., Vol 32, 1997, p 863–872
S.K. Das, E.M. Norin, and R.L. Bye, Ni-Mo-Cr-B Alloys: Corrosion Resistant Amorphous Hardfacing Coatings, Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc., Vol 28, B.H. Kear and M. Cohen, Ed., Elsevier Science Publishing Co., 1984, p 233–237
R. Ray, Hot Consolidation/Devitrification of Metallic Glasses, Rapidly Solidified Amorphous and Crystalline Alloys, B.H. Kear, B.C. Giessen, and M. Cohen, Ed., Elsevier Science Publishing Co., 1982
W.L. Johnson, Metallic Glasses, ASM Metals Handbook, Vol 2, Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and Special-Purpose Materials, ASM International, 1990, p 804–821
S. Sampath, R.A. Neiser, H. Herman, J.P. Kirkland, and W.T. Elam, A Structural Investigation of a Plasma Sprayed Ni-Cr Based Alloy Coating, J. Mater. Res., Vol 8 (No. 1), 1993, p 78–86
V. Panchanathan, C.L. Tsai, and S. Wang, Nickel Base Metallic Glass Powders for Applications as Plasma Sprayed Coatings, Rapidly Solidified Amorphous and Crystalline Alloys, B.H. Kear, B.C. Giessen, and M. Cohen, Ed., Elsevier Science Publishing Co., 1982
K. Kishitake, H. Era, and F. Otsubo, Characterization of Plasma Sprayed Fe-10Cr-10Mo-(C, B) Amorphous Coatings, J. Therm. Spray Technol., Vol 5 (No. 2), 1996, p 145–153
K. Kishitake, H. Era, and F. Otsubo, Characterization of Plasma Sprayed Fe-17Cr-38Mo-4C Amorphous Coatings Crystallizing at Extremely High Temperature, J. Therm. Spray Technol., Vol 5 (No. 3), 1996, p 283–288
T. Shmyreva, A. Mukhin, and L. Mukhina, Detonation Gun and Plasma Spraying of Amorphous Metal Coatings with Improved Corrosion Resistance, Thermal Spray Science and Technology, C.C. Berndt and S. Sampath, Ed., ASM International, 1995, p 243–247
A.H. Dent, A.J. Horlock, D.G. McCartney, and S.J. Harris, The Structure and Properties of Two Fe-Cr-B Based Coatings Sprayed Using HVOF, Thermal Spray: A United Forum for Scientific and Technological Advances, C.C. Berndt, Ed., ASM International, 1997, p 917–923
ASTM Designation G 5-94, Annual Book of ASTM Standards, ASTM, 1994, p 48–58
P. Siitonen, S.L. Chen, K. Niemi, and P. Vuoristo, Electrochemical Method for Evaluating the Corrosion Resistance and Porosity of Thermal Sprayed Coatings, Thermal Spray: International Advances in Coatings Technology, C.C. Berndt, Ed., ASM International, 1992, p 853–858
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This paper originally appeared in Thermal Spray: Meeting the Challenges of the 21st Century; Proceedings of the 15th International Thermal Spray Conference, C. Coddet, Ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1998. This proceedings paper has been extensively reviewed according to the editorial policy of the Journal of Thermal Spray Technology.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dent, A.H., Horlock, A.J., McCartney, D.G. et al. The corrosion behavior and microstructure of high-velocity oxy-fuel sprayed nickel-base amorphous/nanocrystalline coatings. J Therm Spray Tech 8, 399–404 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1361/105996399770350340
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1361/105996399770350340