Abstract
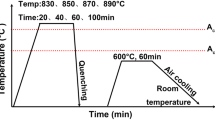
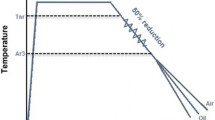
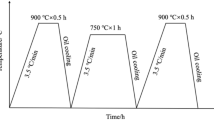
This study focused on tempered martensite embrittlement in a 32NiCrMoV125 steel through examination of the effects of austenite grain size and tempering temperature on the mechanical properties and fracture morphology of this material. Two different austenite grain sizes were obtained by austenitizing at 870 and 950 °C. After quenching, the specimens were tempered in the temperature range of 200–650 °C. The results obtained in this research indicate that by increasing the tempering temperature, the strength and hardness decrease, but ductility increases. However, impact testing indicated that tempered martensite embrittlement occurred when samples were tempered in the range of 250–400 °C. Fractography revealed intergranular and quasi-cleavage fracture. In summary, increasing the austenite grain size decreased strength, but increased impact toughness, except for samples tempered between 200 and 350 °C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Tomita, Development of Fracture Toughness of Ultrahigh Strength, Medium Carbon, Low Alloy Steels for Areospace Applications, Int. Mater. Rev., Vol 45 (No. 1), 2000, p 27–37
V. Placaniro, Properties of NiCrMoV Steels Used in Pressure Vessel Forging, Industrial Heating, Vol 53, 1986, p 27–30
W.S. Lee and T.T. Su, Mechanical Properties and Microstructure Features of AISI 4340 High-Strength Alloy Steel Under Quenched and Tempered Conditions, J. Mater. Proc. Technol., Vol 87, 1999, p 198–206
A.K. Sinha, Ferrous Physical Metallurgy, Butterworths, Stoneham, UK, 1989, p 523–571
M. Saeglitz and G. Krauss, Deformation, Fracture, and Mechanical Properties of Low-Temperature-Tempered Martensite in SAE 43xx Steels, Metall. Trans. A, Vol 28A, 1997, p 377–387
R.M. Horn, and R.O. Richie, Mechanisms of Tempered Martensite Emberittlement in Low Alloy Steel, Metall. Trans. A, Vol 9A, 1978, p 1039–1053
S. Lee, D.Y. Lee, and R.J. Asaro, Correlation of Microstructure and Tempered Martensite Embrittlement in Two 4340 Steels, Metall. Trans. A, Vol 20A, 1989, p 1089–1103
G. Thomas, Retained Austenite and Tempered Martensite Embrittlement, Metall. Trans. A, Vol 9A, 1978, p 439–450
M. Sarikaya, A.K. Jhingan, and G. Thomas, Retained Austenite and Tempered Martensite Embrittlement in Medium Carbon Steels, Metall. Trans. A, Vol 14A, 1983, p 1121–1131
S.K. Banerji, C.J. McMahon, Jr., and H.C. Feng, Intergranular Fracture in 4340-Type Steels: Effect of Impurities and Hydrogen, Metall. Trans. A, Vol 9A, 1978, p 237–247
J.P. Materkowski and G. Krauss, Tempered Martensite Embrittlement in SAE 4340 Steel, Metall. Trans. A, Vol 10A, 1979, p 1643–1651
B.C. Kim, S. Lee, D.Y. Lee, and N.J. Kim, On Tempered Martensite Embrittlement in an AISI 4340 Steel, Metall. Trans. A, Vol 22A, 1991, p 1889–1892
F.A. Darwish, L. Pereira, and M.L. Graca, On the Tempered Martensite Embrittlement in AISI 4140 Low Alloy Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng., Vol A132, 1991, p L5-L9
K. Hoon, J.C. Cha, and C.H. Kim, The Effect of Grain Size on Fracture Behaviour in Tempered Martensite Embrittlement for AISI 4340 Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng., Vol 100, 1988, p 121–128.
R. Homma, Studies on Austenite Grain of 3.5%NiCrMoV Steels, Trans. ISIJ, Vol 14, 1974, p 434–443
L.J. Klingler, W.J. Barnett, R.P. Frohmberg, and A.R. Troiano, The Embrittlement of Alloy Steel at High Strength Levels, Trans. ASM, Vol 46, 1953, p 1557–1589
Metals Handbook, ASM, Materials Park, OH, Vol 1, 1992, p 703–706
G. Krauss, Steels: Heat Treatment and Processing Principles, ASM International, 1980, p 205–212
D.L. Willamson, R.G. Schupmann, J.P. Materkowski, and G. Krauss, Determination of Small Amount of Austenite and Carbide in Hardened Medium Carbon Steels by Mossbauer Spectroscopy, Metall. Trans. A, Vol 10A, 1979, p 379–389
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdollah-Zadeh, A., Jafari-Pirlari, A. & Barzegari, M. Tempered martensite embrittlement in a 32NiCrMoV125 steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 14, 569–573 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1361/105994905X64657
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1361/105994905X64657