Abstract
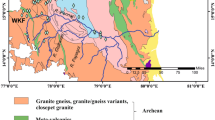
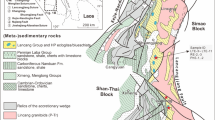
Mineralogical and geochemical variations among the Carboniferous and Cretaceous sedimentary kaolin deposits from Sinai provided an opportunity to examine the effect of the source area on compositions of the deposits. The Carboniferous kaolin deposits are mineralogically and geochemically heterogeneous. The Khaboba and Hasbar deposits consist of kaolinite, quartz, anatase, illite, chlorite, zircon, and leucoxene. The shale-normalized rare earth element (REE) patterns of the Khaboba deposit showed a slight LREE over HREE enrichment ((La/Yb)SN = 1.19–1.51) with a MREE depletion (Gd/Gd*SN = 0.51–0.75), while the Hasbar kaolin had a MREE enrichment. The Abu Natash kaolin deposit consisted of kaolinite, anatase, and a little quartz with larger TiO2, Cr, and V and smaller Zr and Nb contents compared to other Carboniferous deposits. The shale-normalized REE patterns of the Abu Natash deposit exhibited a positive Eu anomaly (Eu/Eu*SN = 1.28–1.40) and a MREE enrichment (Gd/Gd*SN = 1.41–2.05). The Cretaceous deposits were relatively homogeneous in terms of mineralogical composition and geochemistry and are composed of kaolinite, quartz, anatase, rutile, zircon, and leucoxene. The Cretaceous kaolin deposits showed mostly flat shale-normalized REE patterns with a variable LREE depletion.
The presence of illite and chlorite, the absence of rutile, large Zr and Nb contents, and the REE patterns suggested a component of weathered low-grade metasediments as a source for the Carboniferous deposits in the Khaboba and Hasbar areas, while the large Ti, Cr, and V, and small quartz contents indicated mafic source rocks for the Abu Natash deposit. The abundance of high-Cr rutile and the absence of illite and chlorite, and large Zr, Ti, Cr, and V contents suggested a mixture of medium- to high-grade metamafic and granitic rocks as source rocks for the Cretaceous kaolin deposits. The occurrence of alkaline rocks in the source of the deposits studied was identified by high-Nb contents and the presence of bastnaesite. The mineralogical and geochemical heterogeneity and lesser maturity of the Carboniferous deposits suggested local sources for each deposit and their deposition in basins close to the sources. The mineralogical and geochemical homogeneity and maturity of the Cretaceous deposits, on the other hand, indicated common sources for all deposits and their deposition in relatively remote basins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah, A.M., Adindani, A., and Fahmy, N. (1963) Stratigraphy of Upper Paleozoic Rocks, Western Side of the Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Egyptian Geological Survey, 18 pp.
Aboul-Ela, N.M., Abdel-Gawad, G.I., and Saber, S.C. (1990) Contribution to the stratigraphy of Gebel El-Minshera area, northern Sinai, Egypt. Abstracts, 28th Annual Meeting, The Geological Society of Egypt, Cairo, 18 pp.
Abu-Zied, R.H. (2008) Lithostratigraphy and biostratigraphy of some Lower Cretaceous outcrops from Northern Sinai, Egypt. Cretaceous Research, 29, 603–624.
Akarish, A.I.M. and El-Gohary, A.M. (2008) Petrography and geochemistry of lower Paleozoic sandstones, East Sinai, Egypt: Implications for provenance and tectonic setting. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 52, 43–54.
Beeri-Shlevin, Y., Katzir, Y., and Valley, J.W. (2009) Crustal evolution and recycling in a juvenile continent: Oxygen isotope ratio of zircon in the northern Arabian Nubian Shield. Lithos, 107, 169–184.
Baioumy, H. and Gilg, H.A. (2011) Pisolitic flint kaolin from Kalabsha, Egypt: A laterite-derived facies. Sedimentary Geology, 236, 141–152.
Boulis, S.N. and Attia, A.K. (2001) Mineralogy and origin of Carboniferous and Cretaceous kaolin deposits from a number of localities in Egypt. Pp. 221–229 in: Mineral Deposits at the Beginning of the 21stCentury (A. Piestrzyrisk, editor). Swets and Zeitinger Publications, Lisse, The Netherlands.
Boynton, W.V. (1984) Geochemistry of the REE: Meteorite studies. Pp. 63–114 in: Rare Earth Element Geochemistry (P. Henderson, editor). Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Condie, K.C. (1991) Another look at rare earth elements in shales. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 39, 1691–1703.
Costa, M.L. and Moraes, E.L. (1998) Mineralogy, geochemistry and genesis of kaolin deposits from the Amazon region. Mineralium Deposita, 33, 283–297.
Cullers, R.L., Chaudhuri, S., Arnold, B., Lee, M., and Wolf, C.W. (1975) Rare earth distributions in clay minerals and in the clay-sized fraction of the lower Permian Havensville and Eskridge shales of Kansas and Oklahoma. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 39, 691–1703.
Dombrowski, T. and Murray, H.H. (1984) Thorium — a key element in differentiating Cretaceous and Tertiary kaolin deposits in Georgia and South Carolina. Proceedings of 27th International Geological Congress, 15, 305–317.
El-Agami, N.L., Ibrahim, E.H., and Oda, H.H. (2000) Sedimentary origin of the Mn-Fe ore of Um Bogma, southwest Sinai: Geochemical and paleomagnetic evidence. Economic Geology, 95, 607–620.
El Hazek, M.N., Ahmed, F.Y., El Kasaby, M.A., and Attia, R.M. (2008) Sulfuric acid leaching of polymetallic Abu Zeneima gibbsite-shale. Hydrometallurgy, 90, 34–39.
El-Shishtawy, A.M., Salem, I.A., Al-Dosuky, B.T., El-Assy, I.E., and Aly, G.A. (2006) Carboniferous kaolin deposits: Its petrology, radioactivity and genesis, Sinai, Egypt. International Conference on Geochemistry, Alexandria, Egypt, II, 107–132.
El-Shishtawy, A.M., Al-Dosuky, B.T., Salem, I.A., El-Assy, I.E., and Aly, G.A. (2008) Mineralogical and geochemical characteristics of Cretaceous kaolin deposits from west central Sinai, Egypt. 9th International Conference on the Geology of the Arab World (GAW-9), pp. 130–148.
Elzea Kogel, J., Pickering, S.M., Shelobolina, E.S., Chowns, T.M., Yuan, J., and Avant, D.M. (2002) The Georgia Kaolin deposits: Geology and Utilization. Society for Mining, Metallurgy, and Exploration, USA, 96 pp.
Eyal, M., Litvinovsky, B., Jahn, B.M., Zanvilevich, A., and Katzir, Y. (2010) Origin and evolution of post-collisional magmatism: Coeval Neoproterozoic calc-alkaline and alkaline suites of the Sinai Peninsula. Chemical Geology, 269, 153–179.
Force, E.R. (1980) The provenance of rutile. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 50, 485–488.
Force, E.R. (1991) Geology of titanium-mineral deposits. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 259, 112 pp.
Galán, E., Aparicio, P., Gonzales, I., and Laiglesia, A. (1994) Influence of associated components of kaolin on the degree of disorder of kaolinite as determined by XRD. Geologica Carpathica Clays, 45, 59–75.
Ghorab, M.A. (1961) Abnormal stratigraphic features in Ras Gharib Oilfield, Egypt. Proceedings of the Third Arab Petroleum Congress, Alexandria, Egypt, pp. 1–10.
Goldbery, R. and Beyth, M. (1984) Laterization and ground water alteration phenomena in the Triassic Budra Formation, south-western Sina. Sedimentology, 31, 575–594.
Gromet, L.P., Dymek, R.F., Haskin, L.A., and Korotev, R.L. (1984) The North American Shale composite: its compilation, major and trace element characteristics. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 48, 2469–2482.
Haskin,M.A. and Haskin, L.A. (1966) Rare Earths in European shales: a redetermination. Science, 154, 507–509.
Hinckley, D. (1963) Variability in crystallinity values among the kaolin deposits of the Coastal Plain of Georgia and South Carolina. Proceedings of the 11thInternational Conference of Clays and Clay Minerals, pp. 229–235.
Hurst, V.J. and Pickering, S.M. (1997) Origin and classification of Coastal Plain kaolin deposits, southeastern USA, and the role of groundwater and microbial action. Clays and Clay Minerals, 45, 274–285.
Khalifa, M.A., Soliman, H.E., and Wanas, H.A. (2006) The Cambrian Araba Formation in northeastern Egypt: Facies and depositional environments. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 27, 873–884.
Kleeberg, R. and Bergmann, J. (1998) Quantitative Röntgenphasenanalyse mit den Rietveld-Programmen BGMN und AUTOQUANT in der täglichen Laborpraxis. Pp. 237–250 in: Tone in der Geotechnik und Baupraxis (K.H. Henning and J. Kasbohm, editor). Beiträge zur Jahrestagung Greifswald, Berichte der DTTG, Greifswald, Germany.
Knill, J.L. (1978) Industrial Geology. Oxford University Press, London, 344 pp.
Kogel, J.E. and Lewis, S.A. (2001) Baseline studies of the Clay Minerals Society source clays: chemical analysis by inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy (ICP-MS). Clays and Clay Minerals, 49, 387–392.
Kolodner, K., Avigad, D., McWilliams, M., Wooden J.L., Weissbrod, T., and Feinstein, S. (2009) Provenance of north Gondwana Cambrian-Ordovician sandstone: U-Pb SHRIMP dating of detrital zircons from Israel and Jordan. Geological Magazine, 143, 367–391.
Kora, M., El-Shahat, A., and Abu Shabana, M. (1994) Lithost ratigraphy of the Mn-bearing Um Bogma Formation, west-central Sinai, Egypt. Journal of African Earth Science, 18, 151–162.
Ma, L., Jin, L. and Brantley, S.L. (2011) How mineralogy and slope aspect affect REE release and fractionation during shale weathering in the Susquehanna/Shale Hills Critical Zone Observatory. Chemical Geology, 290, 31–49.
McLaughlin, J.R.W. (1959) The geochemistry of some kaolinitic clays. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 17, 11–16.
McLennan S.M. (1989) Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks: influence of the provenance and sedimentary process. Pp. 169–200 in: Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Rare Earth Elements (B.R. Lipin and G.A. McKay, editors). Reviews in Mineralogy, 21, Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, D.C.
McLennan, S.M., Taylor, S.R., McCulloch, M.T., and Maynard, J.B. (1990) Geochemical and Nd-Sr isotopic composition of deep-sea turbidites: Crustal evolution and plate tectonic associations. Geochimica et Cosmochimca Acta, 54, 2012–2050.
Murray, H.H. (2007) Applied Clay Mineralogy. Developments in Clay Science, 2, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 180 pp.
Murray, H.H. and Keller, W.D. (1993) Kaolin, kaolin and kaolin. Pp. 1–24 in: Kaolin Genesis and Utilization (H.H. Murray, W. Bondy, and C. Harvey, editors). Special Publication 1, The Clay Minerals Society.
Nabawy, B. (2010) Impacts of dolomitization on the petrophysical properties of the Cenomanian El-Halal Formation in its type section, north Sinai, Egypt. Geophysical Research Abstracts, 12, EGU2010-8821.
Nagy, G., Draganits, E., Demeny, A., Panto, G., and Arkai, P. (2002) Genesis and transformations of monazite, florencite and rhabdophane during medium grade metamorphism: examples from the Sopron Hills, Eastern Alps. Chemical Geology, 191, 25–46.
Nance, W.B. and Taylor, S.R. (1976) Rare earth element pattern and crustal evolution: I. Australian post-Archean sedimentary rocks. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 40, 1539–1551.
Plank, T. and Langmuir, C.H. (1998) The chemical composition of subducting sediment and its consequences for the crust and mantle. Chemical Geology, 145, 325–394.
Prudêncio, M.I., Gouveia, M.A., and Braga, S.M.A. (1995) REE distribution in present day and ancient surface environments of basaltic rocks (central Portugal). Clay Minerals, 30, 239–248.
Pruett, R.J. and Murray, H.H. (1993) The mineralogical and geochemical controls that source rocks impose on sedimentary kaolin deposits. Pp. 149–170 in: Kaolin Genesis and Utilization (H.H. Murray, W. Bundy, and C. Harvey, editors). Special Publication 1, The Clay Minerals Society, Indiana, USA.
Pruett, R.J. and Pickering, Jr., S.M. (2006) Kaolin. Pp. 390–427 in: Industrial Minerals and Rocks (J. Elzea Kogel, N.C. Trivedi, J.M. Barker, and S.T. Krukowski, editors). Society for Mining, Metallurgy, and Exploration, Inc., Littleton, Colorado, USA.
Rashed, A.F. and Amer, M.N. (1994) Geological and mineralogical studies on some west-central Sinai kaolin deposits and their industrial applications. Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Industrial Applications of Clays, Cairo, pp. 306–314.
Saad, N., Zidan, B.I., and Khalil, K.I. (1994) Geochemistry and origin of the manganese deposits in the Um Bogma region, west central Sinai, Egypt. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 19, 109–116.
Schroeder, P.A., Pruett, R.J., and Melear, N.D. (2004) Crystal-chemical changes in an oxidative weathering front in a Georgia kaolin deposit. Clays and Clay Minerals, 52, 211–220.
Shimron, A.S. (1975) Petrogenesis of the Tarr albitite-carbonatite complex, Sinai Peninsula. Mineralogical Magazine, 40, l3–24.
Sousa, D.J.L., Varajão, A.F.D.C., and Yvon, J. (2006) Geochemical evolution of the Capim River kaolin, Northern Brazil. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 88, 329–331.
Sousa, D.J.L., Varajao, A.F.D.C., Yvon, J., Scheller, T., and Moura, C.A.V. (2007) Ages and possible provenance of the sediments of the Capim River kaolin, northern Brazil. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 24, 25–33.
Taylor, S.R. and McLennan, S.H. (1985) The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution. Blackwell, Oxford, UK, 312 pp.
Turekian, K.K. and Wedepohl, K.H. (1961) Distribution of the elements in some major units of the Earth’s crust. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 72, 175–191.
Walley El-Dine, N., Sroor, A., El-Shershaby, A., El-Bahi, S.M., and Ahmed, F. (2004) Radioactivity in local and imported kaolin types used in Egypt. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 60, 105–109.
Weissbrod, T. (1969) The Paleozoic of Israel and adjacent countries, Part II: The Paleozoic outcrops in Southwestern Sinai and their correlation with those of southern Israel. Israel Geological Survey Bulletin, 48, 32 pp.
Zack, T., Eynatten, H.V., and Kronz, A. (2004) Rutile geochemistry and its potential use in quantitative provenance studies. Sedimentary Geology, 171, 37–58.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baioumy, H.M., Gilg, A. & Taubald, H. Mineralogy and Geochemistry of the Sedimentary Kaolin Deposits from Sinai, Egypt: Implications for Control by the Source Rocks. Clays Clay Miner. 60, 633–654 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2012.0600608
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2012.0600608