Abstract
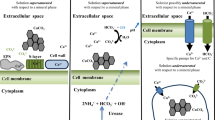
Mineralization of microbial biomass is a common phenomenon in geothermal habitats, but knowledge of the structure of the minerals formed in these environments is limited. A combination of spectroscopic, microscopic, and stable isotopic methods, as well as the chemical analysis of spring water, were employed in the present study to characterize calcium carbonate minerals deposited in filamentous cyanobacterial mats in different locations of La Duke hot spring, a circumneutral thermal feature near the north entrance of Yellowstone National Park, Montana, USA. Calcite was the primary crystalline mineral phase associated with biofilm-containing deposits closest to the source of the spring and the suspended microbial biomass in a pool further from the source. The carbonate minerals at all sites occurred as aggregated granules, ~2 μm in diameter, in close association with the microbial biomass. Only in the deposits closest to the source were the granules organized as laminated structures interspersed with microbial biomass. The calcium carbonate grains contained two distinct regions: a dense monolithic calcite core and a porous dendritic periphery containing organic matter (OM). Electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) indicated that the voids were infilled with OM and carbonates. The EELS technique was employed to distinguish the source of carbon in the organic matter and carbonate mixture. The studies of carbon isotope compositions of the calcium carbonates and the saturation indices for calcite in the spring waters suggest that processes (abiotic vs. biotic) controlling the carbonate formation may vary among the sampling sites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atekwana, E.A., Atekwana, E., Legall, F.D., and Krishnamurthy, R.V. (2004) Field evidence for geophysical detection of subsurface zones of enhanced microbial activity. Geophysical Research Letters, 31, 1–5.
Aloisi, G. (2008) The calcium carbonate saturation state in cyanobacterial mats throughout Earth’s history. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 72, 6037–6060.
Aloisi, G., Gloter, A., Krüger, M., Wallmann, K., Guyot, F., and Zuddas, P. (2006) Nucleation of calcium carbonate on bacterial nanoglobules. Geology Society of America, 34, 1017–1020.
Arp, G., Reimer, A., and Reitner, J. (2001) Photosynthesis-induced biofilm calcification and calcium concentrations in Phanerozoic Oceans. Science, 292, 1701–1704.
Baronnet, A., Cuif, J.P., Dauphin, Y., Farre, B., and Nouet, J. (2008) Crystallization of biogenic Ca-carbonate within organo-mineral micro-domains. Structure of the calcite prisms of the Pelecypod Pinctada margaritifera (Mollusca) at the submicron to nanometre ranges. Mineralogical Magazine, 72, 617–626.
Benzerara, K., Yoon, T.H., Menguy N., Tyliszczak, T., and Brown Jr., G.E. (2005) Nanoscale environments associated with bioweathering of a Mg-Fe-pyroxene. The National Academy of Sciences, 102, 979–982.
Bethke, C.M. (1996) Geochemical Reaction Modeling: Concept and Applications. Oxford University Press, New York.
Bethke, C.M. (1998) The Geochemist’s Workbench, Version 3.0: A Users Guide to Rxn, Act2, Tact, React, and Gtplot. Hydrogeology Program, University of Illinois, Urbana, Illinois, USA.
Bosak, T. and Newman, D.K. (2003) Microbial nucleation of calcium carbonate in the Precambrian. Geology, 31, 577–580.
Casanova, J. (1986) East African rift stromatolites. Pp. 201–210 in: Sedimentation in the African Rifts (I.E. Frostick, R.W. Renaut, I. Reid, and J.J. Tiercelin, editors). Special Publication, 25. Geological Society of London.
Castanier, S., Métayer-Levrel, G.L., and Perthuisot, J.P. (1999) Ca-carbonates precipitation and limestone genesis - the microbiogeologist point of view. Sedimentary Geology, 126, 9–23.
Chafetz, H.S. and Folk, R.L. (1984) Travertines: depositional morphology and the bacterially constructed constituents. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 54, 289–316.
Cummings, C.E. and McCarthy, H.M. (1982) Stable carbon isotope ratios in Astrangia danae: evidence for algal modification of carbon pools used in calcification. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 6, 1125–1129.
Dittrich, M., Muller, B., Mavrocordatos, D., and Wehrli, B. (2003) Induced calcite precipitation by cyanobacterium Synechococcus. Acta Hydrochimica et Hydrobiologica, 31, 162–169.
Folk, R.L., Chafetz, H.S., and Tiezzi, P.A. (1985) Bizarre forms of depositional and diagenetic calcite in hot spring travertines, central Italy. Pp. 349–369 in: Carbonate Cements (N. Schneidermann and P. Harris, editors). SEPM Special Publication, 36, Society for Sedimentary Geology, Tulsa, Oklahoma, USA.
Ford, T.D. and Pedley, H.M. (1996) A review of tufa and travertine deposits of the world. Earth-Science Reviews, 41, 117–175.
Fouke, B.W., Farmer, J.D., Marais, D.J.D., Pratt, L., Sturchio, N.C., Burns, P.C., and Discipulo, M.K. (2000) Depositional facies and aqueous-solid geochemistry of travertine-depositing hot springs (Angel Terrace, Mammoth Hot Springs, Yellowstone National Park, U.S.A.). Journal of Sedimentary Research, 70, 565–585.
Fouke, B.W., Bonheyo, G.T., Sanzenbacher, B., and Frias-Lopez, J. (2003) Partitioning of bacterial communities between travertine depositional facies at Mammoth Hot Springs, Yellowstone National Park, U.S.A. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 40, 1531–1548.
Guo, L., Andrews, J., Riding, R., Dennis, P., and Dresser, Q. (1996) Possible microbial effects on stable carbon isotopes in hot-spring travertines. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 66, 468–473.
Jacobson, R.L. and Usdowski, E. (1975) Geochemical controls on a calcite precipitating spring. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 51, 65–74.
Kameda, J., Saruwatari, K., Beaufort, D., and Kogure, T. (2008) Textures and polytypes in vermiform kaolins diagenetically formed in a sandstone reservoir: a FIB-TEM investigation. European Journal of Mineralogy, 20, 199–204.
Kandianis, M.T., Fouke, B.W., Johnson, R.W., Veysey, J., and Inskeep, W.P. (2008) Microbial biomass: A catalyst for CaCO3 precipitation in advection-dominated transport regimes. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 120, 442–450.
Kim, J.W. and Dong, H. (2011) Application of electron energy-loss spectroscopy (EELS) and energy-filtered transmission electron microscopy (EFTEM) to the study of mineral transformation associated with microbial Fe-reduction of magnetite. Clays and Clay Minerals, 59, 176–188.
Knorre, H.V. and Krumbein, W.E. (2000) Bacterial calcification. Pp. 25–31 in: Microbial Sediments (R.E. Riding and S.M. Awramik, editors). Springer, Berlin.
Kogure, T. (2003) A program to assist Kikuchi pattern analysis. Journal of the Crystallographic Society of Japan, 45, 391–395.
McConaughey, T. (1989) 13C and 18O isotopic disequilibrium in biological carbonates: I. patterns. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 53, 151–162.
McCrea, J.M. (1950) On the isotopic chemistry of carbonates and a paleotemperature scale. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 18, 849–857.
Merz-preib, M. (2000) Calcification in cyanobacteria. Pp. 50–56 in: Microbial Sediments (R.E. Riding and S.M. Awramik, editors). Springer, Berlin.
Merz-Preib, M. and Riding, R. (1999) Cyanobacterial tufa calcification in two freshwater streams: ambient environment, chemical thresholds and biological processes. Sedimentary Geology, 126, 103–124.
Obst, M., Wehrli, B., and Dittrich, M. (2009a) CaCO3 nucleation by cyanobacteria: laboratory evidence for a passive, surface-induced mechanism. Geobiology, 7, 324–347.
Obst, M., Dynes, J.J., Lawrence, J.R., Swerhone, G.D.W., Benzerara, K., Karunakaran, C., Kaznatcheev, K., Tyliszczak, T., and Hitchcock, A.P. (2009b) Precipitation of amorphous CaCO3 (aragonite-like) by cyanobacteria: A STXM study of the influence of EPS on the nucleation process. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 73, 4180–4198.
Pentecost, A. (1985) Association of cyanobacteria with tufa deposits: identity, enumeration and nature of the sheath material revealed by histochemistry. Geomicrobiology Journal, 4, 285–298.
Pentecost, A. (2003) Cyanobacteria associated with hot spring travertines. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 40, 1447–1457.
Pentecost, A. and Riding, R. (1986) Calcification in cyanobacteria. Pp. 73–90 in: Biomineralization in Lower Plants and Animals (B.S.C. Leadbeater and R. Riding, editors). Special Publication, 30, Systematics Association, UK.
Pratt, B.R. (2001) Calcification of cyanobacterial filaments: Girvanella and the origin of lower Paleozoic lime mud. Geological Society of America, 29, 763–766.
Reksten, K. (1990) Superstructures in calcite. American Mineralogist, 75, 807–812.
Robbins, L.L. and Yates, K.K. (1998) Production of carbonate sediments by a unicellular green alga. American Mineralogist, 83, 1503–1509.
Schultze-Lam, S., Fortina, D., Davisa, B.S., and Beveridge, T.J. (1996) Mineralization of bacterial surfaces. Chemical Geology, 132, 171–181.
Shiraishi, F., Reimer, A., Bissett, A., Beer, D., and Arp, G. (2008) Microbial effects on biofilm calcification, ambient water chemistry and stable isotope records in a highly supersaturated setting (Westerhöfer Bach, Germany). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 262, 91–106.
Shiraishi, F., Okumura, T., Takahashib, Y., and Kanoa, A. (2010) Influence of microbial photosynthesis on tufa stromatolite formation and ambient water chemistry, SW Japan. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 74, 5289–5304.
Stumm, W. and Morgan, J.J. (1996) Aquatic Chemistry: Chemical Equilibria and Rates in Natural Waters. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Thompson, J.B. and Ferris, F.G. (1990) Cyanobacterial precipitation of gypsum, calcite, and magnesite from natural alkaline lake water. American Mineralogist, 18, 995–998.
Weiss, I.M., Tuross, N., Addadi, L., and Weiner, S. (2002) Mollusc larval shell formation: amorphous calcium carbonate is a precursor phase for aragonite. Journal of Experimental Zoology, 293, 478–491.
Weisse, D.J., Cretzmeyer, J.W., Crespi, A.M., Howard, W.G., and Skarstad, P.M. (1993) Electrochemical cells with endof- service indicator. United States patent, H01M 614
Whitton, B. A. and Potts, M. (2000) The Ecology of Cyanobacteria: their Diversity in Time and Space. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 669 pp.
Yvon, K., Jeitschko, W., and Parthe, E. (1977) LAZY PULVERIX, a computer program, for calculating X-ray and neutron diffraction power patterns. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 10, 73–74.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JW., Kogure, T., Yang, K. et al. The Characterization Of CaCO3 in a Geothermal Environment: A Sem/Tem-Eels Study. Clays Clay Miner. 60, 484–495 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2012.0600505
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2012.0600505