Abstract
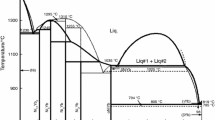
The Ni-Zn binary phase diagram has been evaluated using the CALPHAD method. In this analysis, the intermetallic β, β1, and γ phases are described using the sublattice model. The δ (Ni2Zn15) phase is treated as a stoichiometric compound because of its narrow solution range. The parameters used for the model were derived from an optimization procedure using the available experimental data in the literature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Tafel: “Zinc and Nickel,” Metallurgie, 1907, 4, p. 871.
V. Tafel: “Studies on the Constitution of the Zn-Cu-Ni Alloys,” Metallurgie, 1908, 5, pp. 413–14 and 428–30.
G. Voss: “Alloys of Nickel-Tin, Nickel-Lead, Nickel-Thallium, Nickel-Bismuth, Nickel-Chromium, Nickel-Zinc, and Nickel-Cadmium,” Z. Anorg. Chem., 1908, 57, pp. 34–71.
W. Ekman: “Structure Analysis of the Binary Alloys of the Transition Elements with Zn, Cd, and Al,” Z. Phys. Chem. B, 1931, 12, pp. 57–77.
W. Heike, J. Schramm, and O. Vaupel: “The Structure of Nickel-Zinc Alloys,” Metallwirtschaft, 1932, 11, pp. 325–30 and 539–42.
K. Tamaru: “On the Equilibrium Diagram of the Nickel-Zinc System,” Sci. Rep. Tohoku Imp Univ., 1932, 21, pp. 344–46.
W. Heike, J. Schramm, and O. Vaupel: “The Structure of Nickel-Zinc Alloys II,” Metallwirtschaft, 1933, 12, pp. 115–20.
K. Tamaru and A. Osawa: “On Further Investigation of the Equilibrium Diagram of the Nickel-Zinc System,” Sci. Rep. Tohoku Imp Univ., 1934, 23, pp. 794–815.
M. Hansen: Der Aufbau von Zweistofflegierungen, Springer Verlag, Berlin, Germany, 1936, pp. 963–69.
W. Heike, J. Schramm, and O. Vaupel: “The System Nickel-Zinc,” Metallwirtschaft, 1936, 15, pp. 655–62.
J. Schramm: “X-ray Investigation of the Ternary System Ci-Cu-Zn,” Metallwirtschaft, 1936, 15, pp. 723–26.
V. Marian: “The Ferromagnetic Curie Points and Absolute Saturation of Several Nickel Alloys,” Ann. Phys., 1937, 7, pp. 459–527.
J. Schramm: “X-ray Investigation of Phase Limits of the Zinc Alloy System with Fe, Co, Ni,” Z. Metallkde., 1938, 30, pp. 122–30.
J. Schramm: “Magnetic Susceptibility of Alloys of Zinc with Ni, Co, and Fe,” Z. Metallkde., 1938, 30, pp. 327–34.
J. Schramm: “Heat of Formation for 3 Phase Transformations in the Binary Alloys of Zn with Ni, Co, Fe, and Mn,” Z. Metallkde., 1938, 30, pp. 131–35.
F. Pawlek: “The Effect of the Fe-Group Metals on the Properties of Zn,” Z. Metallkde., 1938, 30, pp. 105–11.
O. Redlich and A. Kister: “Algebraic Representation of Thermodynamic Properties and Classification of Solutions,” Indust. Eng. Chem., 1948, 40, pp. 345–48.
H. Nowotny and H. Bittner: “The Problem of Anomalous Diamagnetism,” Monatsh. Chem., 1950, 81, pp. 887–906.
E.V. Clougherty and L. Kaufman: “The Thermodynamic Properties of α fcc Nickel-Zinc Alloys,” Acta Metall., 1963, 11, pp. 1043–50.
T.G. Chart, J.K. Critchley, and R. Williams: “Thermodynamic Data for Nickel-Zinc Alloys,” J. Inst. Met., 1968, 96, p. 228.
A. Johansson, H. Ljung, and S. Westman: “X-ray and Neutron Diffraction Studies on Gamma-Nickel-Zinc and Gamma-Iron-Zinc,” Acta Chem. Scan., 1968 22(9), pp. 2743–53.
L. Kaufman and H. Bernstein: Computer Calculation of Phase Diagrams, Academic Press, New York, 1970.
B.I. Lyazgin, V.A. Lebedev, G.N. Kazantsev, I.F. Nichkov, S.P. Raspopin, and V.I. Tynkavkin: “Thermodynamic Properties of Zn-Ni Alloys,” Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Met., 1979, 4, pp. 157–61 (in Russian); TR: Russ. Metall., 1970, 4, pp. 115–17.
M. Hillert and L.-I. Staffansson: “Regular Solution Model for Stoichiometric Phases and Ionic Melts,” Acta Chem. Scand., 1970, 24, pp. 3618–26.
Y.A. Chang, I. Gyuk, and J. Franks: “Thermodynamic of Lattice Disorder of CsCl-Type Intermetallic Phase at Nonstoichiometric Compositions and the Thermodynamic Properties of β-AuCd and βAgMg,” Acta Metall., 1971, 19, pp. 939–53.
I. Gyuk and Y. A. Chang: “Thermodynamic and Lattice Disorder in CsCl Phases,” Scripta Metall., 1972, 6, pp. 267–76.
S.A. Ali and V.A. Geiderik: “Thermodynamic Properties of Nickel and Zinc Solid Alloys,” J. Phys. Chem., 1972, 46(10), pp. 2514–18.
W.W. Liang, J.W. Franks, and Y.A. Chang: “Thermodynamic Activity of β-NiZn Phase by the Dew Point Method,” Metall. Trans., 1972, 3, pp. 2555–56.
W.W. Liang, Y.A. Chang and S. Lau: “The Effect of Lattice Disorder on the Thermodynamic Properties of the β1 Ni-Zn Alloys,” Acta Metall., 1973, 21, pp. 629–37.
R.P. Anantatmula and D.B. Masson: “Thermodynamic Properties of Solid Ni-Zn Alloys by Atomic Absorption,” Metall. Trans., 1974, 5, pp. 605–13.
S. Budurov, G. Vasily, and N. Nenchev: “Nickel-Rich Side of the Ni-Zn Phase Diagram Z,” Z. Metallkd., 1974, 65(11), pp. 681–83.
S. Lau, Y.A. Chang and S. Kou: “Thermodynamics of the β Ni-Zn Intermetallic Phase Exhibiting the CsCl Structure,” Metall. Trans. A, 1974, 5, pp. 1979–86.
Y.A. Chang, G. Henning, and D. Naujick: “Thermodynamics of the Terminal fcc Ni-Zn Solid Solutions,” Acta Metall., 1974, 22(1), pp. 7–11.
S. Kou and Y.A. Chang: “Thermodynamics of β-NiZn and αNiZn Phases,” Metall. Trans. A, 1975, 6, pp. 245–48.
S. Budurov, G. Wassilew, and L. Mandadshieva: “Thermodynamics of Co-Zn and Ni-Zn Austenites,” Z. Metallkd., 1976, 67, pp. 307–10.
S. Budurov and G. Wassilew: “The Thermodynamics of Beta and Gamma Intermetallic Compounds of Ni-Zn and Co-Zn Systems,” Z. Metallkd., 1977, 68, pp. 795–98.
H. Hagiwara, S. Sugino, and K. Yamaguchi: “Activity of Zinc in Liquid Nickel-Zinc Alloys,” Bull. Univ. Osaka Proj., 1977, 26, pp. 81–86.
A. J. Morton: “Inversion Domains in Gamma-Brass Type Phases. Stabilization Mechanism-Role of Electron Concentration,” Phys. Status Solidi, 1977, 44(1), pp. 205–14.
M. Hillert and M. Jarl: “A Model for Alloying Effect in Ferromagnetic Metals,” CALPHAD, 1978, 2, pp. 227–38.
A.J. Morton: “The Gamma-Phase Regions of the CuZn, Ni-Zn and Pd-Zn Binary Systems,” Acta Metall., 1979, 27(5), pp. 863–67.
N. Ahmad and J.N. Pratt: “On the Enthalpies and Entropies of Formation of Solid Nickel-Zinc Alloys,” Thermochim. Acta, 1981, 45, pp. 139–51.
C. Cunat, M. Dirand, J.P. Hilger, and J. Hertz: “Thermodynamic Properties of Binary System Ni-Zn in Solid Phase,” Ann. Chim., 1982, 7, pp. 353–68.
W. Vogelbein, B. Predel, and Y.A. Chang: “Thermodynamic Properties of Binary System Ni-Zn in Solid Phase,” Z. Metallkd., 1982, 73, pp. 530–33.
B. Sundman, B. Janson, and J.-O. Anderson: “The Thermo-Cal Data Bank System,” CALPHAD, 1985, 9(2), pp. 153–90.
P. Nash and Y.Y. Pan: “The Ni-Zn System,” Bull. Alloy Phase Diagrams, 1987, 8, pp. 422–30.
A.T. Dinsdale: “SGTE Data for Pure Elements,” CALPHAD, 1991, 15(4), pp. 317–425.
G.P. Vassilev: “Thermodynamic Evaluation of the Nickel-Rich Part of the Ni-Zn System,” Cryst. Res. Technol., 1992, 27(4), pp. 523–27.
G.P. Vassilev: “Thermodynamic Evaluation of the Ni-Zn System,” J. Alloys Compds, 1992, 190, pp. 107–112.
V.I. Dybkov and O.V. Duchenko: “The Homogeneity Ranges of the Delta and Gamma Phases of the Ni-Zn Binary System,” J. Phase Equilibria, 1998, 19, pp. 434–40.
G.P. Vassilev, T. Gomez-Acebo, and J.-C. Tedenac: “Thermodynamic Optimization of the Ni-Zn System,” J. Phase Equilibria, 2000, 21(3), pp. 287–301.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, X., Tang, NY. & Toguri, J.M. Thermodynamic assessment of the Ni-Zn system. JPE 23, 140 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1361/1054971023604125
Received:
Revised:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1361/1054971023604125