Abstract
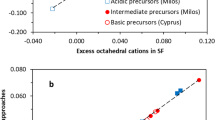
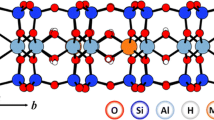
The layer charge density (LCD) of montmorillonite represents the permanent negative charge, its most important property. The LCD can be determined by two different methods, the structural formula method(SF M) and the alkylammonium method(AAM). Other methods of determining the LCD are calibrated against one or the other of these. The results of the two methods differ systematically: SFM values are larger than AAM values and the difference increases with increasing layer charge density. In the present study, the critical parameters of both methods were considered quantitatively in order to identify the most likely reason for the systematic difference. One particularly important argument against the validity of the SFM is that typical SFM values correspond to unrealistically large CEC values that have never been reported. In addition, SFM does not consider the variable charge which causes cations to be adsorbed to the outer surface (at pH >4). In contrast to minor constituents, which can of course also affect SFM values, the variable charge can explain only part of the systematic difference. The exchange of pure smectite samples with both Cu-trien andalkyla mmonium revealedthe presence of non-exchangeable, nonstructural cations (Na, K, Ca). These cations, together with 10% (or more) variable charge, may explain the differences in LCD values. The non-exchangeable, non-structural cations could stem from undetected traces of feldspar or volcanic glass. The present samples indicated that the systematic difference in LCD values between the two methods is related to the amount of non-exchangeable, non-structural cations only, indicating that the two LCD methods probe different features of smectites. Using the SFM on pure smectite provides a value for the total number of charges (permanent with andwithout fixed(= non-exchangeable, non-structural) cations plus variable charge). The AAM, on the other hand, provides the charge density of the exchangeable cations (without variable charge).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammann, L., Bergya, F., and Lagaly, G. (2005) Determination of the cation exchange capacity of clays with copper complexes revisited. Clay Minerals, 40, 441–453.
Brindley, G.W. and Pedro, G. (1976) Meeting of the Nomenclature Committee of AIPEA, Mexico City, July 21, 1975. AIPEA Newsletter, 12, 5–6.
Čičel, B. and Komadel, P. (1994) Structural formulae of layer silicates. Pp. 114–136 in: Quantitative Methods in Soil Mineralogy (J.E. Amonette and L.W. Zelazny, editors). Soil Science Society of America, Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
Dohrmann, R. and Kaufhold, S. (2009) Three new, quick CEC methods for determining the amounts of exchangeable calcium cations in calcareous clays. Clays and Clay Minerals, 57, 251–265.
Emmerich, K., Wolters, F., Kahr, G., and Lagaly, G. (2009) Clay profiling: the classification of montmorillonites. Clays and Clay Minerals, 57, 104–114.
Grim, R.E. and Güven, N. (1978) Bentonites–Geology, Mineralogy, Properties and Uses. Developments in Sedimentology, 46, Elsevier, New York, pp. 254.
Janek, M. and Komadel, P. (1999) Acidity of proton saturated and auto transformed montmorillonites characterisedwith proton affinity distribution. Geologica Carpathica, 50, 373–378.
Kamil, J. and Shainberg, I. (1968) Hydrolysis of sodium montmorillonite on sodium chloride solutions. Soil Science, 106, 193–199.
Kaufhold, S. (2005) Influence of layer charge density on the determination of the internal surface area of montmorillonites. Pp. 20–26 in: Berichte der Deutschen Ton- und Tonmineralgruppe, 11 (R. Dohrmann and S. Kaufhold, editors). ISSN 1432–7007.
Kaufhold, S. (2006) Comparison of methods for the determination of the layer charge density (LCD) of montmorillonites. Applied Clay Science, 34, 14–21.
Kaufhold, S. and Dohrmann, R. (2008) Detachment of colloidal particles from bentonites in water. Applied Clay Science, 39, 50–59.
Kaufhold, S. and Dohrmann, R. (2010) Stability of bentonites in salt solutions II. Potassium chloride solution–Initial step of illitization? Applied Clay Science, 49, 98–107.
Kaufhold, S., Dohrmann, R., Ufer, K., and Meyer, F.M. (2002) Comparison of methods for the quantification of montmorillonite in bentonites. Applied Clay Science, 22, 145–151.
Kaufhold, S., Dohrmann, R., Koch, D., and Houben, G. (2008) The pH of aqueous bentonite suspensions. Clays and Clay Minerals, 56, 338–343.
Kaufhold, S., Dohrmann, R., Ufer, K., Kleeberg, R., and Stanjek, H. (2011) Termination of swelling capacity of smectites by Cutrien exchange. Clay Minerals, (in press).
Komadel, P. and Stucki, J.W. (1988) Quantitative assay of minerals for Fe2+ and Fe3+ using 1,10-phenanthroline: III. A rapidphot ochemical method. Clays and Clay Minerals, 36, 379–381.
Köster, H.M. (1977) Die Berechnung kristallchemischer Strukturformeln von 2:1–Schichtsilikaten unter Berücksichtigung der gemessenen Zwischenschichtladungen und Kationenumtauschkapazitäten, sowie die Darstellung der Ladungsverteilung in der Struktur mittels Dreieckskoordinaten. Clay Minerals, 12, 45–54.
Lagaly, G. (1994) Layer charge determination by alkylammonium ions. Pp. 1–46 in: Layer Charge Characteristics of 2:1 Silicate Clay Minerals (A.R. Mermut, editor). CMS Workshop Lectures Vol. 6, The Clay Minerals Society, Boulder, Colorado, USA.
Lagaly, G. and Weiss, A. (1969) Determination of the layer charge in mica-type layer silicates. Pp. 61–80 in: Proceedings ofthe International Clay Conference, Tokyo (L. Heller, editor). Israel University Press, Jerusalem.
Laird, D.A. (1994) Evaluation of the structural formula and alkylammonium methods of determining layer charge. Pp. 79–104 in: Layer Charge Characteristics of 2:1 Silicate Clay Minerals (A.R. Mermut, editor). CMS Workshop Lectures Vol. 6, Clay Minerals Society, Boulder, Colorado, USA.
Laird, D.A., Scott, A.D., and Fenton, T.E. (1989) Evaluation of the alkylammonium methodof determining layer charge. Clays and Clay Minerals, 37, 41–46.
Maes, A., Stul, M.S., and Cremers, A. (1979) Layer chargecation-exchange capacity relationships in montmorillonite. Clays and Clay Minerals, 27, 387–392.
McBride, M.B. (1979) An interpretation of cation selectivity variations in M (super +)–M (super +) exchange on clays. Clays and Clay Minerals, 27, 417–422.
Meier, L.P. and Kahr, G. (1999) Determination of the cation exchange capacity (CEC) of clay minerals using the complexes of Copper (II) ion with Triethylenetetramine and Tretraethylenepentamine. Clays and Clay Minerals, 47, 386–388.
Mermut, A.R. (1994) Problems associated with layer charge characterisation of 2:1 phyllosilicates. Pp. 79–104 in: Layer Charge Characteristics of 2:1 Silicate Clay Minerals (A.R. Mermut, editor). CMS Workshop Lectures Vol. 6, The Clay Minerals Society, Boulder, Colorado, USA.
Newman, A.C.D. and Brown, G. (1987) The chemical constitution of clays. Pp. 1–128 in: Chemistry of Clays and Clay Minerals (A.C.D. Newman, editor). Mineralogical Society Monograph No. 6, John Wiley andSons, New York.
Ross, C.S. and Hendricks, S.B. (1945) Minerals of the montmorillonite group. U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 205-B, pp. 23–79.
Senkayi, A.D., Dixon, J.B., Hossner, L.R., and Kippenberger, L.A. (1985) Layer charge evaluation of expandable soil clays by an alkylammonium method. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 49, 1054–1060.
Stevens, R.E. (1946) A system for calculating analyses of micas and related minerals to end members. Contributions to Geochemistry, 1942–45, Geological Survey Bulletin, 950, 101–119.
Środoń, J. and McCarty, D.K. (2008) Surface area and layer charge of montmorillonite from CEC and EGM E/H2O retention measurements. Clays and Clay Minerals, 56, 155–174.
Tributh, H. and Lagaly, G. (1986) Aufbereitung und Identifizierung von Boden- und Lagerstättentonen. I. Aufbereitung der Proben im Labor. GIT-Fachzeitschrift für das Laboratorium, 30, 524–529.
Ufer, K., Stanjek, H., Roth, G., Dohrmann, R., Kleeberg, R., and Kaufhold, S. (2008) Quantitative phase analysis of bentonites by the Rietveldmet hod. Clays and Clay Minerals, 56, 272–282.
Verburg, K., Baveye, P., and McBride, M.B. (1995) Cation-exchange hysteresis andd ynamics of formation and breakdown of montmorillonite quasi-crystals. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 59, 1268–1273.
Vogt, K. and Köster, H.M. (1978) Zur Mineralogie, Kristallchemie und Geochemie einiger Montmorillonite aus Bentoniten. Clay Minerals, 13, 25–43.
Wolters, F., Lagaly, G., Kahr, G., Nüesch, R., and Emmerich, K. (2009) A comprehensive characterization of dioctahedral smectites. Clays and Clay Minerals, 57, 115–133.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaufhold, S., Dohrmann, R., Stucki, J.W. et al. Layer Charge Density of Smectites — Closing the Gap Between the Structural Formula Method and the Alkyl Ammonium Method. Clays Clay Miner. 59, 200–211 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2011.0590208
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2011.0590208