Abstract
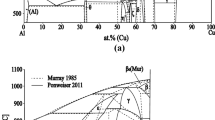
Thermodynamic modeling of the Pb-Bi-Hg ternary system was done with the help of the calculation phase diagram (CALPHAD) method. This work included a thermodynamic characterization of the three binary borders: the parameters relating to the Pb-Bi system were taken from the literature, whereas those of Pb-Hg and Bi-Hg systems were determined during this study, and were primarily based on particular calorimetric measurements. Some differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) data for the ternary system allowed us to verify the existence of a ternary compound with a composition close to Pb0.45Bi0.35Hg0.2 and the presence of two peritectic invariants. With these results, it was possible to carry out the assessment of the ternary interaction parameter of the liquid phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.U. Knebel, X. Cheng, C.H. Lefhalm, G. Muller, G. Schumacher, J. Konys, and H. Glasbrenner: “Design and Corrosion Study of a Closed Spallation Target Module of an Accelerator-Driven System (ADS),” Nucl. Eng. Des., 2000, 202, pp. 279–96.
D. Gorse: Conference on Compatibility of Structural Materials with Lead Alloys, GEDEON Research Group, Paris La Défense, 2000.
W. Vrieze: “Low Pressure Mercury Vapour Discharge Lamp,” European Patent Application 0157440 A1, 1985.
Y. Takashi and K. Seiko: “Amalgam Suitable for Use in a Low Mercury Vapor Discharge Lamp,” European Patent Application 0327346 A2, 1989.
M.H.R. Lankhorst, W. Keur, and H.A.M. Van Hal: “Amalgams for Fluorescent Lamps. Part II: The Systems Bi-Pb-Hg and Bi-Pb-Au-Hg,” J. Alloys Compd., 2000, 309, pp. 188–96.
N. Saunders and A.P. Niodownik: “CALPHAD (Calculation of Phase Diagram): A Comprehensive Guide” in Materials Series, 1, R.M. Cahn, ed., Pergamon, Oxford, UK, 1998.
S.W. Yoon and H.M. Lee: “A Thermodynamic Study of Phase Equilibria in the Sn-Bi-Pb Solder System,” CALPHAD, 1998, 22, pp. 167–78.
N.A. Gokcen: “The Bi-Pb (Bismuth-Lead) System,” J. Phase Equilib., 1992, 13, pp. 21–32.
A.T. Dinsdale: “SGTE Data for Pure Elements,” CALPHAD, 1991, 15, pp. 317–425.
T. Takase: Nippon Kinzoku Gakkaishi, 1937, 1, p. 43 (in Japanese).
M.V. Nosek, S.H. Yang, and N.M. Semibratova: “Phase Diagram of Lead-Bismuth System,” Tr. Inst. Khim. Nauk, Akad. Nauk Kaz. SSR, 1967, 15, pp. 150–57 (in Russian).
B. Predel and W. Schwermann: “Analysis of the Thermodynamic Properties of Solid Lead-Bismuth Alloys,” Z. Metallkd., 1967, 58, pp. 553–57 (in German).
Z. Wojtaszek: “Intermediate Phase in the Bismuth-Lead System,” Ser. Nauk Mat. Przyrod., Mat., Fiz., Chem., 1956, 2, pp. 151–61.
M. Hayasi: Nippon Kinzoku Gakkaishi, 1939, 3, p. 123.
M. Azzaoui and J. Hertz: “Darken and Redlich-Kister Modeling of Liquid Metallic Phases. The Pb-Sn-Bi Mixing Enthalpy,” Z. Metallkd., 1995, 86, pp. 776–83.
W.A. Badawi: “Behavior of the Enthalpy of Mixing in the Ternary Systems Lead-Antimony-Tin, Bismuth-Lead-Tin, and Bismuth-Cadmium-Tin at 950 K. I. Experimental Investigation,” Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 1988, 61, pp. 1351–55.
W.A. Badawi, M. El-Talbi, and A.M. Qun: “The Behavior of Mixing in Liquid Binary Alloys. Enthalpies of Mixing in the Systems Lead-Tin, Lead-Antimony, Lead-Bismuth, and Lead-Thallium,” Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 1990, 63, pp. 1795–800.
Z. Moser: “Thermodynamic Properties of Liquid Lead-Bismuth Solutions,” Z. Metallkd., 1973, 64, pp. 40–46.
U. Gonser: J. Phys. Chem., 1954, 181, p. 1.
K. Niwa, M. Shimojii, and O. Mikumi: Nippon Kinzoku Gakkaishi, 1960, 24, p. 668 (in Japanese).
R.J. Fruehan: “Mass Spectrometric Determination of Activities for Alloys with Complex Vapor Species: Bismuth-Palladium and Bismuth-Thallium,” Met. Trans., 1971, 2, pp. 1213–18.
P. Moldovan: “Experimental Determination of the Thermodynamic Properties of Molten Lead-Bismuth Alloys,” Bull. Inst. Politeh, Ser. Chim. Metal., 1977, 39, pp. 107–12.
P. Roy, R.L. Orr, and R. Hultgren: J. Phys. Chem., 1960, 64, p. 1034.
W. Oelsen and R. Bennewitz: “Thermodynamic Analysis. X. Calorimetry and Thermodynamics of Lead-Bismuth Alloys,” Arch. Einsenhuettenwes., 1958, 29, pp. 663–72.
M.V. Nosek and S.H. Yang: “Phase Diagram of the Bi-Hg System,” Izv. Akad. Nauk Kaz. SSR, Ser. Khim. Nauk, 1965, 15, pp. 26–32 (in Russian).
G. Petot-Ervas, M. Allibert, C. Petot, P. Desré, and E. Bonnier: “Thermodynamic Study of the Mercury-Bismuth System,” Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr., 1969, 5, pp. 1477–81 (in French).
E. Janecke: “The Ternary System Lead-Cadmium-Mercury,” Z. Phys. Chem., 1908, 60, pp. 399–413 (in Russian).
S.H. Yang, M.V. Nosek, N.M. Semibratova, and A.E. Shalamov: “Phase Diagram of the Lead-Mercury System,” Tr. Inst. Khim. Nauk, Akad. Nauk Kaz. SSR, 1967, 15, pp. 139–49 (in Russian).
L.A. Zabdyr and C. Guminski: “The Bi-Hg (Bismuth-Mercury) System,” J. Phase Equilib., 1996, 17, pp. 230–36.
L.A. Zabdyr and C. Guminski: “The Hg-Pb (Mercury-Lead) System,” J. Phase Equilib., 1993, 14, pp. 734–42.
E.D. Eastmann and J.H. Hildebrand: “Vapor Pressure of Silver, Gold, and Bismuth Amalgams,” J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1914, 36, pp. 2020–30.
B. Predel and D. Rothacker: “Thermodynamic Investigation of Mercury-Cadmium and Mercury-Bismuth Alloys,” J. Less-Common Met., 1966, 10, pp. 392–401 (in German).
B. Predel and D. Rothacker: “Thermodynamic Studies on Molten Mercury-Thallium and Mercury-Lead Alloys,” J. Less-Common Met., 1969, 17, pp. 223–34 (in German).
Z.C. Wang, X.H. Zhang, Y.Z. He, and Y.H. Bao: “A New Form of the High-Temperature Isopiestic Technique and Its Application to Mercury-Bismuth, Mercury-Cadmium, Mercury-Gallium, Mercury-Indium, and Mercury-Tin Binary Amalgams,” J. Chem. Faraday Trans., 1, 1988, 84, pp. 4369–76.
X. Zhang, Y. He, Y. Bao, and Z. Wang: Acta Metall. Sin., 1989, 25, pp. 286–87 (in Chinese).
O.J. Kleppa: “Thermodynamic Analysis of Binary Liquid Alloys of Group IIB Metals. III. The Solutions of Zinc, Cadmium, Indium, Tin, Thallium, Lead, and Bismuth in Mercury,” Acta Metall., 1960, 8, pp. 435–45.
E. Wittig and P. Scheidt: Naturwissenchaften, 1960, 47, pp. 250–51 (in German).
F. Marco, J. Navarro, and V. Torra: “Applications of Flow Calorimetry to the Study of Alloy Formation. I. Enthalpies of Solution of In, Tl, Cd, Zn, Pb, Ga, Sn, and Bi in Hg at 298.15 K,” J. Chem. Thermodyn., 1975, 7, pp. 1059–66.
R.Sh. Nigmetova and L.F. Kozin: “Thermodynamic Properties of a Lead-Bismuth-Mercury System,” Izv. Akad. Nauk SSR, Met., 1970, 1, pp. 214–20 (in Russian).
G.V. Malyutin and M.V. Nosek: “Nonvariant Equilibriums in the Lead-Bismuth-Mercury System,” Izv. Akad. Nauk Kaz. SSR, Ser. Khim., 1975, 25, pp. 51–53 (in Russian).
M. Ellner and B. Predel: “Structure of Thallium-Tin(h) and Its Crystal Chemical Relation to Similar Phases,” Z. Metallkd., 1975, 66, pp. 503–06 (in German).
T. Kaemmel, E.P. Mueller, L. Krossner, J. Nebel, H. Unger, and H. Ungethuem: “Are Mercury-Lead (HgPb2) and Mercury-Lead) Minerals Formed of Natural Accessory Components of Natural Gases of Altmark Deposits,” Z. Angew. Geol., 1978, 24, pp. 90–96 (in German).
B. Sundman, B. Jansson, and J.O. Anderson: “The Thermo-Calc Databank System,” CALPHAD, 1985, 9, pp. 153–90.
N.A. Pushin: Z. Anorg. Chem., 1903, 36, p. 201 (in German).
J.P. Dumas, L. Bougarfa, and J. Bansaid: “Phase Changes During Electrolysis of Mercury-Thallium, Mercury-Tin, Mercury-Lead, and Mercury-Zinc Systems,” J. Phys., 1984, 45, pp. 1543–48 (in French).
G. Tammann: Z. Phys. Chem., 1889, 3, p. 441 (in German).
A.S. Moshkevich and A.A. Ravdel: “Kinetics of the Dissolution of Lead in Mercury,” Zh. Prikl. Khim., 1970, 43, pp. 71–75 (in Russian).
B.N. Aleksandrov and O.I. Lomonos: “Solubility of Metals in Solid Mercury,” Zh. Fiz. Khim., 1971, 45, pp. 3003–06 (in Russian).
H. Schenk, E. Steinmetz, and M.G. Frohberg: Arch. Einsenhuettenwes., 1963, 34, p. 561 (in German).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maitre, A., Fiorani, J.M. & Vilasi, M. Thermodynamic study of phase equilibria in the Pb-Bi-Hg system. JPE 23, 329 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1361/105497102770331578
Received:
Revised:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1361/105497102770331578