Abstract
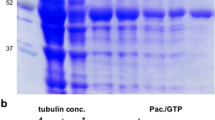
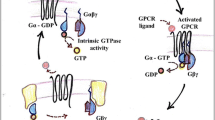
GAP-43 and Go are peripheral membrane proteins enriched in neuronal growth cone. GAP-43 was highly purified from bovine cerebral cortex and myristoylated Goα was highly purified from Escherichia coli cotransformed with pQE60 Goα and pBB131 (NMT). GAP-43 stimulated GTPγS binding to Goα and the stimulation effect was dependent on concentration of GAP-43. Protein-protein binding experiments using CaM-Sepharose affinity media revealed that Goα GDP bound GAP-43 directly to form intermolecular complex. This interaction induced conformational change of Goα. In the presence of GAP-43, fluorescence spectrum of Goα GDP blue shifted 4 nm; fluorescence intensity increased 35.3% and apparent quenching constant (Ksv) increased from (1.1 ±0.22) ×105 to (4.1±0.43) × 105 (M−1). However, no obvious changes of fluorescence spectra of Goα GTPγS were observed in the absence or presence of GAP-43. Our results indicated that GAP-43 induced conformational change of Goα GDP so as to accelerate GDP release and subsequent GTPγS binding, which activates G proteins to trigger signal transduction and amplification. These results provided insights into understanding the function of G proteins in coupling between receptors and effectors and the key role of GDP/GTP exchange mode in GTPase cycle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gispen, W. H., Nielander, H. B., De Graan, P. N. E. et al., Role of the growth-associated protein B-50/GAP-43 in neuronal plasticity, Mol. Neurobiol., 1991, 5: 61–85.
Skene, J. H., Axonal growth-associated proteins, Annu. Rev. Neurosci., 1989, 12: 127–156.
Strittmatter, S. M., GAP-43 as a modulator of G protein transduction in the growth cone, Perspect Dev. Neurobiol., 1992, 1: 13–19.
Aigner, L., Caroni, P., Depletion of 43-kD growth-associated protein in primary sensory neurons leads to diminished formation and spreading of growth cones, J. Cell Biol., 1993, 123: 417–429.
Strittmatter, S. M., Fankhauser, C., Huang, P. L. et al., Neuronal pathfinding is abnormal in mice lacking the neuronal growth cone protein GAP-43, Cell, 1995, 80: 445–452.
Strittmatter, S. M., Valenzuela, D., Kennedy, T. E. et al., Go is a major growth cone protein subject to regulation by GAP-43, Nature, 1990, 344: 836–841.
Gilman, A. G., G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals, Annu. Rev. Biochem., 1987, 56: 615–649.
Igarashi, M., Strittmatter, S. M., Vartanian, T. et al., Mediation by G proteins of signals that cause collapse of growth cones, Science, 1993, 259: 77–79.
Strittmatter, S. M., Valenzuela, D., Sudo, Y. et al., An intracellular guanine nucleotide release protein for Go, GAP-43 stimulates isolated alpha subunits by a novel mechanism, J. Biol. Chem., 1991, 266: 22465–22471.
Strittmatter, S. M., Cannon, S. C., Ross, E. M. et al., GAP-43 augments G protein-coupled receptor transduction in Xenopus laevis oocytes, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1993, 90: 5327–5331.
Mumby, M., Linder, M., Myristoylation of G-protein α subunits, Method Enzymology, 1994, 237: 254–268.
Oestreicher, A. B., van Duin, M., Zwiers, H. et al., Cross-reaction of anti-rat B-50: Characterization and isolation of a “B-50 phosphoprotein“ from bovine brain, J. Neurochem., 1984, 43: 935–943.
Andreasen, T. J., Luetje, C. W., Heideman, W. et al., Purification of a novel calmodulin binding protein from bovine cerebral cortex membranes, Biochemistry, 1983, 22: 4615–4618.
Horigome, T., Sugano, H., A rapid method for removal of detergents from protein solution, Anal. Biochem., 1983, 130: 393–396.
Sudo, Y., Valenzuela, D., Beck_Sickinger, A. G. et al., Palmitoylation alters protein activity: blockade of G(o) stimulation by GAP-43, EMBO J., 1992, 11: 2095–2102.
Duncan, J. A., Gilman, A. G., Autoacylation of G protein α subunits, J. Biol. Chem., 1996, 271: 23594–23600.
Yang, S., Huang, Y., In vitro palmitoylation of native bovine brain Goα, Science in China, Ser. C, 2000, 43(5): 482–488.
Bollag, D. M., Rozycki, M. D., Edelstein, S. J., Protein Methods, 2nd ed., New York: Wiley-Liss, Inc., 1996.
Basi, G. S., Jacobson, R. D., Virag, I. et al., Primary structure and transcriptional regulation of GAP-43, a protein associated with nerve growth, Cell, 1987, 49: 785–791.
Alexander, K. A., Wakim, B. T., Doyle, G. S. et al., Identification and characterization of the calmodulin-binding domain of neuromodulin, a neurospecific calmodulin-binding protein, J. Biol. Chem., 1988, 263: 7544–7549.
Lan, K. L., Remmers, A. E., Neubig, R. R., Roles of G(o)alpha tryptophans in GTP hydrolysis, GDP release, and fluorescence signals, Biochemistry, 1998, 37: 837–843.
Lambright, D. G., Noel, J. P., Hamm, H. E. et al., Structural determinants for activation of the α-subunit of a heterotrimeric G protein, Nature, 1994, 369: 621–628.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Huang, Y. Stimulation and conformational change of Goα induced by GAP-43. Sci. China Ser. C.-Life Sci. 46, 174–183 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1360/03yc9019
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1360/03yc9019