Abstract
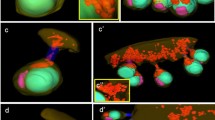
To study whether integrins on cell membrane ligate with intracellular cytoskeletal proteins and mediate their reorganization in egg activation, female mice were used for superovulation. The zona-free oocytes were incubated separately with specific ligand of integrins, an active RGD peptide, in vitro for certain period of time. RGE peptide and mouse capacitated sperm were used as controls. Freshly ovulated oocytes and those treated with different factors were immunostained with FITC-labeled anti-actin antibody, then detected with confocal microscope. The results demonstrated that freshly ovulated mouse oocytes, oocytes incubated for 2 h in vitro and those treated with control RGE peptide for 15 min showed hardly visible fluorescene or only thin fluorescence in plasma membrane region. Oocytes coincubated with sperms for 15 min and those treated with active RGD peptide for 10 min, 30 min and 2 hours respectively had strong and thick fluorescence in the plasma membrane and cortical region of oocytes, and some of them showed asymmetrically fluorescent distribution. It is proved that integrins on membrane are ligated directly with cytoskeletal protein. Integrins binding with their ligands regulate reorganization of cytoskelal protein, which may be involved in transmembrane signaling in egg activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schaffert, C. S., Sorrell, M. F., Tuma, D. J., Expression and cytoskeletal association of integrin subunits is selectively increased in rat perivenous hepatocytes after chronic ethanol administration, Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res., 2001, 25(12): 1749–1757.
Takahashi, K., The linkage between beta1 integrin and the actin cytoskeleton is differentially regulated by tyrosine and serine/threonine phosphorylation of beta1 integrin in normal and cancerous human breast cells, BMC Cell Biol., 2001, 2(1): 23.
Geiger, B., Bershadsky, A., Pankov, R. et al., Transmembrane crosstalk between the extracellular matrix-cytoskeleton crosstalk, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2001, 2(11): 793–805.
Wu, C., Dedhar, S., Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) and its interactors: A new paradigm for the coupling of extracellular matrix to actin cytoskeleton and signaling complexes, J. Cell Biol., 2001, 155(4): 505–510.
Clark, E. A., Brugge, J. S., Integrin and signal transduction pathway: The road taken, Science, 1995, 268:233–239.
Meredith, Jr. J. E., Winitz, S., Lewis, J. M. et al., The regulation of growth and intracellular signalling by integrins, Endocrine Rev., 1996, 17(3): 207–220.
Evans, J. P., Schultz, R. M., Kopf, G. S., Identification and localization of integrin subunits in oocytes and eggs of the mouse, Mol. Reprod. Dev., 1995, 40: 211–220.
Mabuchi, I., Hamaguchi, Y., Kobayashi, T. et al., Alpha-actinin from sea urchin eggs: Biochemical properties, interaction with actin, and distribution in the cell during fertilization and cleavage, J. Cell Biol., 1985, 100: 375–383.
Hamaguchi, Y., Mabuchi, I., Accumulation of fluorescently labeled actin in the cortical layer in sea urchin eggs after fertilization, Cell Motil Cytoskeleton, 1988, 9(2): 153–163.
Lehtonen, E., Reima, I., Changes in the distribution of vinculin during preimplantation mouse development, Differentiation, 1986, 32: 125–134.
Dale, B., De-Santis, A., The effect of cytochalasin B and D on the fertilization of sea urchins, Dev. Biol., 1981, 83(2): 232–237.
Gallicano, G. I., Composition, regulation, and function of the cytoskeleton in mammalian eggs and embryos, Front Biosci., 2001, 6: D1089–1108.
Connors, S. A., Kanatsu-Shinohara, M., Schultz, R. M. et al., Involvement of the cytoskeleton in the movement of cortical granules during oocyte maturation, and cortical granule anchoring in mouse eggs, Dev. Biol., 1998, 200: 103–115.
Kim, N.-H., Chung, K. S., Day, B. N., The distribution and requirement of microtubules and microfilaments during fertilization and parthenesis in pig oocytes, J. Reprod. Fert., 1997, 111: 143–149.
Kim, N-H., Simerly, C., Funahashi, H. et al., Microtubule organization in porcine oocytes during fertilization and parthenogenesis, Bio. Reprod., 1996, 54: 1397–1404.
Nadai, C., Fenichel, P., Donzeau, M. et al., Characterization and role of integrins during gametic interaction and egg activation, Zygote, 1996, 4:31–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, L., Zhang, L., He, Y. et al. Reorganization of cytoskeletal proteins of mouse oocytes mediated by integrins. Sci. China Ser. C.-Life Sci. 47, 540–544 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1360/03yc0155
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1360/03yc0155