Abstract
Rotating relativistic stars have been studied extensively in recent years, both theoretically and observationally, because of the information they might yield about the equation of state of matter at extremely high densities and because they are considered to be promising sources of gravitational waves. The latest theoretical understanding of rotating stars in relativity is reviewed in this updated article. The sections on the equilibrium properties and on the nonaxisymmetric instabilities in f-modes and r-modes have been updated and several new sections have been added on analytic solutions for the exterior spacetime, rotating stars in LMXBs, rotating strange stars, and on rotating stars in numerical relativity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Rotating relativistic stars are of fundamental interest in physics. Their bulk properties constrain the proposed equations of state for densities greater than nuclear density. Accreted matter in their gravitational fields undergoes high-frequency oscillations that could become a sensitive probe for general relativistic effects. Temporal changes in the rotational period of millisecond pulsars can also reveal a wealth of information about important physical processes inside the stars or of cosmological relevance. In addition, rotational instabilities can produce gravitational waves, the detection of which would initiate a new field of observational asteroseismology of relativistic stars.
There exist several independent numerical codes for obtaining accurate models of rotating neutron stars in full general relativity, including one that is freely available. One recent code achieves near machine accuracy even for uniform density models near the mass-shedding limit. The uncertainty in the high-density equation of state still allows numerically constructed maximum mass models to differ by as much as a factor of two in mass, radius and angular velocity, and a factor of eight in the moment of inertia. Given these uncertainties, an absolute upper limit on the rotation of relativistic stars can be obtained by imposing causality as the only requirement on the equation of state. It then follows that gravitationally bound stars cannot rotate faster than 0.28 ms.
In rotating stars, nonaxisymmetric perturbations have been studied in the Newtonian and post-Newtonian approximations, in the slow rotation limit and in the Cowling approximation, but fully relativistic quasi-normal modes (except for neutral modes) have yet to be obtained. A new method for obtaining such frequencies is the time evolution of the full set of nonlinear equations. Frequencies of quasi-radial modes have already been obtained this way. Time evolutions of the linearized equations have also improved our understanding of the spectrum of axial and hybrid modes in relativistic stars.
Nonaxisymmetric instabilities in rotating stars can be driven by the emission of gravitational waves (CFS instability) or by viscosity. Relativity strengthens the former, but weakens the latter. Nascent neutron stars can be subject to the l = 2 bar mode CFS instability, which would turn them into a strong gravitational wave source.
Axial fluid modes in rotating stars (r-modes) have received considerable attention since it was discovered that they are generically unstable to the emission of gravitational waves. The r-mode instability could slow down newly-born relativistic stars and limit their spin during accretion-induced spin-up, which would explain the absence of millisecond pulsars with rotational periods less than ∼ 1:5 ms. Gravitational waves from the r-mode instability could become detectable if the amplitude of r-modes is of order unity. Recent 3D simulations show that this is possible on dynamical timescales, but nonlinear effects seem to set a much smaller saturation amplitude on longer timescales. Still, if the signal persists for a long time (as has been found to be the case for strange stars) even a small amplitude could become detectable.
Recent advances in numerical relativity have enabled the long-term dynamical evolution of rotating stars. Several interesting phenomena, such as dynamical instabilities, pulsation modes, and neutron star and black hole formation in rotating collapse have now been studied in full general relativity. The current studies are limited to relativistic polytropes, but new 3D simulations with realistic equations of state should be expected in the near future.
The goal of this article is to present a summary of theoretical and numerical methods that are used to describe the equilibrium properties of rotating relativistic stars, their oscillations and their dynamical evolution. It focuses on the most recently available preprints, in order to rapidly communicate new methods and results. At the end of some sections, the reader is directed to papers that could not be presented in detail here, or to other review articles. As new developments in the field occur, updated versions of this article will appear.
2 The Equilibrium Structure of Rotating Relativistic Stars
2.1 Assumptions
A relativistic star can have a complicated structure (such as a solid crust, magnetic field, possible superfluid interior, possible quark core, etc.). Still, its bulk properties can be computed with reasonable accuracy by making several simplifying assumptions.
The matter can be modeled to be a perfect fluid because observations of pulsar glitches have shown that the departures from a perfect fluid equilibrium (due to the presence of a solid crust) are of order 10-5 (see [112]). The temperature of a cold neutron star does not affect its bulk properties and can be assumed to be 0 K, because its thermal energy (≪ 1 MeV ∼ 1010 K) is much smaller than Fermi energies of the interior (> 60 MeV). One can then use a zero-temperature, barotropic equation of state (EOS) to describe the matter:
where ε is the energy density and P is the pressure. At birth, a neutron star is expected to be rotating differentially, but as the neutron star cools, several mechanisms can act to enforce uniform rotation. Kinematical shear viscosity is acting against differential rotation on a timescale that has been estimated to be [101, 102, 78]
where ρ, T and R are the central density, temperature, and radius of the star. It has also been suggested that convective and turbulent motions may enforce uniform rotation on a timescale of the order of days [153]. In recent work, Shapiro [267] suggests that magnetic braking of differential rotation by Alfvén waves could be the most effective damping mechanism, acting on short timescales of the order of minutes.
Within roughly a year after its formation, the temperature of a neutron star becomes less than 109 K and its outer core is expected to become superfluid (see [227] and references therein). Rotation causes superfluid neutrons to form an array of quantized vortices, with an intervortex spacing of
where Ω2 is the angular velocity of the star in 102 s-1. On scales much larger than the intervortex spacing, e.g. on the order of 1 cm, the fluid motions can be averaged and the rotation can be considered to be uniform [285]. With such an assumption, the error in computing the metric is of order
assuming R ∼ 10 km to be a typical neutron star radius.
The above arguments show that the bulk properties of an isolated rotating relativistic star can be modeled accurately by a uniformly rotating, zero-temperature perfect fluid. Effects of differential rotation and of finite temperature need only be considered during the first year (or less) after the formation of a relativistic star.
2.2 Geometry of spacetime
In general relativity, the spacetime geometry of a rotating star in equilibrium can be described by a stationary and axisymmetric metric gab of the form
where ν, ψ, ω and μ are four metric functions that depend on the coordinates r and θ only (see e.g. Bardeen and Wagoner [26]). Unless otherwise noted, we will assume c=G=1. In the exterior vacuum, it is possible to reduce the number of metric functions to three, but as long as one is interested in describing the whole spacetime (including the source-region of nonzero pressure), four different metric functions are required. It is convenient to write \({e^\psi }\) in the the form
where B is again a function of r and θ only [24].
One arrives at the above form of the metric assuming that i) the space-time has a timelike Killing vector field ta and a second Killing vector field φa corresponding to axial symmetry, ii) the spacetime is asymptotically flat, i.e. tata=-1, φaφa=+∞ and taφa=0 at spatial infinity. According to a theorem by Carter [57], the two Killing vectors commute and one can choose coordinates x0=t and x3=φ (where xa, a=0, …3 are the coordinates of the spacetime), such that ta and φa are coordinate vector fields. If, furthermore, the source of the gravitational field satisfies the circularity condition (absence of meridional convective currents), then another theorem [58] shows that the 2-surfaces orthogonal to ta and φa can be described by the remaining two coordinates x1 and x2. A common choice for x1 and x2 are quasi-isotropic coordinates, for which \({g_{r\theta }} = 0\) and \({g_{\theta \theta }} = {r^2}{g_{rr}}\) (in spherical polar coordinates), or and \({g_{\varpi z}} = 0\) and \({g_{rr}} = {r^2}{g_{\varpi \varpi }}\) (in cylindrical coordinates). In the slow rotation formalism by Hartle [143], a different form of the metric is used, requiring \({g_{\theta \theta }} = {g_{\phi \phi }}/{\sin ^2}\theta\).
The three metric functions ν, ψ and ω can be written as invariant combinations of the two Killing vectors ta and φa, through the relations
while the fourth metric function μ determines the conformal factor \({e^{2\mu }}\) that characterizes the geometry of the orthogonal 2-surfaces.
There are two main effects that distinguish a rotating relativistic star from its nonrotating counterpart: The shape of the star is flattened by centrifugal forces (an effect that first appears at second order in the rotation rate), and the local inertial frames are dragged by the rotation of the source of the gravitational field. While the former effect is also present in the Newtonian limit, the latter is a purely relativistic effect. The study of the dragging of inertial frames in the spacetime of a rotating star is assisted by the introduction of the local Zero-Angular-Momentum-Observers (ZAMO) [23, 24]. These are observers whose worldlines are normal to the t=const: hypersurfaces, and they are also called Eulerian observers. Then, the metric function ω is the angular velocity of the local ZAMO with respect to an observer at rest at infinity. Also, \({e^{ - \nu }}\) is the time dilation factor between the proper time of the local ZAMO and coordinate time t (proper time at infinity) along a radial coordinate line. The metric function ψ has a geometrical meaning: \({e^\psi }\) is the proper circumferential radius of a circle around the axis of symmetry. In the nonrotating limit, the metric (5) reduces to the metric of a nonrotating relativistic star in isotropic coordinates (see [321] for the definition of these coordinates).
In rapidly rotating models, an ergosphere can appear, where gtt>0. In this region, the rotational frame-dragging is strong enough to prohibit counter-rotating time-like or null geodesics to exist, and particles can have negative energy with respect to a stationary observer at infinity. Radiation fields (scalar, electromagnetic, or gravitational) can become unstable in the ergosphere [108], but the associated growth time is comparable to the age of the universe [68].
The asymptotic behaviour of the metric functions ν and ω is
where M, J and Q are the gravitational mass, angular momentum and quadrupole moment of the source of the gravitational field (see Section 2.5 for definitions). The asymptotic expansion of the dragging potential ω shows that it decays rapidly far from the star, so that its effect will be significant mainly in the vicinity of the star.
2.3 The rotating fluid
When sources of non-isotropic stresses (such as a magnetic field or a solid state of parts of the star), viscous stresses, and heat transport are neglected in constructing an equilibrium model of a relativistic star, then the matter can be modeled as a perfect fluid, described by the stress-energy tensor
where ua is the fluid’s 4-velocity. In terms of the two Killing vectors ta and φa, the 4-velocity can be written as
where v is the 3-velocity of the fluid with respect to a local ZAMO, given by
and \(\Omega \equiv {u^\phi }/{u^t} = d\phi /dt\) is the angular velocity of the fluid in the coordinate frame, which is equivalent to the angular velocity of the fluid as seen by an observer at rest at infinity. Stationary configurations can be differentially rotating, while uniform rotation (Ω=const.) is a special case (see Section 2.5).
2.4 Equations of structure
Having specified an equation of state of the form ε=ε(P), the structure of the star is determined by solving four components of Einstein’s gravitational field equations
(where Rab is the Ricci tensor and T=T aa ) and the equation of hydrostationary equilibrium. Setting \(\zeta = \mu + \nu\), one common choice for the gravitational field equations is [55]
supplemented by a first order differential equation for ζ (see [55]). Above, ∇ is the 3-dimensional derivative operator in a flat 3-space with spherical polar coordinates r, θ, φ.
Thus, three of the four gravitational field equations are elliptic, while the fourth equation is a first order partial differential equation, relating only metric functions. The remaining nonzero components of the gravitational field equations yield two more elliptic equations and one first order partial differential equation, which are consistent with the above set of four equations.
The equation of hydrostationary equilibrium follows from the projection of the conservation of the stress-energy tensor normal to the 4-velocity \(({\delta ^c}_b + {u^c}{u_b}){\nabla _a}{T^{ab}} = 0\), and is written as
where a comma denotes partial differentiation and i=1, …,3. When the equation of state is barotropic then the hydrostationary equilibrium equation has a first integral of motion
where \(F(\Omega ) = {u_\phi }{u^t}\) is some specifiable function of Ω only, and Ωc is the angular velocity on the symmetry axis. In the Newtonian limit, the assumption of a barotropic equation of state implies that the differential rotation is necessarily constant on cylinders, and the existence of the integral of motion (20) is a direct consequence of the Poincaré-Wavre theorem (which implies that when the rotation is constant on cylinders, the effective gravity can be derived from a potential; see [302]).
2.5 Rotation law and equilibrium quantities
A special case of rotation law is uniform rotation (uniform angular velocity in the coordinate frame), which minimizes the total mass-energy of a configuration for a given baryon number and total angular momentum [49, 147]. In this case, the term involving F(Ω) in (20) vanishes.
More generally, a simple choice of a differential-rotation law is
where A is a constant [184, 185]. When A→∞, the above rotation law reduces to the uniform rotation case. In the Newtonian limit and when A→0, the rotation law becomes a so-called j-constant rotation law (specific angular momentum constant in space), which satisfies the Rayleigh criterion for local dynamical stability against axisymmetric disturbances (j should not decrease outwards, dj/dΩ<0). The same criterion is also satisfied in the relativistic case [185]. It should be noted that differentially rotating stars may also be subject to a shear instability that tends to suppress differential rotation [335].
The above rotation law is a simple choice that has proven to be computationally convenient. More physically plausible choices must be obtained through numerical simulations of the formation of relativistic stars.
Equilibrium quantities for rotating stars, such as gravitational mass, baryon mass, or angular momentum, for example, can be obtained as integrals over the source of the gravitational field. A list of the most important equilibrium quantities that can be computed for axisymmetric models, along with the equations that define them, is displayed in Table 1. There, ρ is the rest-mass density, \(u = \varepsilon - \rho {c^2}\) is the internal energy density, \({\hat n^a} = {\nabla _a}t/{\left| {{\nabla _b}t{\nabla ^b}t} \right|^{1/2}}\) is the unit normal vector field to the t=const: spacelike hypersurfaces, and \(dV = \sqrt {{|^3}g|{d^3}x}\) is the proper 3-volume element (with 3g being the determinant of the 3-metric). It should be noted that the moment of inertia cannot be computed directly as an integral quantity over the source of the gravitational field. In addition, there exists no unique generalization of the Newtonian definition of the moment of inertia in general relativity and I=J/Ω is a common choice.
2.6 Equations of state
2.6.1 Relativistic polytropes
An analytic equation of state that is commonly used to model relativistic stars is the adiabatic, relativistic polytropic EOS of Tooper [312]:
where K and Γ are the polytropic constant and polytropic exponent, respectively. Notice that the above definition is different from the form \(P = K{\varepsilon ^\Gamma }\) (also due to Tooper [311]) that has also been used as a generalization of the Newtonian polytropic EOS. Instead of Γ, one often uses the polytropic index N, defined through
For the above equation of state, the quantity \({c^{(\Gamma - 2)/(\Gamma - 1)}}\sqrt {{K^{1/(\Gamma - 1)}}/G}\) has units of length. In gravitational units (c=G=1), one can thus use KN/2 as a fundamental length scale to define dimensionless quantities. Equilibrium models are then characterized by the polytropic index N and their dimensionless central energy density. Equilibrium properties can be scaled to different dimensional values, using appropriate values for K. For N<1.0 (N>1.0) one obtains stiff (soft) models, while for N∼0.5–1.0, one obtains models with bulk properties that are comparable to those of observed neutron star radii and masses.
Notice that for the above polytropic EOS, the polytropic index Γ coincides with the adiabatic index of a relativistic isentropic fluid
This is not the case for the polytropic equation of state \(P = K{\varepsilon ^\Gamma }\), which satisfies (25) only in the Newtonian limit.
2.6.2 Hadronic equations of state
The true equation of state that describes the interior of compact stars is, still, largely unknown. This comes as a consequence of our inability to verify experimentally the different theories that describe the strong interactions between baryons and the many-body theories of dense matter, at densities larger than about twice the nuclear density (i.e. at densities larger than about 5×1014 g cm-3).
Many different so-called realistic EOSs have been proposed to date that all produce neutron star models that satisfy the currently available observational constraints. The two most accurate constraints are that the EOS must admit nonrotating neutron stars with gravitational mass of at least 1.44M⊙ and allow rotational periods at least as small as 1.56 ms (see [243, 187]). Recently, the first direct determination of the gravitational redshift of spectral lines produced in the neutron star photosphere has been obtained [74]. This determination (in the case of the low-mass X-ray binary EXO 0748-676) yielded a redshift of z=0:35 at the surface of the neutron star, corresponding to a mass to radius ratio of M/R=0.23 (in gravitational units), which is compatible with most normal nuclear matter EOSs and incompatible with some exotic matter EOSs.
The theoretically proposed EOSs are qualitatively and quantitatively very different from each other. Some are based on relativistic many-body theories while others use nonrelativistic theories with baryon-baryon interaction potentials. A classic collection of early proposed EOSs was compiled by Arnett and Bowers [20], while recent EOSs are used in Salgado et al. [261] and in [84]. A review of many modern EOSs can be found in a recent article by Haensel [138]. Detailed descriptions and tables of several modern EOSs, especially EOSs with phase transitions, can be found in Glendenning’s book [125].
High density equations of state with pion condensation have been proposed by Migdal [228] and Sawyer and Scalapino [264]. The possibility of kaon condensation is discussed by Brown and Bethe [51] (but see also Pandharipande et al. [241]). Properties of rotating Skyrmion stars have been computed in [237].
The realistic EOSs are supplied in the form of an energy density vs. pressure table and intermediate values are interpolated. This results in some loss of accuracy because the usual interpolation methods do not preserve thermodynamical consistency. Swesty [301] devised a cubic Hermite interpolation scheme that does preserve thermodynamical consistency and the scheme has been shown to indeed produce higher accuracy neutron star models in Nozawa et al. [236].
Usually, the interior of compact stars is modeled as a one-component ideal fluid. When neutron stars cool below the superfluid transition temperature, the part of the star that becomes superfluid can be described by a two-fluid model and new effects arise. Andersson and Comer [9] have recently used such a description in a detailed study of slowly rotating superfluid neutron stars in general relativity, while the first rapidly rotating models are presented in [248].
2.6.3 Strange quark equations of state
Strange quark stars are likely to exist, if the ground state of matter at large atomic number is in the form of a quark fluid, which would then be composed of about equal numbers of up, down, and strange quarks together with electrons, which give overall charge neutrality [38, 98]. The strangeness per unit baryon number is ≃-1. The first relativistic models of stars composed of quark matter were computed by Ipser, Kislinger, and Morley [157] and by Brecher and Caporaso [50], while the first extensive study of strange quark star properties is due to Witten [325].
The strange quark matter equation of state can be represented by the following linear relation between pressure and energy density:
where ε0 is the energy density at the surface of a bare strange star (neglecting a possible thin crust of normal matter). The MIT bag model of strange quark matter involves three parameters, the bag constant, \({\mathcal B} = {\varepsilon _0}/4\), the mass of the strange quark, ms, and the QCD coupling constant, αc. The constant a in (26) is equal to 1/3 if one neglects the mass of the strange quark, while it takes the value of a=0.289 for ms=250 MeV. When measured in units of \({{\mathcal B}_{60}} = {\mathcal B}/(60\;{\rm{MeV}}\;{\rm{f}}{{\rm{m}}^{ - 3}})\), the constant B is restricted to be in the range
assuming ms=0. The lower limit is set by the requirement of stability of neutrons with respect to a spontaneous fusion into strangelets, while the upper limit is determined by the energy per baryon of 56Fe at zero pressure (930.4 MeV). For other values of ms the above limits are modified somewhat.
A more recent attempt to describe deconfined strange quark matter is the Dey et al. EOS [87], which has asymptotic freedom built in. It describes deconfined quarks at high densities and confinement at zero pressure. The Dey et al. EOS can be approximated by a linear relation of the same form as the MIT bag model strange star EOS (26). In such a linear approximation, typical values of the constant a are 0.45–0.46 [128].
-
Going further A review of strange quark star properties can be found in [320]. Hybrid stars that have a mixed-phase region of quark and hadronic matter, have also been proposed (see e.g. [125]). A study of the relaxation effect in dissipative relativistic fluid theories is presented in [200].
2.7 Numerical schemes
All available methods for solving the system of equations describing the equilibrium of rotating relativistic stars are numerical, as no analytical self-consistent solution for both the interior and exterior spacetime has been found. The first numerical solutions were obtained by Wilson [323] and by Bonazzola and Schneider [48]. Here, we will review the following methods: Hartle’s slow rotation formalism, the Newton-Raphson linearization scheme due to Butterworth and Ipser [55], a scheme using Green’s functions by Komatsu et al. [184, 185], a minimal surface scheme due to Neugebauer and Herold [235], and spectral-method schemes by Bonazzola et al. [47, 46] and by Ansorg et al. [19]. Below we give a description of each method and its various implementations (codes).
2.7.1 Hartle
To order \({\mathcal O}({\Omega ^2})\), the structure of a star changes only by quadrupole terms and the equilibrium equations become a set of ordinary differential equations. Hartle’s [143, 148] method computes rotating stars in this slow rotation approximation, and a review of slowly rotating models has been compiled by Datta [82]. Weber et al. [317, 319] also implement Hartle’s formalism to explore the rotational properties of four new EOSs.
Weber and Glendenning [318] improve on Hartle’s formalism in order to obtain a more accurate estimate of the angular velocity at the mass-shedding limit, but their models still show large discrepancies compared to corresponding models computed without the slow rotation approximation [261]. Thus, Hartle’s formalism is appropriate for typical pulsar (and most millisecond pulsar) rotational periods, but it is not the method of choice for computing models of rapidly rotating relativistic stars near the mass-shedding limit.
2.7.2 Butterworth and Ipser (BI)
The BI scheme [55] solves the four field equations following a Newton-Raphson-like linearization and iteration procedure. One starts with a nonrotating model and increases the angular velocity in small steps, treating a new rotating model as a linear perturbation of the previously computed rotating model. Each linearized field equation is discretized and the resulting linear system is solved. The four field equations and the hydrostationary equilibrium equation are solved separately and iteratively until convergence is achieved.
Space is truncated at a finite distance from the star and the boundary conditions there are imposed by expanding the metric potentials in powers of 1/r. Angular derivatives are approximated by high-accuracy formulae and models with density discontinuities are treated specially at the surface. An equilibrium model is specified by fixing its rest mass and angular velocity.
The original BI code was used to construct uniform density models and polytropic models [55, 54]. Friedman et al. [113, 114] (FIP) extend the BI code to obtain a large number of rapidly rotating models based on a variety of realistic EOSs. Lattimer et al. [196] used a code that was also based on the BI scheme to construct rotating stars using “exotic” and schematic EOSs, including pion or kaon condensation and strange quark matter.
2.7.3 Komatsu, Eriguchi, and Hachisu (KEH)
In the KEH scheme [184, 185], the same set of field equations as in BI is used, but the three elliptic-type field equations are converted into integral equations using appropriate Green’s functions. The boundary conditions at large distance from the star are thus incorporated into the integral equations, but the region of integration is truncated at a finite distance from the star. The fourth field equation is an ordinary first order differential equation. The field equations and the equation of hydrostationary equilibrium are solved iteratively, fixing the maximum energy density and the ratio of the polar radius to the equatorial radius, until convergence is achieved. In [184, 185, 95] the original KEH code is used to construct uniformly and differentially rotating stars for both polytropic and realistic EOSs.
Cook, Shapiro, and Teukolsky (CST) improve on the KEH scheme by introducing a new radial variable that maps the semi-infinite region [0, ∞) to the closed region [0, 1]. In this way, the region of integration is not truncated and the model converges to a higher accuracy. Details of the code are presented in [69] and polytropic and realistic models are computed in [71] and [70].
Stergioulas and Friedman (SF) implement their own KEH code following the CST scheme. They improve on the accuracy of the code by a special treatment of the second order radial derivative that appears in the source term of the first order differential equation for one of the metric functions. This derivative was introducing a numerical error of 1–2% in the bulk properties of the most rapidly rotating stars computed in the original implementation of the KEH scheme. The SF code is presented in [295] and in [293]. It is available as a public domain code, named rns, and can be downloaded from [292].
2.7.4 Bonazzola et al. (BGSM)
In the BGSM scheme [47], the field equations are derived in the 3+1 formulation. All four chosen equations that describe the gravitational field are of elliptic type. This avoids the problem with the second order radial derivative in the source term of the ODE used in BI and KEH. The equations are solved using a spectral method, i.e. all functions are expanded in terms of trigonometric functions in both the angular and radial directions and a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is used to obtain coefficients. Outside the star a redefined radial variable is used, which maps infinity to a finite distance.
In [261, 262] the code is used to construct a large number of models based on recent EOSs. The accuracy of the computed models is estimated using two general relativistic virial identities, valid for general asymptotically flat spacetimes [132, 43] (see Section 2.7.7).
While the field equations used in the BI and KEH schemes assume a perfect fluid, isotropic stress-energy tensor, the BGSM formulation makes no assumption about the isotropy of Tab. Thus, the BGSM code can compute stars with a magnetic field, a solid crust, or a solid interior, and it can also be used to construct rotating boson stars.
2.7.5 Lorene/rotstar
Bonazzola et al. [46] have improved the BGSM spectral method by allowing for several domains of integration. One of the domain boundaries is chosen to coincide with the surface of the star and a regularization procedure is introduced for the divergent derivatives at the surface (that appear in the density field when stiff equations of state are used). This allows models to be computed that are nearly free of Gibbs phenomena at the surface. The same method is also suitable for constructing quasi-stationary models of binary neutron stars. The new method has been used in [133] for computing models of rapidly rotating strange stars and it has also been used in 3D computations of the onset of the viscosity-driven instability to bar-mode formation [129].
2.7.6 Ansorg et al. (AKM)
A new multi-domain spectral method has been introduced in [19, 18]. The method can use several domains inside the star, one for each possible phase transition. Surface-adapted coordinates are used and approximated by a two-dimensional Chebyshev expansion. Requiring transition conditions to be satisfied at the boundary of each domain, the field and fluid equations are solved as a free boundary value problem by a Newton-Raphson method, starting from an initial guess. The field equations are simplified by using a corotating reference frame. Applying this new method to the computation of rapidly rotating homogeneous relativistic stars, Ansorg et al. achieve near machine accuracy, except for configurations at the mass-shedding limit (see Section 2.7.8)! The code has been used in a systematic study of uniformly rotating homogeneous stars in general relativity [265].
2.7.7 The virial identities
Equilibrium configurations in Newtonian gravity satisfy the well-known virial relation
This can be used to check the accuracy of computed numerical solutions. In general relativity, a different identity, valid for a stationary and axisymmetric spacetime, was found in [40]. More recently, two relativistic virial identities, valid for general asymptotically flat spacetimes, have been derived by Bonazzola and Gourgoulhon [132, 43]. The 3-dimensional virial identity (GRV3) [132] is the extension of the Newtonian virial identity (28) to general relativity. The 2-dimensional (GRV2) [43] virial identity is the generalization of the identity found in [40] (for axisymmetric spacetimes) to general asymptotically flat spacetimes. In [43], the Newtonian limit of GRV2, in axisymmetry, is also derived. Previously, such a Newtonian identity had only been known for spherical configurations [59].
The two virial identities are an important tool for checking the accuracy of numerical models and have been repeatedly used by several authors [47, 261, 262, 236, 19].
2.7.8 Direct comparison of numerical codes
The accuracy of the above numerical codes can be estimated, if one constructs exactly the same models with different codes and compares them directly. The first such comparison of rapidly rotating models constructed with the FIP and SF codes is presented by Stergioulas and Friedman in [295]. Rapidly rotating models constructed with several EOSs agree to 0.1–1.2% in the masses and radii and to better than 2% in any other quantity that was compared (angular velocity and momentum, central values of metric functions, etc.). This is a very satisfactory agreement, considering that the BI code was using relatively few grid points, due to limitations of computing power at the time of its implementation.
In [295], it is also shown that a large discrepancy between certain rapidly rotating models (constructed with the FIP and KEH codes) that was reported by Eriguchi et al. [95], resulted from the fact that Eriguchi et al. and FIP used different versions of a tabulated EOS.
Nozawa et al. [236] have completed an extensive direct comparison of the BGSM, SF, and the original KEH codes, using a large number of models and equations of state. More than twenty different quantities for each model are compared and the relative differences range from 10-3 to 10-4 or better, for smooth equations of state. The agreement is also excellent for soft polytropes. These checks show that all three codes are correct and successfully compute the desired models to an accuracy that depends on the number of grid points used to represent the spacetime.
If one makes the extreme assumption of uniform density, the agreement is at the level of 10-2. In the BGSM code this is due to the fact that the spectral expansion in terms of trigonometric functions cannot accurately represent functions with discontinuous first order derivatives at the surface of the star. In the KEH and SF codes, the three-point finite-difference formulae cannot accurately represent derivatives across the discontinuous surface of the star.
The accuracy of the three codes is also estimated by the use of the two virial identities. Overall, the BGSM and SF codes show a better and more consistent agreement than the KEH code with BGSM or SF. This is largely due to the fact that the KEH code does not integrate over the whole spacetime but within a finite region around the star, which introduces some error in the computed models.
A new direct comparison of different codes is presented by Ansorg et al. [19]. Their multi-domain spectral code is compared to the BGSM, KEH, and SF codes for a particular uniform density model of a rapidly rotating relativistic star. An extension of the detailed comparison in [19], which includes results obtained by the Lorene/rotstar code in [129] and by the SF code with higher resolution than the resolution used in [236], is shown in Table 2. The comparison confirms that the virial identity GRV3 is a good indicator for the accuracy of each code. For the particular model in Table 2, the AKM code achieves nearly double-precision accuracy, while the Lorene/rotstar code has a typical relative accuracy of 2×10-4 to 7×10-6 in various quantities. The SF code at high resolution comes close to the accuracy of the Lorene/rotstar code for this model. Lower accuracies are obtained with the SF, BGSM, and KEH codes at the resolutions used in [236].
The AKM code converges to machine accuracy when a large number of about 24 expansion coefficients are used at a high computational cost. With significantly fewer expansion coefficients (and comparable computational cost to the SF code at high resolution) the achieved accuracy is comparable to the accuracy of the Lorene/rotstar and SF codes. Moreover, at the mass-shedding limit, the accuracy of the AKM code reduces to about 5 digits (which is still highly accurate, of course), even with 24 expansion coefficients, due to the nonanalytic behaviour of the solution at the surface. Nevertheless, the AKM method represents a great achievement, as it is the first method to converge to machine accuracy when computing rapidly rotating stars in general relativity.
-
Going further A review of spectral methods in general relativity can be found in [42]. A formulation for nonaxisymmetric, uniformly rotating equilibrium configurations in the second post-Newtonian approximation is presented in [22].
2.8 Analytic approximations to the exterior spacetime
The exterior metric of a rapidly rotating neutron star differs considerably from the Kerr metric. The two metrics agree only to lowest order in the rotational velocity [149]. At higher order, the multipole moments of the gravitational field created by a rapidly rotating compact star are different from the multipole moments of the Kerr field. There have been many attempts in the past to find analytic solutions to the Einstein equations in the stationary, axisymmetric case, that could describe a rapidly rotating neutron star. An interesting solution has been found recently by Manko et al. [220, 221]. For non-magnetized sources of zero net charge, the solution reduces to a 3-parameter solution, involving the mass, specific angular momentum, and a parameter that depends on the quadrupole moment of the source. Although this solution depends explicitly only on the quadrupole moment, it approximates the gravitational field of a rapidly rotating star with higher nonzero multipole moments. It would be interesting to determine whether this analytic quadrupole solution approximates the exterior field of a rapidly rotating star more accurately than the quadrupole, \({\mathcal O}({\Omega ^2})\), slow rotation approximation.
The above analytic solution and an earlier one that was not represented in terms of rational functions [219] have been used in studies of energy release during disk accretion onto a rapidly rotating neutron star [279, 280]. In [276], a different approximation to the exterior spacetime, in the form of a multipole expansion far from the star, has been used to derive approximate analytic expressions for the location of the innermost stable circular orbit (ISCO). Even though the analytic solutions in [276] converge slowly to an exact numerical solution at the surface of the star, the analytic expressions for the location and angular velocity at the ISCO are in good agreement with numerical results.
2.9 Properties of equilibrium models
2.9.1 Bulk properties of equilibrium models
Neutron star models constructed with various realistic EOSs have considerably different bulk properties, due to the large uncertainties in the equation of state at high densities. Very compressible (soft) EOSs produce models with small maximum mass, small radius, and large rotation rate. On the other hand, less compressible (stiff) EOSs produce models with a large maximum mass, large radius, and low rotation rate.
The gravitational mass, equatorial radius, and rotational period of the maximum mass model constructed with one of the softest EOSs (EOS B) (1.63M⊙, 9.3 km, 0.4 ms) are a factor of two smaller than the mass, radius, and period of the corresponding model constructed by one of the stiffest EOSs (EOS L) (3.27M⊙, 18.3 km, 0.8 ms). The two models differ by a factor of 5 in central energy density and by a factor of 8 in the moment of inertia!
Not all properties of the maximum mass models between proposed EOSs differ considerably, at least not within groups of similar EOSs. For example, most realistic hadronic EOSs predict a maximum mass model with a ratio of rotational to gravitational energy T/W of 0.11±0.02, a dimensionless angular momentum cJ/GM2 of 0.64±0.06, and an eccentricity of 0.66±0.04 [112]. Hence, within the set of realistic hadronic EOSs, some properties are directly related to the stiffness of the EOS while other properties are rather insensitive to stiffness. On the other hand, if one considers strange quark EOSs, then for the maximum mass model T/W can become a factor of about two larger than for hadronic EOSs.
Compared to nonrotating stars, the effect of rotation is to increase the equatorial radius of the star and also to increase the mass that can be sustained at a given central energy density. As a result, the mass of the maximum mass rotating model is roughly 15–20% higher than the mass of the maximum mass nonrotating model, for typical realistic hadronic EOSs. The corresponding increase in radius is 30–40%. The effect of rotation in increasing the mass and radius becomes more pronounced in the case of strange quark EOSs (see Section 2.9.8).
The deformed shape of a rapidly rotating star creates a distortion, away from spherical symmetry, in its gravitational field. Far from the star, the dominant multipole moment of the rotational distortion is measured by the quadrupole-moment tensor Qab. For uniformly rotating, axisymmetric, and equatorially symmetric configurations, one can define a scalar quadrupole moment Q, which can be extracted from the asymptotic expansion of the metric function ν at large r, as in Equation (10).
Laarakkers and Poisson [188] numerically compute the scalar quadrupole moment Q for several equations of state, using the rotating neutron star code rns [292]. They find that for fixed gravitational mass M, the quadrupole moment is given as a simple quadratic fit,
where J is the angular momentum of the star and a is a dimensionless quantity that depends on the equation of state. The above quadratic fit reproduces Q with remarkable accuracy. The quantity a varies between a∼2 for very soft EOSs and a∼8 for very stiff EOSs, for M=1.4M⊙ neutron stars. This is considerably different from a Kerr black hole, for which a=1 [305].
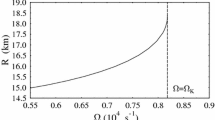
For a given zero-temperature EOS, the uniformly rotating equilibrium models form a 2-dimensional surface in the 3-dimensional space of central energy density, gravitational mass, and angular momentum [295], as shown in Figure 1 for EOS L. The surface is limited by the nonrotating models (J=0) and by the models rotating at the mass-shedding (Kepler) limit, i.e. at the maximum allowed angular velocity (above which the star sheds mass at the equator). Cook et al. [69, 71, 70] have shown that the model with maximum angular velocity does not coincide with the maximum mass model, but is generally very close to it in central density and mass. Stergioulas and Friedman [295] show that the maximum angular velocity and maximum baryon mass equilibrium models are also distinct. The distinction becomes significant in the case where the EOS has a large phase transition near the central density of the maximum mass model; otherwise the models of maximum mass, baryon mass, angular velocity, and angular momentum can be considered to coincide for most purposes.
-
Going further Although rotating relativistic stars are nearly perfectly axisymmetric, a small degree of asymmetry (e.g. frozen into the solid crust during its formation) can become a source of gravitational waves. A recent review of this can be found in [165].
2D surface of equilibrium models for EOS L. The surface is bounded by the nonrotating (J=0) and mass-shedding (Ω=ΩK) limits and formed by constant J and constant M0 sequences (solid lines). The projection of these sequences in the J-M plane are shown as long-dashed lines. Also shown are the axisymmetric instability sequence (short-dashed line). The projection of the 2D surface in the J-M plane shows an overlapping (see dotted lines). (Figure 7 of Stergioulas and Friedman [295].)
2.9.2 Mass-shedding limit and the empirical formula
Mass-shedding occurs when the angular velocity of the star reaches the angular velocity of a particle in a circular Keplerian orbit at the equator, i.e. when
where
In differentially rotating stars, even a small amount of differential rotation can significantly increase the angular velocity required for mass-shedding. Thus, a newly-born, hot, differentially rotating neutron star or a massive, compact object created in a binary neutron star merger could be sustained (temporarily) in equilibrium by differential rotation, even if a uniformly rotating configuration with the same rest mass does not exist.
In the Newtonian limit the maximum angular velocity of uniformly rotating polytropic stars is approximately \({\Omega _{\max }} \simeq {(2/3)^{3/2}}{(GM/{R^3})^{1/2}}\) (this is derived using the Roche model, see [268]). For relativistic stars, the empirical formula [142, 114, 109]
gives the maximum angular velocity in terms of the mass and radius of the maximum mass nonrotating model with an accuracy of 5–7%, without actually having to construct rotating models. A revised empirical formula, using a large set of EOSs, has been computed in [141].
The empirical formula results from universal proportionality relations that exist between the mass and radius of the maximum mass rotating model and those of the maximum mass nonrotating model for the same EOS. Lasota et al. [193] find that, for most EOSs, the coefficient in the empirical formula is an almost linear function of the parameter
The Lasota et al. empirical formula
with \(C({\chi _{\rm{s}}}) = 0.468 + 0.378{\chi _{\rm{s}}}\), reproduces the exact values with a relative error of only 1.5%.
Weber and Glendenning [317, 318] derive analytically a similar empirical formula in the slow rotation approximation. However, the formula they obtain involves the mass and radius of the maximum mass rotating configuration, which is different from what is involved in (32).
2.9.3 Upper limits on mass and rotation: Theory vs. observation
The maximum mass and minimum period of rotating relativistic stars computed with realistic hadronic EOSs from the Arnett and Bowers collection [20] are about 3.3M⊙ (EOS L) and 0.4 ms (EOS B), while 1.4M⊙ neutron stars, rotating at the Kepler limit, have rotational periods between 0.53 ms (EOS B) and 1.7 ms (EOS M) [70]. The maximum, accurately measured, neutron star mass is currently still 1.44M⊙ (see e.g. [314]), but there are also indications for 2.0M⊙ neutron stars [167]. Core collapse simulations have yielded a bi-modal mass distribution of the remnant, with peaks at about 1.3M⊙ and 1.7M⊙ [310] (the second peak depends on the assumption for the high-density EOS — if a soft EOS is assumed, then black hole formation of this mass is implied). Compact stars of much higher mass, created in a neutron star binary merger, could be temporarily supported against collapse by strong differential rotation [30].
When magnetic field effects are ignored, conservation of angular momentum can yield very rapidly rotating neutron stars at birth. Recent simulations of the rotational core collapse of evolved rotating progenitors [151, 119] have demonstrated that rotational core collapse can easily result in the creation of neutron stars with rotational periods of the order of 1 ms (and similar initial rotation periods have been estimated for neutron stars created in the accretion-induced collapse of a white dwarf [212]). The existence of a magnetic field may complicate this picture. Spruit and Phinney [288] have presented a model in which a strong internal magnetic field couples the angular velocity between core and surface during most evolutionary phases. The core rotation decouples from the rotation of the surface only after central carbon depletion takes place. Neutron stars born in this way would have very small initial rotation rates, even smaller than the ones that have been observed in pulsars associated with supernova remnants. In this model, an additional mechanism is required to spin up the neutron star to observed periods. On the other hand, Livio and Pringle [213] argue for a much weaker rotational coupling between core and surface by a magnetic field, allowing for the production of more rapidly rotating neutron stars than in [288]. A new investigation by Heger et al., yielding intermediate initial rotation rates, is presented in [152]. Clearly, more detailed computations are needed to resolve this important question.
The minimum observed pulsar period is still 1.56 ms [187], which is close to the experimental sensitivity of most pulsar searches. New pulsar surveys, in principle sensitive down to a few tenths of a millisecond, have not been able to detect a sub-millisecond pulsar [52, 81, 75, 94]. This is not too surprising, as there are several explanations for the absence of sub-millisecond pulsars. In one model, the minimum rotational period of pulsars could be set by the occurrence of the r-mode instability in accreting neutron stars in Low Mass X-ray Binaries (LMXBs) [12]. Other models are based on the standard magnetospheric model for accretion-induced spin-up [322] or on the idea that gravitational radiation (produced by accretion-induced quadrupole deformations of the deep crust) balances the spin-up torque [35, 313]. It has also been suggested [53] that the absence of sub-millisecond pulsars in all surveys conducted so far could be a selection effect: Sub-millisecond pulsars could be found more likely only in close systems (of orbital period Porb∼1 hr), however the current pulsar surveys are still lacking the required sensitivity to easily detect such systems. The absence of sub-millisecond pulsars in wide systems is suggested to be due to the turning-on of the accreting neutron stars as pulsars, in which case the pulsar wind is shown to halt further spin-up.
-
Going further A review by J.L. Friedman concerning the upper limit on the rotation of relativistic stars can be found in [110].
2.9.4 The upper limit on mass and rotation set by causality
If one is interested in obtaining upper limits on the mass and rotation rate, independently of the proposed EOSs, one has to rely on fundamental physical principles. Instead of using realistic EOSs, one constructs a set of schematic EOSs that satisfy only a minimal set of physical constraints, which represent what we know about the equation of state of matter with high confidence. One then searches among all these EOSs to obtain the one that gives the maximum mass or minimum period. The minimal set of constraints that have been used in such searches are that
-
1.
the high density EOS matches to the known low density EOS at some matching energy density εm, and
-
2.
the matter at high densities satisfies the causality constraint (the speed of sound is less than the speed of light).
In relativistic perfect fluids, the speed of sound is the characteristic velocity of the evolution equations for the fluid, and the causality constraint translates into the requirement
(see [120]). It is assumed that the fluid will still behave as a perfect fluid when it is perturbed from equilibrium.
For nonrotating stars, Rhoades and Ruffini showed that the EOS that satisfies the above two constraints and yields the maximum mass consists of a high density region as stiff as possible (i.e. at the causal limit, dP/dε=1), that matches directly to the known low density EOS. For a chosen matching density εm, they computed a maximum mass of 3.2M⊙. However, this is not the theoretically maximum mass of nonrotating neutron stars, as is often quoted in the literature. Hartle and Sabbadini [146] point out that Mmax is sensitive to the matching energy density and Hartle [144] computes Mmax as a function of εm:
In the case of rotating stars, Friedman and Ipser [111] assume that the absolute maximum mass is obtained by the same EOS as in the nonrotating case and compute Mmax as a function of matching density, assuming the BPS EOS holds at low densities. A more recent computation [186] uses the FPS EOS at low densities, arriving at a similar result as in [111]:
where 2×1014 g cm-3 is roughly nuclear saturation density for the FPS EOS.
A first estimate of the absolute minimum period of uniformly rotating, gravitationally bound stars was computed by Glendenning [124] by constructing nonrotating models and using the empirical formula (32) to estimate the minimum period. Koranda, Stergioulas, and Friedman [186] improve on Glendenning’s results by constructing accurate, rapidly rotating models; they show that Glendenning’s results are accurate to within the accuracy of the empirical formula.
Furthermore, they show that the EOS satisfying the minimal set of constraints and yielding the minimum period star consists of a high density region at the causal limit (CL EOS), \(P = (\varepsilon - {\varepsilon _{\rm{c}}})\), (where εc is the lowest energy density of this region), which is matched to the known low density EOS through an intermediate constant pressure region (that would correspond to a first order phase transition). Thus, the EOS yielding absolute minimum period models is as stiff as possible at the central density of the star (to sustain a large enough mass) and as soft as possible in the crust, in order to have the smallest possible radius (and rotational period).
The absolute minimum period of uniformly rotating stars is an (almost linear) function of the maximum observed mass of nonrotating neutron stars,
and is rather insensitive to the matching density εm (the above result was computed for a matching number density of 0.1 fm-3). In [186], it is also shown that an absolute limit on the minimum period exists even without requiring that the EOS matches to a known low density EOS, i.e. if the CL EOS, \(P = (\varepsilon - {\varepsilon _{\rm{c}}})\), terminates at a surface energy density of εc. This is not so for the causal limit on the maximum mass. Thus, without matching to a low-density EOS, the causality limit on Pmin is lowered by only 3%, which shows that the currently known part of the nuclear EOS plays a negligible role in determining the absolute upper limit on the rotation of uniformly rotating, gravitationally bound stars.
The above results have been confirmed in [139], where it is shown that the CL EOS has χs=0.7081, independent of εc, and the empirical formula (34) reproduces the numerical result (38) to within 2%.
2.9.5 Supramassive stars and spin-up prior to collapse
Since rotation increases the mass that a neutron star of given central density can support, there exist sequences of neutron stars with constant baryon mass that have no nonrotating member. Such sequences are called supramassive, as opposed to normal sequences that do have a nonrotating member. A nonrotating star can become supramassive by accreting matter and spinning-up to large rotation rates; in another scenario, neutron stars could be born supramassive after a core collapse. A supramassive star evolves along a sequence of constant baryon mass, slowly losing angular momentum. Eventually, the star reaches a point where it becomes unstable to axisymmetric perturbations and collapses to a black hole.
In a neutron star binary merger, prompt collapse to a black hole can be avoided if the equation of state is sufficiently stiff and/or the equilibrium is supported by strong differential rotation. The maximum mass of differentially rotating supramassive neutron stars can be significantly larger than in the case of uniform rotation. A detailed study of this mass-increase has recently appeared in [215].
Cook et al. [69, 71, 70] have discovered that a supramassive relativistic star approaching the axisymmetric instability will actually spin up before collapse, even though it loses angular momentum. This potentially observable effect is independent of the equation of state and it is more pronounced for rapidly rotating massive stars. Similarly, stars can spin up by loss of angular momentum near the mass-shedding limit, if the equation of state is extremely stiff or extremely soft.
If the equation of state features a phase transition, e.g. to quark matter, then the spin-up region is very large, and most millisecond pulsars (if supramassive) would need to be spinning up [289]; the absence of spin-up in known millisecond pulsars indicates that either large phase transitions do not occur, or that the equation of state is sufficiently stiff so that millisecond pulsars are not supramassive.
2.9.6 Rotating magnetized neutron stars
The presence of a magnetic field has been ignored in the models of rapidly rotating relativistic stars that were considered in the previous sections. The reason is that the observed surface dipole magnetic field strength of pulsars ranges between 108 G and 2×1013 G. These values of the magnetic field strength imply a magnetic field energy density that is too small, compared to the energy density of the fluid, to significantly affect the structure of a neutron star. However, one cannot exclude the existence of neutron stars with higher magnetic field strengths or the possibility that neutron stars are born with much stronger magnetic fields, which then decay to the observed values (of course, there are also many arguments against magnetic field decay in neutron stars [243]). In addition, even though moderate magnetic field strengths do not alter the bulk properties of neutron stars, they may have an effect on the damping or growth rate of various perturbations of an equilibrium star, affecting its stability. For these reasons, a fully relativistic description of magnetized neutron stars is desirable and, in fact, Bocquet et al. [37] achieved the first numerical computation of such configurations. Following we give a brief summary of their work.
A magnetized relativistic star in equilibrium can be described by the coupled Einstein-Maxwell field equations for stationary, axisymmetric rotating objects with internal electric currents. The stress-energy tensor includes the electromagnetic energy density and is non-isotropic (in contrast to the isotropic perfect fluid stress-energy tensor). The equilibrium of the matter is given not only by the balance between the gravitational force, centrifugal force, and the pressure gradient; the Lorentz force due to the electric currents also enters the balance. For simplicity, Bocquet et al. consider only poloidal magnetic fields that preserve the circularity of the spacetime. Also, they only consider stationary configurations, which excludes magnetic dipole moments non-aligned with the rotation axis, since in that case the star emits electromagnetic and gravitational waves. The assumption of stationarity implies that the fluid is necessarily rigidly rotating (if the matter has infinite conductivity) [47]. Under these assumptions, the electromagnetic field tensor Fab is derived from a potential four-vector Aa with only two non-vanishing components, At and \({A_\phi }\), which are solutions of a scalar Poisson and a vector Poisson equation respectively. Thus, the two equations describing the electromagnetic field are of similar type as the four field equations that describe the gravitational field.
For magnetic field strengths larger than about 1014 G, one observes significant effects, such as a flattening of the equilibrium configuration. There exists a maximum value of the magnetic field strength of the order of 1018 G, for which the magnetic field pressure at the center of the star equals the fluid pressure. Above this value no stationary configuration can exist.
A strong magnetic field allows a maximum mass configuration with larger Mmax than for the same EOS with no magnetic field and this is analogous to the increase of Mmax induced by rotation. For nonrotating stars, the increase in Mmax due to a strong magnetic field is 13–29%, depending on the EOS. Correspondingly, the maximum allowed angular velocity, for a given EOS, also increases in the presence of a strong magnetic field.
Another application of general relativistic E/M theory in neutron stars is the study of the evolution of the magnetic field during pulsar spin-down. A detailed analysis of the evolution equations of the E/M field in a slowly rotating magnetized neutron star has revealed that effects due to the spacetime curvature and due to the rotational frame-dragging are present in the induction equations, when one assumes finite electrical conductivity (see [252] and references therein). Numerical solutions of the evolution equations of the E/M have shown, however, that for realistic values of the electrical conductivity, the above relativistic effects are small, even in the case of rapid rotation [336].
-
Going further An \(\mathcal{O}(\Omega )\) slow rotation approach for the construction of rotating magnetized relativistic stars is presented in [137].
2.9.7 Rapidly rotating proto-neutron stars
Following the gravitational collapse of a massive stellar core, a proto-neutron star (PNS) is born. Initially it has a large radius of about 100 km and a temperature of 50–100 MeV. The PNS may be born with a large rotational kinetic energy and initially it will be differentially rotating. Due to the violent nature of the gravitational collapse, the PNS pulsates heavily, emitting significant amounts of gravitational radiation. After a few hundred pulsational periods, bulk viscosity will damp the pulsations significantly. Rapid cooling due to deleptonization transforms the PNS, shortly after its formation, into a hot neutron star of T∼10 MeV. In addition, viscosity or other mechanisms (see Section 2.1) enforce uniform rotation and the neutron star becomes quasi-stationary. Since the details of the PNS evolution determine the properties of the resulting cold NSs, proto-neutron stars need to be modeled realistically in order to understand the structure of cold neutron stars.
Hashimoto et al. [150] and Goussard et al. [134] construct fully relativistic models of rapidly rotating, hot proto-neutron stars. The authors use finite-temperature EOSs [239, 195] to model the interior of PNSs. Important (but largely unknown) parameters that determine the local state of matter are the lepton fraction Yl and the temperature profile. Hashimoto et al. consider only the limiting case of zero lepton fraction, Yl=0, and classical isothermality, while Goussard et al. consider several nonzero values for Yl and two different limiting temperature profiles — a constant entropy profile and a relativistic isothermal profile. In both [150] and [239], differential rotation is neglected to a first approximation.
The construction of numerical models with the above assumptions shows that, due to the high temperature and the presence of trapped neutrinos, PNSs have a significantly larger radius than cold NSs. These two effects give the PNS an extended envelope which, however, contains only roughly 0.1% of the total mass of the star. This outer layer cools more rapidly than the interior and becomes transparent to neutrinos, while the core of the star remains hot and neutrino opaque for a longer time. The two regions are separated by the “neutrino sphere”.
Compared to the T=0 case, an isothermal EOS with temperature of 25 MeV has a maximum mass model of only slightly larger mass. In contrast, an isentropic EOS with a nonzero trapped lepton number features a maximum mass model that has a considerably lower mass than the corresponding model in the T=0 case and, therefore, a stable PNS transforms to a stable neutron star. If, however, one considers the hypothetical case of a large amplitude phase transition that softens the cold EOS (such as a kaon condensate), then Mmax of cold neutron stars is lower than the Mmax of PNSs, and a stable PNS with maximum mass will collapse to a black hole after the initial cooling period. This scenario of delayed collapse of nascent neutron stars has been proposed by Brown and Bethe [51] and investigated by Baumgarte et al. [31].
An analysis of radial stability of PNSs [127] shows that, for hot PNSs, the maximum angular velocity model almost coincides with the maximum mass model, as is also the case for cold EOSs.
Because of their increased radius, PNSs have a different mass-shedding limit than cold NSs. For an isothermal profile, the mass-shedding limit proves to be sensitive to the exact location of the neutrino sphere. For the EOSs considered in [150] and [134], PNSs have a maximum angular velocity that is considerably less than the maximum angular velocity allowed by the cold EOSs. Stars that have nonrotating counterparts (i.e. that belong to a normal sequence) contract and speed up while they cool down. The final star with maximum rotation is thus closer to the mass-shedding limit of cold stars than was the hot PNS with maximum rotation. Surprisingly, stars belonging to a supramassive sequence exhibit the opposite behavior. If one assumes that a PNS evolves without losing angular momentum or accreting mass, then a cold neutron star produced by the cooling of a hot PNS has a smaller angular velocity than its progenitor. This purely relativistic effect was pointed out in [150] and confirmed in [134].
It should be noted here that a small amount of differential rotation significantly affects the mass-shedding limit, allowing more massive stars to exist than uniform rotation allows. Taking differential rotation into account, Goussard et al. [135] suggest that proto-neutron stars created in a gravitational collapse cannot spin faster than 1.7 ms. A similar result has been obtained by Strobel et al. [298]. The structure of a differentially rotating proto-neutron star at the mass-shedding limit is shown in Figure 2. The outer layers of the star form an extended disk-like structure.
Iso-energy density lines of a differentially rotating proto-neutron star at the mass-shedding limit, of rest mass M0=1.5M⊙. (Figure 5a of Goussard, Haensel and Zdunik [135]; used with permission.)
The above stringent limits on the initial period of neutron stars are obtained assuming that the PNS evolves in a quasi-stationary manner along a sequence of equilibrium models. It is not clear whether these limits will remain valid if one studies the early evolution of PNS without the above assumption. It is conceivable that the thin hot envelope surrounding the PNS does not affect the dynamics of the bulk of the star. If the bulk of the star rotates faster than the (stationary) mass-shedding limit of a PNS model, then the hot envelope will simply be shed away from the star in the equatorial region (if it cannot remain bounded to the star even when differentially rotating). Such a fully dynamical study is needed to obtain an accurate upper limit on the rotation of neutron stars.
-
Going further The thermal history and evolutionary tracks of rotating PNSs (in the second order slow rotation approximation) have been studied recently in [300].
2.9.8 Rotating strange quark stars
Most rotational properties of strange quark stars differ considerably from the properties of rotating stars constructed with hadronic EOSs. First models of rapidly rotating strange quark stars were computed by Friedman ([107], quoted in [123, 122]) and by Lattimer et al. [196]. Colpi and Miller [66] use the \({\mathcal O}(\Omega )\) approximation and find that the spin of strange stars (newly-born, or spun-up by accretion) may be limited by the CFS instability to the l=m=2 f-mode, since rapidly rotating strange stars tend to have T/W>0.14. Rapidly rotating strange stars at the mass-shedding limit have been computed first by Gourgoulhon et al. [133], and the structure of a representative model is displayed in Figure 3.
Meridional plane cross section of a rapidly rotating strange star at the mass-shedding limit, obtained with a multi-domain spectral code. The various lines are isocontours of the log-enthalpy H, as defined in [ 133 ]. Solid lines indicate a positive value of H and dashed lines a negative value (vacuum). The thick solid line denotes the stellar surface. The thick dot-dashed line denotes the boundary between the two computational domains. (Figure 4 of Gourgoulhon, Haensel, Livine, Paluch, Bonazzola, and Marck [ 133 ]; used with permission.)
Nonrotating strange stars obey scaling relations with the constant \({\mathcal B}\) in the MIT bag model of the strange quark matter EOS (Section 2.6.3); Gourgoulhon et al. [133] also obtain scaling relations for the model with maximum rotation rate. The maximum angular velocity scales as
while the allowed range of \({\mathcal B}\) implies an allowed range of 0.513 ms < Pmin < 0.640 ms. The empirical formula (32) also holds for rotating strange stars with an accuracy of better than 2%. A derivation of the empirical formula in the case of strange stars, starting from first principles, has been presented by Cheng and Harko [62], who found that some properties of rapidly rotating strange stars can be reproduced by approximating the exterior spacetime by the Kerr metric.
Since both the maximum mass nonrotating and maximum mass rotating models obey similar scalings with B, the ratios
are independent of \({\mathcal B}\) (where Rmax is the radius of the maximum mass model). The maximum mass increases by 44% and the radius of the maximum mass model by 54%, while the corresponding increase for hadronic stars is, at best, ∼20% and ∼40%, correspondingly. The rotational properties of strange star models that are based on the Dey et al. EOS [87] are similar to those of the MIT bag model EOS [38, 325, 98], but some quantitative differences exist [128].
Accreting strange stars in LMXBs will follow different evolutionary paths than do accreting hadronic stars in a mass vs. central energy density diagram [341]. When (and if) strange stars reach the mass-shedding limit, the ISCO still exists [297] (while it disappears for most hadronic EOSs). Stergioulas, Kluźniak, and Bulik [297] show that the radius and location of the ISCO for the sequence of mass-shedding models also scales as \({{\mathcal B}^{1/2}}\), while the angular velocity of particles in circular orbit at the ISCO scales as \({{\mathcal B}^{1/2}}\). Additional scalings with the constant a in the strange quark EOS (that were proposed in [196]) are found to hold within an accuracy of better than ∼9% for the mass-shedding sequence
In addition, it is found that models at mass-shedding can have T/W as large as 0.28 for M=1.34 M⊙.
As strange quark stars are very compact, the angular velocity at the ISCO can become very large. If the 1066 Hz upper QPO frequency in 4U 1820–30 (see [167] and references therein) is the frequency at the ISCO, then it rules out most models of slowly rotating strange stars in LMXBs. However, in [297] it is shown that rapidly rotating bare strange stars are still compatible with this observation, as they can have ISCO frequencies < 1 kHz even for 1.4 M⊙ models. On the other hand, if strange stars have a thin solid crust, the ISCO frequency at the mass-shedding limit increases by about 10% (compared to a bare strange star of the same mass), and the above observational requirement is only satisfied for slowly rotating models near the maximum nonrotating mass, assuming some specific values of the parameters in the strange star EOS [342, 340]. Moderately rotating strange stars, with spin frequencies around 300 Hz can also be accommodated for some values of the coupling constant αc [338] (see also [131] for a detailed study of the ISCO frequency for rotating strange stars). The 1066 Hz requirement for the ISCO frequency depends, of course, on the adopted model of kHz QPOs in LMXBs, and other models exist (see next section).
If strange stars can have a solid crust, then the density at the bottom of the crust is the neutron drip density \({\varepsilon _{{\rm{nd}}}} \simeq 4.1 \times {10^{11}}\;{\rm{g}}\;{\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^{ - 3}}\), as neutrons are absorbed by strange quark matter. A strong electric field separates the nuclei of the crust from the quark plasma. In general, the mass of the crust that a strange star can support is very small, of the order of 10-5M⊙. Rapid rotation increases by a few times the mass of the crust and the thickness at the equator becomes much larger than the thickness at the poles [340]. Zdunik, Haensel, and Gourgoulhon [340] also find that the mass Mcrust and thickness tcrust of the crust can be expanded in powers of the spin frequency \({\nu _3} = \nu /({10^3}\;{\rm{Hz)}}\) as
where a subscript “0” denotes nonrotating values. For ν≤500 Hz, the above expansion agrees well with the quadratic expansion derived previously by Glendenning and Weber [126]. In a spinning down magnetized strange quark star with crust, parts of the crust will gradually dissolve into strange quark matter, in a strongly exothermic process. In [340], it is estimated that the heating due to deconfinement may exceed the neutrino luminosity from the core of a strange star older than ∼ 1000 yr and may therefore influence the cooling of this compact object (see also [334]).
2.10 Rotating relativistic stars in LMXBs
2.10.1 Particle orbits and kHz quasi-periodic oscillations
In the last few years, X-ray observations of accreting sources in LMXBs have revealed a rich phenomenology that is waiting to be interpreted correctly and could lead to significant advances in our understanding of compact objects (see [192, 168, 249]). The most important feature of these sources is the observation of (in most cases) twin kHz quasi-periodic oscillations (QPOs). The high frequency of these variabilities and their quasi-periodic nature are evidence that they are produced in high-velocity flows near the surface of the compact star. To date, there exist a large number of different theoretical models that attempt to explain the origin of these oscillations. No consensus has been reached, yet, but once a credible explanation is found, it will lead to important constraints on the properties of the compact object that is the source of the gravitational field in which the kHz oscillations take place. The compact stars in LMXBs are spun up by accretion, so that many of them may be rotating rapidly; therefore, the correct inclusion of rotational effects in the theoretical models for kHz QPOs is important. Under simplifying assumptions for the angular momentum and mass evolution during accretion, one can use accurate rapidly rotating relativistic models to follow the possible evolutionary tracks of compact stars in LMXBs [72, 341].
In most theoretical models, one or both kHz QPO frequencies are associated with the orbital motion of inhomogeneities or blobs in a thin accretion disk. In the actual calculations, the frequencies are computed in the approximation of an orbiting test particle, neglecting pressure terms. For most equations of state, stars that are massive enough possess an ISCO, and the orbital frequency at the ISCO has been proposed to be one of the two observed frequencies. To first order in the rotation rate, the orbital frequency at the prograde ISCO is given by (see Kluźniak, Michelson, and Wagoner [171])
where j=J/M2. At larger rotation rates, higher order contributions of j as well as contributions from the quadrupole moment Q become important and an approximate expression has been derived by Shibata and Sasaki [276], which, when written as above and truncated to the lowest order contribution of Q and to \({\mathcal O}({j^2})\), becomes
where \({Q_2} = - Q/{M^3}\).
Notice that, while rotation increases the orbital frequency at the ISCO, the quadrupole moment has the opposite effect, which can become important for rapidly rotating models. Numerical evaluations of fISCO for rapidly rotating stars have been used in [229] to arrive at constraints on the properties of the accreting compact object.
In other models, orbits of particles that are eccentric and slightly tilted with respect to the equatorial plane are involved. For eccentric orbits, the periastron advances with a frequency νpa that is the difference between the Keplerian frequency of azimuthal motion νK and the radial epicyclic frequency νr. On the other hand, particles in slightly tilted orbits fail to return to the initial displacement ψ from the equatorial plane, after a full revolution around the star. This introduces a nodal precession frequency νpa, which is the difference between νK and the frequency of the motion out of the orbital plane (meridional frequency) νψ. Explicit expressions for the above frequencies, in the gravitational field of a rapidly rotating neutron star, have been derived recently by Marković [222], while in [223] highly eccentric orbits are considered. Morsink and Stella [231] compute the nodal precession frequency for a wide range of neutron star masses and equations of state and (in a post-Newtonian analysis) separate the precession caused by the Lense-Thirring (frame-dragging) effect from the precession caused by the quadrupole moment of the star. The nodal and periastron precession of inclined orbits have also been studied using an approximate analytic solution for the exterior gravitational field of rapidly rotating stars [278]. These precession frequencies are relativistic effects and have been used in several models to explain the kHz QPO frequencies [291, 250, 2, 169, 5].
It is worth mentioning that it has recently been found that an ISCO also exists in Newtonian gravity, for models of rapidly rotating low-mass strange stars. The instability in the circular orbits is produced by the large oblateness of the star [170, 339, 5].
2.10.2 Angular momentum conservation during burst oscillations
Some sources in LMXBs show signatures of type I X-ray bursts, which are thermonuclear flashes on the surface of the compact star [198]. Such bursts show nearly-coherent oscillations in the range 270–620 Hz (see [168, 299] for recent reviews). One interpretation of the burst oscillations is that they are the result of rotational modulation of surface asymmetries during the burst. In such a case, the oscillation frequency should be nearly equal to the spin frequency of the star. This model currently has difficulties in explaining some observed properties, such as the oscillations seen in the tail of the burst, the frequency increase during the burst, and the need for two anti-podal hot spots in some sources that ignite at the same time. Alternative models also exist (see e.g. [249]).
In the spin-frequency interpretation, the increase in the oscillation frequency by a few Hz during the burst is explained as follows: The burning shell is supposed to first decouple from the neutron star and then gradually settle down onto the surface. By angular momentum conservation, the shell spins up, giving rise to the observed frequency increase. Cumming et al. [76] compute the expected spin-up in full general relativity and taking into account rapid rotation. Assuming that the angular momentum per unit mass is conserved, the change in angular velocity with radius is given by
where R is the equatorial radius of the star and all quantities are evaluated at the equator. The slow rotation limit of the above result was derived previously by Abramowicz et al. [3]. The fractional change in angular velocity during spin-up can then be estimated as
where Δr is the coordinate expansion of the burning shell, a quantity that depends on the shell’s composition. Cumming et al. find that the spin down expected if the atmosphere rotates rigidly is a factor of two to three times smaller than observed values. More detailed modeling is needed to fully explain the origin and properties of burst oscillations.
-
Going further A very interesting topic is the modeling of the expected X-ray spectrum of an accretion disk in the gravitational field of a rapidly rotating neutron star as it could lead to observational constraints on the source of the gravitational field. See e.g. [303, 279, 280, 34, 33], where work initiated by Kluzniak and Wilson [172] in the slow rotation limit is extended to rapidly rotating relativistic stars.
3 Oscillations and Stability
The study of oscillations of relativistic stars is motivated by the prospect of detecting such oscillations in electromagnetic or gravitational wave signals. In the same way that helioseismology is providing us with information about the interior of the Sun, the observational identification of oscillation frequencies of relativistic stars could constrain the high-density equation of state [13]. The oscillations could be excited after a core collapse or during the final stages of a neutron star binary merger. Rapidly rotating relativistic stars can become unstable to the emission of gravitational waves.
When the oscillations of an equilibrium star are of small magnitude compared to its radius, it will suffice to approximate them as linear perturbations. Such perturbations can be described in two equivalent ways. In the Lagrangian approach, one studies the changes in a given fluid element as it oscillates about its equilibrium position. In the Eulerian approach, one studies the change in fluid variables at a fixed point in space. Both approaches have their strengths and weaknesses.
In the Newtonian limit, the Lagrangian approach has been used to develop variational principles [216, 118], but the Eulerian approach proved to be more suitable for numerical computations of mode frequencies and eigen-functions [162, 218, 158, 160, 159]. Clement [64] used the Lagrangian approach to obtain axisymmetric normal modes of rotating stars, while nonaxisymmetric solutions were obtained in the Lagrangian approach by Imamura et al. [156] and in the Eulerian approach by Managan [218] and Ipser and Lindblom [158]. While a lot has been learned from Newtonian studies, in the following we will focus on the relativistic treatment of oscillations of rotating stars.
3.1 Quasi-normal modes of oscillation
A general linear perturbation of the energy density in a static and spherically symmetric relativistic star can be written as a sum of quasi-normal modes that are characterized by the indices (l, m) of the spherical harmonic functions Y m l and have angular and time dependence of the form
where δ indicates the Eulerian perturbation of a quantity, ωi is the angular frequency of the mode as measured by a distant inertial observer, f(r) represents the radial dependence of the perturbation, and P m l (cos θ) are the associated Legendre polynomials. Normal modes of nonrotating stars are degenerate in m and it suffices to study the axisymmetric (m=0) case.
The Eulerian perturbation in the fluid 4-velocity δua can be expressed in terms of vector harmonics, while the metric perturbation δgab can be expressed in terms of spherical, vector, and tensor harmonics. These are either of “polar” or “axial” parity. Here, parity is defined to be the change in sign under a combination of re ection in the equatorial plane and rotation by π. A polar perturbation has parity (-1)l, while an axial perturbation has parity (-1)l+1. Because of the spherical background, the polar and axial perturbations of a nonrotating star are completely decoupled.
A normal mode solution satisfies the perturbed gravitational field equations,
and the perturbation of the conservation of the stress-energy tensor,
with suitable boundary conditions at the center of the star and at infinity. The latter equation is decomposed into an equation for the perturbation in the energy density δε and into equations for the three spatial components of the perturbation in the 4-velocity δua. As linear perturbations have a gauge freedom, at most six components of the perturbed field equations (49) need to be considered.
For a given pair (l, m), a solution exists for any value of the frequency ωi, consisting of a mixture of ingoing and outgoing wave parts. Outgoing quasi-normal modes are defined by the discrete set of eigenfrequencies for which there are no incoming waves at infinity. These are the modes that will be excited in various astrophysical situations.
The main modes of pulsation that are known to exist in relativistic stars have been classified as follows (f0 and τ0 are typical frequencies and damping times of the most important modes in the nonrotating limit):
-
1.
Polar fluid modes are slowly damped modes analogous to the Newtonian fluid pulsations:
-
f(undamental)-modes: surface modes due to the interface between the star and its surroundings (f0∼2 kHz, τ0<1 s),
-
p(ressure)-modes: nearly radial (f0>4 kHz, τ0>1 s),
-
g(ravity)-modes: nearly tangential, only exist in stars that are non-isentropic or that have a composition gradient or first order phase transition (f0<500 Hz, τ0>5 s).
-
-
2.
Axial and hybrid fluid modes:
-
inertial modes: degenerate at zero frequency in nonrotating stars. In a rotating star, some inertial modes are generically unstable to the CFS instability; they have frequencies from zero to kHz and growth times inversely proportional to a high power of the star’s angular velocity. Hybrid inertial modes have both axial and polar parts even in the limit of no rotation.
-
r(otation)-modes: a special case of inertial modes that reduce to the classical axial r-modes in the Newtonian limit. Generically unstable to the CFS instability with growth times as short as a few seconds at high rotation rates.
-
-
3.
Polar and axial spacetime modes:
-
w(ave)-modes: Analogous to the quasi-normal modes of a black hole (very weak coupling to the fluid). High frequency, strongly damped modes (f0>6 kHz, τ0∼0:1 ms).
-
For a more detailed description of various types of oscillation modes, see [179, 178, 225, 56, 177].
3.2 Effect of rotation on quasi-normal modes
In a continuous sequence of rotating stars that includes a nonrotating member, a quasi-normal mode of index l is defined as the mode which, in the nonrotating limit, reduces to the quasi-normal mode of the same index l. Rotation has several effects on the modes of a corresponding nonrotating star:
-
1.
The degeneracy in the index m is removed and a nonrotating mode of index l is split into 2l + 1 different (l, m) modes.
-
2.
Prograde (m<0) modes are now different from retrograde (m>0) modes.
-
3.
A rotating “polar” l-mode consists of a sum of purely polar and purely axial terms [293], e.g. for l=m,
$$ P_l^{{\rm{rot}}} \sim \sum\limits_{l' = 0}^\infty {({P_{l + 2l'}} + {A_{l + 2l' \pm 1}}} ), $$((51))that is, rotation couples a polar l-term to an axial l±1 term (the coupling to the l+1 term is, however, strongly favoured over the coupling to the l−1 term [61]). Similarly, for a rotating “axial” mode with l=m,
$$ A_l^{{\rm{rot}}}\sim \sum\limits_{l' = 0}^\infty {({A_{l + 2l'}} + {P_{l + 2l' \pm 1}}} ). $$((52)) -
4.
Frequencies and damping times are shifted. In general, frequencies (in the inertial frame) of prograde modes increase, while those of retrograde modes decrease with increasing rate of rotation.
-
5.
In rapidly rotating stars, apparent intersections between higher order modes of different l can occur. In such cases, the shape of the eigenfunction is used in the mode classification.
In rotating stars, quasi-normal modes of oscillation have been studied only in the slow rotation limit, in the post-Newtonian, and in the Cowling approximations. The solution of the fully relativistic perturbation equations for a rapidly rotating star is still a very challenging task and only recently have they been solved for zero-frequency (neutral) modes [293, 296]. First frequencies of quasi-radial modes have now been obtained through 3D numerical time evolutions of the nonlinear equations [105].
-
Going further The equations that describe oscillations of the solid crust of a rapidly rotating relativistic star are derived by Priou in [247]. The effects of superfluid hydrodynamics on the oscillations of neutron stars have been investigated by several authors, see e.g. [203, 67, 8, 10] and references therein.
3.3 Axisymmetric perturbations
3.3.1 Secular and dynamical axisymmetric instability
Along a sequence of nonrotating relativistic stars with increasing central energy density, there is always a model for which the mass becomes maximum. The maximum-mass turning point marks the onset of an instability in the fundamental radial pulsation mode of the star.
Applying the turning point theorem provided by Sorkin [286], Friedman, Ipser, and Sorkin [115] show that in the case of rotating stars a secular axisymmetric instability sets in when the mass becomes maximum along a sequence of constant angular momentum. An equivalent criterion (implied in [115]) is provided by Cook et al. [69]: The secular axisymmetric instability sets in when the angular momentum becomes minimum along a sequence of constant rest mass. The instability first develops on a secular timescale that is set by the time required for viscosity to redistribute the star’s angular momentum. This timescale is long compared to the dynamical timescale and comparable to the spin-up time following a pulsar glitch. Eventually, the star encounters the onset of dynamical instability and collapses to a black hole (see [274] for recent numerical simulations). Thus, the onset of the secular instability to axisymmetric perturbations separates stable neutron stars from neutron stars that will collapse to a black hole.
Goussard et al. [134] extend the stability criterion to hot proto-neutron stars with nonzero total entropy. In this case, the loss of stability is marked by the configuration with minimum angular momentum along a sequence of both constant rest mass and total entropy. In the nonrotating limit, Gondek et al. [127] compute frequencies and eigenfunctions of radial pulsations of hot proto-neutron stars and verify that the secular instability sets in at the maximum mass turning point, as is the case for cold neutron stars.
3.3.2 Axisymmetric pulsation modes
Axisymmetric (m=0) pulsations in rotating relativistic stars could be excited in a number of different astrophysical scenarios, such as during core collapse, in star quakes induced by the secular spin-down of a pulsar or during a large phase transition, or in the merger of two relativistic stars in a binary system, among others. Due to rotational couplings, the eigenfunction of any axisymmetric mode will involve a sum of various spherical harmonics Y 0l , so that even the quasi-radial modes (with lowest order l=0 contribution) would, in principle, radiate gravitational waves.
Quasi-radial modes in rotating relativistic stars have been studied by Hartle and Friedman [145] and by Datta et al. [83] in the slow rotation approximation. Yoshida and Eriguchi [330] study quasi-radial modes of rapidly rotating stars in the relativistic Cowling approximation and find that apparent intersections between quasi-radial and other axisymmetric modes can appear near the mass-shedding limit (see Figure 4). These apparent intersections are due to avoided crossings between mode sequences, which are also known to occur for axisymmetric modes of rotating Newtonian stars. Along a continuous sequence of computed mode frequencies an avoided crossing occurs when another sequence is encountered. In the region of the avoided crossing, the eigenfunctions of the two modes become of mixed character. Away from the avoided crossing and along the continuous sequences of computed mode frequencies, the eigenfunctions are exchanged. However, each “quasi-normal mode” is characterized by the shape of its eigenfunction and thus, the sequences of computed frequencies that belong to particular quasi-normal modes are discontinuous at avoided crossings (see Figure 4 for more details). The discontinuities can be found in numerical calculations, when quasi-normal mode sequences are well resolved in the region of avoided crossings. Otherwise, quasi-normal mode sequences will appear as intersecting.
Apparent intersection (due to avoided crossing) of the axisymmetric first quasi-radial overtone (H1) and the first overtone of the l=4 p-mode (in the Cowling approximation). Frequencies are normalized by \(\sqrt {{\rho _{\rm{c}}}/4\pi }\), where ρc is the central energy density of the star. The rotational frequency frot at the mass-shedding limit is 0.597 (in the above units). Along continuous sequences of computed frequencies, mode eigenfunctions are exchanged at the avoided crossing. Defining quasi-normal mode sequences by the shape of their eigenfunction, the H1 sequence (filled boxes) appears to intersect with the 4p1 sequence (triangle), but each sequence shows a discontinuity, when the region of apparent intersection is well resolved. (Figure 3 of Yoshida and Eriguchi [330]; used with permission.)
Several axisymmetric modes have recently been computed for rapidly rotating relativistic stars in the Cowling approximation, using time evolutions of the nonlinear hydrodynamical equations [104] (see [106] for a description of the 2D numerical evolution scheme). As in [330], Font et al. [104] find that apparent mode intersections are common for various higher order axisymmetric modes (see Figure 5). Axisymmetric inertial modes also appear in the numerical evolutions.
Frequencies of several axisymmetric modes along a sequence of rapidly rotating relativistic polytropes of N=1.0, in the Cowling approximation. On the horizontal axis, the angular velocity of each model is scaled to the angular velocity of the model at the mass-shedding limit. Lower order modes are weakly affected by rapid rotation, while higher order modes show apparent mode intersections. (Figure 10 of Font, Dimmelmeier, Gupta, and Stergioulas [104].)
The first fully relativistic frequencies of quasi-radial modes for rapidly rotating stars (without assuming the Cowling approximation) have been obtained recently, again through nonlinear time evolutions [105] (see Section 4.2).
-
Going further The stabilization, by an external gravitational field, of a relativistic star that is marginally stable to axisymmetric perturbations is discussed in [308].
3.4 Nonaxisymmetric perturbations
3.4.1 Nonrotating limit
Thorne, Campolattaro, and Price, in a series of papers [309, 245, 304], initiated the computation of nonradial modes by formulating the problem in the Regge-Wheeler (RW) gauge [251] and numerically computing nonradial modes for a number of neutron star models. A variational method for obtaining eigenfrequencies and eigenfunctions has been constructed by Detweiler and Ipser [85]. Lindblom and Detweiler [202] explicitly reduced the system of equations to four first order ordinary differential equations and obtained more accurate eigenfrequencies and damping times for a larger set of neutron star models. They later realized that their system of equations is sometimes singular inside the star and obtained an improved set of equations, which is free of this singularity [86].
Chandrasekhar and Ferrari [61] expressed the nonradial pulsation problem in terms of a fifth order system in a diagonal gauge, which is formally independent of fluid variables. Thus, they reformulate the problem in a way analogous to the scattering of gravitational waves off a black hole. Ipser and Price [163] show that in the RW gauge, nonradial pulsations can be described by a system of two second order differential equations, which can also be independent of fluid variables. In addition, they find that the diagonal gauge of Chandrasekhar and Ferrari has a remaining gauge freedom which, when removed, also leads to a fourth order system of equations [246].
In order to locate purely outgoing wave modes, one has to be able to distinguish the outgoing wave part from the ingoing wave part at infinity. This is typically achieved using analytic approximations of the solution at infinity.
W-modes pose a more challenging numerical problem because they are strongly damped and the techniques used for f- and p-modes fail to distinguish the outgoing wave part. The first accurate numerical solutions were obtained by Kokkotas and Schutz [181], followed by Leins, Nollert, and Soffel [197]. Andersson, Kokkotas, and Schutz [15] successfully combine a redefinition of variables with a complex-coordinate integration method, obtaining highly accurate complex frequencies for w modes. In this method, the ingoing and outgoing solutions are separated by numerically calculating their analytic continuations to a place in the complex-coordinate plane, where they have comparable amplitudes. Since this approach is purely numerical, it could prove to be suitable for the computation of quasi-normal modes in rotating stars, where analytic solutions at infinity are not available.
The non-availability of asymptotic solutions at infinity in the case of rotating stars is one of the major difficulties for computing outgoing modes in rapidly rotating relativistic stars. A method that may help to overcome this problem, at least to an acceptable approximation, has been found by Lindblom, Mendell, and Ipser [206].
The authors obtain approximate near-zone boundary conditions for the outgoing modes that replace the outgoing wave condition at infinity and that enable one to compute the eigenfrequencies with very satisfactory accuracy. First, the pulsation equations of polar modes in the Regge-Wheeler gauge are reformulated as a set of two second order radial equations for two potentials — one corresponding to fluid perturbations and the other to the perturbations of the spacetime. The equation for the spacetime perturbation reduces to a scalar wave equation at infinity and to Laplace’s equation for zero-frequency solutions. From these, an approximate boundary condition for outgoing modes is constructed and imposed in the near zone of the star (in fact, on its surface) instead of at infinity. For polytropic models, the near-zone boundary condition yields f-mode eigenfrequencies with real parts accurate to 0.01–0.1% and imaginary parts with accuracy at the 10–20% level, for the most relativistic stars. If the near zone boundary condition can be applied to the oscillations of rapidly rotating stars, the resulting frequencies and damping times should have comparable accuracy.
3.4.2 Slow rotation approximation
The slow rotation approximation is useful for obtaining a first estimate of the effect of rotation on the pulsations of relativistic stars. To lowest order in rotation, a polar l-mode of an initially nonrotating star couples to an axial l±1 mode in the presence of rotation. Conversely, an axial l-mode couples to a polar l±1 mode as was first discussed by Chandrasekhar and Ferrari [61].
The equations of nonaxisymmetric perturbations in the slow rotation limit are derived in a diagonal gauge by Chandrasekhar and Ferrari [61], and in the Regge-Wheeler gauge by Kojima [173, 175], where the complex frequencies \(\sigma = {\sigma _R} + i{\sigma _I}\) for the l=m modes of various polytropes are computed. For counterrotating modes, both σR and σI decrease, tending to zero, as the rotation rate increases (when σ passes through zero, the star becomes unstable to the CFS instability). Extrapolating σR and σI to higher rotation rates, Kojima finds a large discrepancy between the points where σR and σI go through zero. This shows that the slow rotation formalism cannot accurately determine the onset of the CFS instability of polar modes in rapidly rotating neutron stars.
In [174], it is shown that, for slowly rotating stars, the coupling between polar and axial modes affects the frequency of f- and p-modes only to second order in rotation, so that, in the slow rotation approximation, to \({\mathcal O}(\Omega )\), the coupling can be neglected when computing frequencies.
The linear perturbation equations in the slow rotation approximation have recently been derived in a new gauge by Ruoff, Stavridis, and Kokkotas [257]. Using the ADM formalism, a first order hyperbolic evolution system is obtained, which is suitable for numerical integration without further manipulations (as was required in the Regge-Wheeler gauge). In this gauge (which is related to a gauge introduced for nonrotating stars in [27]), the symmetry between the polar and axial equations becomes directly apparent.
The case of relativistic inertial modes is different, as these modes have both axial and polar parts at order \({\mathcal O}(\Omega )\), and the presence of continuous bands in the spectrum (at this order in the rotation rate) has led to a series of detailed investigations of the properties of these modes (see [180] for a review). In a recent paper, Ruoff, Stavridis, and Kokkotas [258] finally show that the inclusion of both polar and axial parts in the computation of relativistic r-modes, at order \({\mathcal O}(\Omega )\), allows for discrete modes to be computed, in agreement with post-Newtonian [214] and nonlinear, rapid-rotation [294] calculations.
3.4.3 Post-Newtonian approximation
A step toward the solution of the perturbation equations in full general relativity has been taken by Cutler and Lindblom [77, 79, 199], who obtain frequencies for the l=m f-modes in rotating stars in the first post-Newtonian (1-PN) approximation. The perturbation equations are derived in the post-Newtonian formalism (see [36]), i.e. the equations are separated into equations of consistent order in 1/c.
Cutler and Lindblom show that in this scheme, the perturbation of the 1-PN correction of the four-velocity of the fluid can be obtained analytically in terms of other variables; this is similar to the perturbation in the three-velocity in the Newtonian Ipser-Managan scheme. The perturbation in the 1-PN corrections are obtained by solving an eigenvalue problem, which consists of three second order equations, with the 1-PN correction to the eigenfrequency of a mode Δω as the eigenvalue.
Cutler and Lindblom obtain a formula that yields Δω if one knows the 1-PN stationary solution and the solution to the Newtonian perturbation equations. Thus, the frequency of a mode in the 1-PN approximation can be obtained without actually solving the 1-PN perturbation equations numerically. The 1-PN code was checked in the nonrotating limit and it was found to reproduce the exact general relativistic frequencies for stars with M/R=0.2, obeying an N=1 polytropic EOS, with an accuracy of 3–8%.
Along a sequence of rotating stars, the frequency of a mode is commonly described by the ratio of the frequency of the mode in the comoving frame to the frequency of the mode in the nonrotating limit. For an N=1 polytrope and for M/R=0.2, this frequency ratio is reduced by as much as 12% in the 1-PN approximation compared to its Newtonian counterpart (for the fundamental l=m modes) which is representative of the effect that general relativity has on the frequency of quasi-normal modes in rotating stars.
3.4.4 Cowling approximation
In several situations, the frequency of pulsations in relativistic stars can be estimated even if one completely neglects the perturbation in the gravitational field, i.e. if one sets δgab=0 in the perturbation equations [226]. In this approximation, the pulsations are described only by the perturbation in the fluid variables, and the scheme works quite well for f, p, and r-modes [209]. A different version of the Cowling approximation, in which δgtr is kept nonzero in the perturbation equations, has been suggested to be more suitable for g-modes [99], since these modes could have large fluid velocities, even though the variation in the gravitational field is weak.
Yoshida and Kojima [331] examine the accuracy of the relativistic Cowling approximation in slowly rotating stars. The first order correction to the frequency of a mode depends only on the eigenfrequency and eigenfunctions of the mode in the absence of rotation and on the angular velocity of the star. The eigenfrequencies of f, p1, and p2 modes for slowly rotating stars with M/R between 0.05 and 0.2 are computed (assuming polytropic EOSs with N=1 and N=1.5) and compared to their counterparts in the slow rotation approximation.
For the l=2 f-mode, the relative error in the eigenfrequency because of the Cowling approximation is 30% for weakly relativistic stars (M/R=0:05) and about 15% for stars with M/R=0.2; the error decreases for higher l-modes. For the p1 and p2 modes the relative error is similar in magnitude but it is smaller for less relativistic stars. Also, for p-modes, the Cowling approximation becomes more accurate for increasing radial mode number.
As an application, Yoshida and Eriguchi [328, 329] use the Cowling approximation to estimate the onset of the f-mode CFS instability in rapidly rotating relativistic stars and to compute frequencies of f-modes for several realistic equations of state (see Figure 6).
Eigenfrequencies (in the Cowling approximation) of f-modes along a M=1.8M⊙ sequence of models, constructed with the WFF3-NV EOS. The vertical line corresponds to the frequency of rotation of the model at the mass-shedding limit of the sequence. (Figure 1 of Yoshida and Eriguchi [329]; used with permission.)
3.5 Nonaxisymmetric instabilities
3.5.1 Introduction
Rotating cold neutron stars, detected as pulsars, have a remarkably stable rotation period. But, at birth or during accretion, rapidly rotating neutron stars can be subject to various nonaxisymmetric instabilities, which will affect the evolution of their rotation rate.
If a proto-neutron star has a sufficiently high rotation rate (so that, e.g. T/W>0.27 in the case of Maclaurin spheroids), it will be subject to a dynamical instability driven by hydrodynamics and gravity. Through the l=2 mode, the instability will deform the star into a bar shape. This highly nonaxisymmetric configuration will emit strong gravitational waves with frequencies in the kHz regime. The development of the instability and the resulting waveform have been computed numerically in the context of Newtonian gravity by Houser et al. [155] and in full general relativity by Shibata et al. [274] (see Section 4.1.3).
At lower rotation rates, the star can become unstable to secular nonaxisymmetric instabilities, driven by gravitational radiation or viscosity. Gravitational radiation drives a nonaxisymmetric instability when a mode that is retrograde in a frame corotating with the star appears as prograde to a distant inertial observer, via the Chandrasekhar-Friedman-Schutz (CFS) mechanism [60, 118]: A mode that is retrograde in the corotating frame has negative angular momentum, because the perturbed star has less angular momentum than the unperturbed one. If, for a distant observer, the mode is prograde, it removes positive angular momentum from the star, and thus the angular momentum of the mode becomes increasingly negative.
The instability evolves on a secular timescale, during which the star loses angular momentum via the emitted gravitational waves. When the star rotates more slowly than a critical value, the mode becomes stable and the instability proceeds on the longer timescale of the next unstable mode, unless it is suppressed by viscosity.
Neglecting viscosity, the CFS instability is generic in rotating stars for both polar and axial modes. For polar modes, the instability occurs only above some critical angular velocity, where the frequency of the mode goes through zero in the inertial frame. The critical angular velocity is smaller for increasing mode number l. Thus, there will always be a high enough mode number l for which a slowly rotating star will be unstable. Many of the hybrid inertial modes (and in particular the relativistic r-mode) are generically unstable in all rotating stars, since the mode has zero frequency in the inertial frame when the star is nonrotating [6, 117].
The shear and bulk viscosity of neutron star matter is able to suppress the growth of the CFS instability except when the star passes through a certain temperature window. In Newtonian gravity, it appears that the polar mode CFS instability can occur only in nascent neutron stars that rotate close to the mass-shedding limit [160, 159, 161, 326, 204], but the computation of neutral f-modes in full relativity [293, 296] shows that relativity enhances the instability, allowing it to occur in stars with smaller rotation rates than previously thought.
-
Going further A numerical method for the analysis of the ergosphere instability in relativistic stars, which could be extended to nonaxisymmetric instabilities of fluid modes, is presented by Yoshida and Eriguchi in [327].
3.5.2 CFS instability of polar modes
The existence of the CFS instability in rotating stars was first demonstrated by Chandrasekhar [60] in the case of the l=2 mode in uniformly rotating, uniform density Maclaurin spheroids. Friedman and Schutz [118] show that this instability also appears in compressible stars and that all rotating, self-gravitating perfect fluid configurations are generically unstable to the emission of gravitational waves. In addition, they find that a nonaxisymmetric mode becomes unstable when its frequency vanishes in the inertial frame. Thus, zero-frequency outgoing modes in rotating stars are neutral (marginally stable).
In the Newtonian limit, neutral modes have been determined for several polytropic EOSs [156, 218, 158, 326]. The instability first sets in through l=m modes. Modes with larger l become unstable at lower rotation rates, but viscosity limits the interesting ones to l≤5. For an N=1 polytrope, the critical values of T/W for the l=3, 4, and 5 modes are 0.079, 0.058, and 0.045, respectively, and these values become smaller for softer polytropes. The l=m=2 “bar” mode has a critical T/W ratio of 0.14 that is almost independent of the polytropic index. Since soft EOSs cannot produce models with high T/W values, the bar mode instability appears only for stiff Newtonian polytropes of N≤0.808 [164, 283]. In addition, the viscosity-driven bar mode appears at the same critical T/W ratio as the bar mode driven by gravitational radiation [162] (we will see later that this is no longer true in general relativity).
The post-Newtonian computation of neutral modes by Cutler and Lindblom [79, 199] has shown that general relativity tends to strengthen the CFS instability. Compared to their Newtonian counterparts, critical angular velocity ratios ‖c/Ω0 (where \({\Omega _0} = {(3{M_0}/4R_0^3)^{1/2}}\), and M0, R0 are the mass and radius of the nonrotating star in the sequence) are lowered by as much as 10% for stars obeying the N=1 polytropic EOS (for which the instability occurs only for l=m≥3 modes in the post-Newtonian approximation).
In full general relativity, neutral modes have been determined for polytropic EOSs of N≥1.0 by Stergioulas and Friedman [293, 296], using a new numerical scheme. The scheme completes the Eulerian formalism developed by Ipser and Lindblom in the Cowling approximation (where δgab was neglected) [161], by finding an appropriate gauge in which the time independent perturbation equations can be solved numerically for δgab. The computation of neutral modes for polytropes of N=1.0, 1.5, and 2.0 shows that relativity significantly strengthens the instability. For the N=1.0 polytrope, the critical angular velocity ratio Ωc/ΩK, where ΩK is the angular velocity at the mass-shedding limit at same central energy density, is reduced by as much as 15% for the most relativistic configuration (see Figure 7). A surprising result (which was not found in computations that used the post-Newtonian approximation) is that the l=m=2 bar mode is unstable even for relativistic polytropes of index N=1.0. The classical Newtonian result for the onset of the bar mode instability (Ncrit<0.808) is replaced by
in general relativity. For relativistic stars, it is evident that the onset of the gravitational-radiation-driven bar mode does not coincide with the onset of the viscosity-driven bar mode, which occurs at larger T/W [39]. The computation of the onset of the CFS instability in the relativistic Cowling approximation by Yoshida and Eriguchi [328] agrees qualitatively with the conclusions in [293, 296].
The l=m neutral f-mode sequences for EOS A. Shown are the ratio of rotational to gravitational energy T/W (upper panel) and the ratio of the critical angular velocity Ωc to the angular velocity at the mass-shedding limit for uniform rotation (lower panel) as a function of gravitational mass. The solid curves are the neutral mode sequences for l=m=2, 3, 4, and 5 (from top to bottom), while the dashed curve in the upper panel corresponds to the mass-shedding limit for uniform rotation. The l=m=2 f-mode becomes CFS-unstable even at 85% of the mass-shedding limit, for 1.4M⊙ models constructed with this EOS. (Figure 2 of Morsink, Stergioulas, and Blattning [230].)
Morsink, Stergioulas, and Blattning [230] extend the method presented in [296] to a wide range of realistic equations of state (which usually have a stiff high density region, corresponding to polytropes of index N=0.5–0.7) and find that the l=m=2 bar mode becomes unstable for stars with gravitational mass as low as 1.0–1.2M⊙. For 1.4M⊙ neutron stars, the mode becomes unstable at 80–95% of the maximum allowed rotation rate. For a wide range of equations of state, the l=m=2 f-mode becomes unstable at a ratio of rotational to gravitational energies T/W∼0.08 for 1.4M⊙ stars and T/W∼0.06 for maximum mass stars. This is to be contrasted with the Newtonian value of T/W∼0.14. The empirical formula
where M sphmax is the maximum mass for a spherical star allowed by a given equation of state, gives the critical value of T/W for the bar f-mode instability, with an accuracy of 4–6%, for a wide range of realistic EOSs.
In newly-born neutron stars the CFS instability could develop while the background equilibrium star is still differentially rotating. In that case, the critical value of T/W, required for the instability in the f-mode to set in, is larger than the corresponding value in the case of uniform rotation [333] (Figure 8). The mass-shedding limit for differentially rotating stars also appears at considerably larger T/W than the mass-shedding limit for uniform rotation. Thus, Yoshida et al. [333] suggest that differential rotation favours the instability, since the ratio (T/W)critical/(T/W)shedding decreases with increasing degree of differential rotation.
Eigenfrequencies (in the Cowling approximation) of the m=2 mode as a function of the parameter \(\beta = T/\left| W \right|\) for three different sequences of differentially rotating neutron stars (the A -1R =0.0 line corresponding to uniform rotation). The filled circle indicates the neutral stability point of a uniformly rotating star computed in full general relativity (Stergioulas and Friedman [296]). Differential rotation shifts the neutral point to higher rotation rates. (Figure 1 of Yoshida, Rezzolla, Karino, and Eriguchi [333]; used with permission.)
3.5.3 CFS instability of axial modes
In nonrotating stars, axial fluid modes are degenerate at zero frequency, but in rotating stars they have nonzero frequency and are called r-modes in the Newtonian limit [242, 260]. To order \({\mathcal O}(\Omega )\), their frequency in the inertial frame is
while the radial eigenfunction of the perturbation in the velocity can be determined at order Ω2 [176]. According to Equation (55), r-modes with m>0 are prograde (ωi<0) with respect to a distant observer but retrograde \(({\omega _{\rm{r}}} = {\omega _{\rm{i}}} + m\Omega > 0)\) in the comoving frame for all values of the angular velocity. Thus, r-modes in relativistic stars are generically unstable to the emission of gravitational waves via the CFS instability, as was first discovered by Andersson [6] for the case of slowly rotating, relativistic stars. This result was proved rigorously by Friedman and Morsink [117], who showed that the canonical energy of the modes is negative.
Two independent computations in the Newtonian Cowling approximation [208, 16] showed that the usual shear and bulk viscosity assumed to exist for neutron star matter is not able to damp the r-mode instability, even in slowly rotating stars. In a temperature window of 105K<T<1010 K, the growth time of the l=m=2 mode becomes shorter than the shear or bulk viscosity damping time at a critical rotation rate that is roughly one tenth the maximum allowed angular velocity of uniformly rotating stars. The gravitational radiation is dominated by the mass current quadrupole term. These results suggested that a rapidly rotating proto-neutron star will spin down to Crab-like rotation rates within one year of its birth, because of the r-mode instability. Due to uncertainties in the actual viscous damping times and because of other dissipative mechanisms, this scenario also is consistent with somewhat higher initial spins, such as the suggested initial spin period of several milliseconds for the X-ray pulsar in the supernova remnant N157B [224]. Millisecond pulsars with periods less than a few milliseconds can then only form after the accretion-induced spin-up of old pulsars and not in the accretion-induced collapse of a white dwarf.
The precise limit on the angular velocity of newly-born neutron stars will depend on several factors, such as the strength of the bulk viscosity, the cooling process, superfluidity, the presence of hyperons, and the influence of a solid crust. In the uniform density approximation, the r-mode instability can be studied analytically to \({\mathcal O}({\Omega ^2})\) in the angular velocity of the star [182]. A study on the issue of detectability of gravitational waves from the r-mode instability was presented in [238] (see Section 3.5.5), while Andersson, Kokkotas, and Stergioulas [17] and Bildsten [35] proposed that the r-mode instability is limiting the spin of millisecond pulsars spun-up in LMXBs and it could even set the minimum observed spin period of ∼ 1.5 ms (see [12]). This scenario is also compatible with observational data, if one considers strange stars instead of neutron stars [11] (see Figure 9).
The r-mode instability window for a strange star of M=1.4M⊙ and R=10 km (solid line). Dashed curves show the corresponding instability windows for normal npe fluid and neutron stars with a crust. The instability window is compared to i) the inferred spin-periods for accreting stars in LMBXs [shaded box], and ii) the fastest known millisecond pulsars (for which observational upper limits on the temperature are available) [horizontal lines]. (Figure 1 of Andersson, Jones, and Kokkotas [11]; used with permission.)
Since the discovery of the r-mode instability, a large number of authors have studied in more detail the development of the instability and its astrophysical consequences. Unlike in the case of the f-mode instability, many different aspects and interactions have been considered. This intense focus on the detailed physics has been very fruitful and we now have a much more complete understanding of the various physical processes that are associated with pulsations in rapidly rotating relativistic stars. The latest understanding of the r-mode instability is that it may not be a very promising gravitational wave source (as originally thought), but the important astrophysical consequences, such as the limits of the spin of young and of recycled neutron stars are still considered plausible. The most crucial factors affecting the instability are magnetic fields [287, 255, 253, 254], possible hyperon bulk viscosity [166, 207, 140] and nonlinear saturation [294, 210, 211, 21]. The question of the possible existence of a continuous spectrum has also been discussed by several authors, but the most recent analysis suggests that higher order rotational effects still allow for discrete r-modes in relativistic stars [332, 258] (see Figure 10).
Relativistic r-mode frequencies for a range of the compactness ratio M/R. The coupling of polar and axial terms, even in the order \({\mathcal O}(\Omega )\) slow rotation approximation has a dramatic impact on the continuous frequency bands (shaded areas), allowing the r-mode to exist even in highly compact stars. The Newtonian value of the r-mode frequency is plotted as a dashed-dotted line. (Figure 3 of Ruoff, Stavridis, and Kokkotas [ 258 ]; used with permission.)
Magnetic fields can affect the r-mode instability, as the r-mode velocity field creates differential rotation, which is both kinematical and due to gravitational radiation reaction (see Figure 11). Under differential rotation, an initially weak poloidal magnetic field is wound-up, creating a strong toroidal field, which causes the r-mode amplitude to saturate. If neutron stars have hyperons in their cores, the associated bulk viscosity is so strong that it could completely prevent the growth of the r-mode instability. However, hyperons are predicted only by certain equations of state and the relativistic mean field theory is not universally accepted. Thus, our ignorance of the true equation of state still leaves a lot of room for the r-mode instability to be considered viable.
Projected trajectories of several fiducial fluid elements (as seen in the corotating frame) for an l=m=2 Newtonian r-mode. All of the fluid elements are initially positioned on the φ0=0 meridian at different latitudes (indicated with stars). Blue dots indicate the position of the fluid elements after each full oscillation period. The r-mode induces a kinematical, differential drift. (Figure 2c of Rezzolla, Lamb, Marković, and Shapiro [253]; used with permission.)
The detection of gravitational waves from r-modes depends crucially on the nonlinear saturation amplitude. A first study by Stergioulas and Font [294] suggests that r-modes can exist at large amplitudes of order unity for dozens of rotational periods in rapidly rotating relativistic stars (Figure 12). The study used 3D relativistic hydrodynamical evolutions in the Cowling approximation. This result was confirmed by Newtonian 3D simulations of nonlinear r-modes by Lindblom, Tohline, and Vallisneri [207, 210]. Lindblom et al. went further, using an accelerated radiation reaction force to artificially grow the r-mode amplitude on a hydrodynamical (instead of the secular) timescale. At the end of the simulations, the r-mode grew so large that large shock waves appeared on the surface of the star, while the amplitude of the mode subsequently collapsed. Lindblom et al. suggested that shock heating may be the mechanism that saturates the r-modes at a dimensionless amplitude of α∼3.
Evolution of the axial velocity in the equatorial plane for a relativistic r-mode in a rapidly rotating N=1.0 polytrope (in the Cowling approximation). Since the initial data used to excite the mode are not exact, the evolution is a superposition of (mainly) the l=m=2 r-mode and several inertial modes. The amplitude of the oscillation decreases due to numerical (finite-differencing) viscosity of the code. A beating between the l=m=2 r-mode and another inertial mode can also be seen. (Figure 2 of Stergioulas and Font [294].)
More recent studies of nonlinear couplings between the r-mode and higher order inertial modes [21] and new 3D nonlinear Newtonian simulations [136] seem to suggest a different picture. The r-mode could be saturated due to mode couplings or due to a hydrodynamical instability at amplitudes much smaller than the amplitude at which shock waves appeared in the simulations by Lindblom et al. Such a low amplitude, on the other hand, modifies the properties of the r-mode instability as a gravitational wave source, but is not necessarily bad news for gravitational wave detection, as a lower spin-down rate also implies a higher event rate for the r-mode instability in LMXBs in our own Galaxy [11, 154]. The 3D simulations need to achieve significantly higher resolutions before definite conclusions can be reached, while the Arras et al. work could be extended to rapidly rotating relativistic stars (in which case the mode frequencies and eigenfunctions could change significantly, compared to the slowly rotating Newtonian case, which could affect the nonlinear coupling coefficients). Spectral methods can be used for achieving high accuracy in mode calculations; first results have been obtained by Villain and Bonazzolla [316] for inertial modes of slowly rotating stars in the relativistic Cowling approximation.
For a more extensive coverage of the numerous articles on the r-mode instability that appeared in recent years, the reader is referred to several excellent recent review articles [14, 116, 201, 180, 7].
-
Going further If rotating stars with very high compactness exist, then w-modes can also become unstable, as was recently found by Kokkotas, Ruoff, and Andersson [183]. The possible astrophysical implications are still under investigation.
3.5.4 Effect of viscosity on the CFS instability
In the previous sections, we have discussed the growth of the CFS instability driven by gravitational radiation in an otherwise nondissipative star. The effect of neutron star matter viscosity on the dynamical evolution of nonaxisymmetric perturbations can be considered separately, when the timescale of the viscosity is much longer than the oscillation timescale. If τgr is the computed growth rate of the instability in the absence of viscosity, and τs, τb are the timescales of shear and bulk viscosity, then the total timescale of the perturbation is
Since τgr<0 and τb, τs>0, a mode will grow only if τgr is shorter than the viscous timescales, so that 1/τ<0.
In normal neutron star matter, shear viscosity is dominated by neutron-neutron scattering with a temperature dependence of T-2 [101], and computations in the Newtonian limit and post-Newtonian approximation show that the CFS instability is suppressed for T<106 K-107 K [160, 159, 326, 199]. If neutrons become a superfluid below a transition temperature Ts, then mutual friction, which is caused by the scattering of electrons off the cores of neutron vortices could significantly suppress the f-mode instability for T<Ts [204], but the r-mode instability remains unaffected [205]. The superfluid transition temperature depends on the theoretical model for superfluidity and lies in the range 108 K-6×109 K [240].
In a pulsating fluid that undergoes compression and expansion, the weak interaction requires a relatively long time to re-establish equilibrium. This creates a phase lag between density and pressure perturbations, which results in a large bulk viscosity [263]. The bulk viscosity due to this effect can suppress the CFS instability only for temperatures for which matter has become transparent to neutrinos [191, 41]. It has been proposed that for T>5×109 K, matter will be opaque to neutrinos and the neutrino phase space could be blocked ([191]; see also [41]). In this case, bulk viscosity will be too weak to suppress the instability, but a more detailed study is needed.
In the neutrino transparent regime, the effect of bulk viscosity on the instability depends crucially on the proton fraction xp. If xp is lower than a critical value (∼1/9), only modified URCA processes are allowed. In this case bulk viscosity limits, but does not completely suppress, the instability [160, 159, 326]. For most modern EOSs, however, the proton fraction is larger than ∼1/9 at sufficiently high densities [194], allowing direct URCA processes to take place. In this case, depending on the EOS and the central density of the star, the bulk viscosity could almost completely suppress the CFS instability in the neutrino transparent regime [337]. At high temperatures, T>5×109 K, even if the star is opaque to neutrinos, the direct URCA cooling timescale to T∼5×109 K could be shorter than the growth timescale of the CFS instability.
3.5.5 Gravitational radiation from CFS instability
Conservation of angular momentum and the inferred initial period (assuming magnetic braking) of a few milliseconds for the X-ray pulsar in the supernova remnant N157B [224] suggests that a fraction of neutron stars may be born with very large rotational energies. The f-mode bar CFS instability thus appears as a promising source for the planned gravitational wave detectors [191]. It could also play a role in the rotational evolution of merged binary neutron stars, if the post-merger angular momentum exceeds the maximum allowed to form a Kerr black hole [28] or if differential rotation temporarily stabilizes the merged object.
Lai and Shapiro [191] have studied the development of the f-mode instability using Newtonian ellipsoidal models [189, 190]. They consider the case when a rapidly rotating neutron star is created in a core collapse. After a brief dynamical phase, the proto-neutron star becomes secularly unstable. The instability deforms the star into a nonaxisymmetric configuration via the l=2 bar mode. Since the star loses angular momentum via the emission of gravitational waves, it spins down until it becomes secularly stable. The frequency of the waves sweeps downward from a few hundred Hz to zero, passing through LIGO’s ideal sensitivity band. A rough estimate of the wave amplitude shows that, at ∼100 Hz, the gravitational waves from the CFS instability could be detected out to the distance of 140 Mpc by the advanced LIGO detector. This result is very promising, especially since for relativistic stars the instability will be stronger than the Newtonian estimate [296]. Whether r-modes should also be considered a promising gravitational wave source depends crucially on their nonlinear saturation amplitude (see Section 3.5.3).
-
Going further The possible ways for neutron stars to emit gravitational waves and their detectability are reviewed in [44, 45, 121, 100, 307, 266, 80].
3.5.6 Viscosity-driven instability
A different type of nonaxisymmetric instability in rotating stars is the instability driven by viscosity, which breaks the circulation of the fluid [256, 164]. The instability is suppressed by gravitational radiation, so it cannot act in the temperature window in which the CFS instability is active. The instability sets in when the frequency of an l=-m mode goes through zero in the rotating frame. In contrast to the CFS instability, the viscosity-driven instability is not generic in rotating stars. The m=2 mode becomes unstable at a high rotation rate for very stiff stars, and higher m-modes become unstable at larger rotation rates.
In Newtonian polytropes, the instability occurs only for stiff polytropes of index N<0.808 [164, 283]. For relativistic models, the situation for the instability becomes worse, since relativistic effects tend to suppress the viscosity-driven instability (while the CFS instability becomes stronger). According to recent results by Bonazzola et al. [39], for the most relativistic stars, the viscosity-driven bar mode can become unstable only if N<0.55. For 1.4M⊙ stars, the instability is present for N<0.67.
These results are based on an approximate computation of the instability in which one perturbs an axisymmetric and stationary configuration, and studies its evolution by constructing a series of triaxial quasi-equilibrium configurations. During the evolution only the dominant nonaxisymmetric terms are taken into account. The method presented in [39] is an improvement (taking into account nonaxisymmetric terms of higher order) of an earlier method by the same authors [41]. Although the method is approximate, its results indicate that the viscosity-driven instability is likely to be absent in most relativistic stars, unless the EOS turns out to be unexpectedly stiff.
An investigation by Shapiro and Zane [269] of the viscosity-driven bar mode instability, using incompressible, uniformly rotating triaxial ellipsoids in the post-Newtonian approximation, finds that the relativistic effects increase the critical T/W ratio for the onset of the instability significantly. More recently, new post-Newtonian [88] and fully relativistic calculations for uniform density stars [129] show that the viscosity-driven instability is not as strongly suppressed by relativistic effects as suggested in [269]. The most promising case for the onset of the viscosity-driven instability (in terms of the critical rotation rate) would be rapidly rotating strange stars [130], but the instability can only appear if its growth rate is larger than the damping rate due to the emission of gravitational radiation — a corresponding detailed comparison is still missing.
4 Rotating Stars in Numerical Relativity
Recently, the dynamical evolution of rapidly rotating stars has become possible in numerical relativity. In the framework of the 3+1 split of the Einstein equations [284], a stationary axisymmetric star can be described by a metric of the standard form
where α is the lapse function, βi is the shift three-vector, and γij is the spatial three-metric, with i=1…3. The spacetime has the following properties:
-
The metric function ω in (5) describing the dragging of inertial frames by rotation is related to the shift vector through \({\beta ^\phi } = - \omega\). This shift vector satisfies the minimal distortion shift condition.
-
The metric satisfies the maximal slicing condition, while the lapse function is related to the metric function ν in (5) through \(\alpha = {e^\nu }\).
-
The quasi-isotropic coordinates are suitable for numerical evolution, while the radial-gauge coordinates [25] are not suitable for nonspherical sources (see [47] for details).
-
The ZAMOs are the Eulerian observers, whose worldlines are normal to the t=const: hypersurfaces.
-
Uniformly rotating stars have Ω=const: in the coordinate frame. This can be shown by requiring a vanishing rate of shear.
-
Normal modes of pulsation are discrete in the coordinate frame and their frequencies can be obtained by Fourier transforms (with respect to coordinate time t) of evolved variables at a fixed coordinate location [106].
Crucial ingredients for the successful long-term evolutions of rotating stars in numerical relativity are the conformal ADM schemes for the spacetime evolution (see [234, 277, 32, 4]) and hydrodynamical schemes that have been shown to preserve well the sharp rotational profile at the surface of the star [106, 294, 105].
4.1 Numerical evolution of equilibrium models
4.1.1 Stable equilibrium
The long-term stable evolution of rotating relativistic stars in 3D simulations has become possible through the use of High-Resolution Shock-Capturing (HRSC) methods (see [103] for a review). Stergioulas and Font [294] evolve rotating relativistic stars near the mass-shedding limit for dozens of rotational periods (evolving only the equations of hydrodynamics) (see Figure 13), while accurately preserving the rotational profile, using the 3rd order PPM method [65]. This method was shown to be superior to other, commonly used methods, in 2D evolutions of rotating relativistic stars [106].
Time evolution of the rotational velocity profile for a stationary, rapidly rotating relativistic star (in the Cowling approximation), using the 3rd order PPM scheme and a 1163 grid. The initial rotational profile is preserved to a high degree of accuracy, even after 20 rotational periods. (Figure 1 of Stergioulas and Font [294].)
Fully coupled hydrodynamical and spacetime evolutions in 3D have been obtained by Shibata [270] and by Font et al. [105]. In [270], the evolution of approximate (conformally flat) initial data is presented for about two rotational periods, and in [105] the simulations extend to several full rotational periods (see Figure 14), using numerically exact initial data and a monotonized central difference (MC) slope limiter [315]. The MC slope limiter is somewhat less accurate in preserving the rotational profile of equilibrium stars than the 3rd order PPM method, but, on the other hand, it is easier to implement in a numerical code.
mpg-Movie (*** MB)Still from a movie showing the simulation of a stationary, rapidly rotating neutron star model in full general relativity, for 3 rotational periods (shown are iso-density contours, in dimensionless units). The stationary shape is well preserved at a resolution of 1293. Simulation by Font, Goodale, Iyer, Miller, Rezzolla, Seidel, Stergioulas, Suen, and Tobias. Visualization by W. Benger and L. Rezzolla at the Albert Einstein Institute, Golm [1]. (For video see appendix)
New evolutions of uniformly and differentially rotating stars in 3D, using different gauges and coordinate systems, are presented in [93], while new 2D evolutions are presented in [273].
4.1.2 Instability to collapse
Shibata, Baumgarte, and Shapiro [275] study the stability of supramassive neutron stars rotating at the mass-shedding limit, for a Γ=2 polytropic EOS. Their 3D simulations in full general relativity show that stars on the mass-shedding sequence, with central energy density somewhat larger than that of the maximum mass model, are dynamically unstable to collapse. Thus, the dynamical instability of rotating neutron stars to axisymmetric perturbations is close to the corresponding secular instability. The initial data for these simulations are approximate, conformally flat axisymmetric solutions, but their properties are not very different from exact axisymmetric solutions even near the mass-shedding limit [73]. It should be noted that the approximate minimal distortion (AMD) shift condition does not prove useful in the numerical evolution, once a horizon forms. Instead, modified shift conditions are used in [275]. In the above simulations, no massive disk around the black hole is formed, as the equatorial radius of the initial model is inside the radius which becomes the ISCO of the final black hole. This could change if a different EOS is chosen.
4.1.3 Dynamical bar-mode instability
Shibata, Baumgarte, and Shapiro [274] study the dynamical bar-mode instability in differentially rotating neutron stars, in fully relativistic 3D simulations. They find that stars become unstable when rotating faster than a critical value of \(\beta \equiv T/W \sim 0.24 - 0.25\). This is only somewhat smaller than the Newtonian value of β∼0.27. Models with rotation only somewhat above critical become differentially rotating ellipsoids, while models with β much larger than critical also form spiral arms, leading to mass ejection (see Figures 15, 16, and 17). In any case, the differentially rotating ellipsoids formed during the bar-mode instability have β>0.2, indicating that they will be secularly unstable to barmode formation (driven by gravitational radiation or viscosity). The decrease of the critical value of β for dynamical bar formation due to relativistic effects has been confirmed by post-Newtonian simulations [259].
Density contours and velocity flow for a neutron star model that has developed spiral arms, due to the dynamical bar-mode instability. The computation was done in full General Relativity. (Figure 4 of Shibata, Baumgarte, and Shapiro [ 274 ]; used with permission).
mpg-Movie (*** MB)Still from a movie showing the development of the dynamical barmode instability in a rapidly rotating relativistic star. Spiral arms form within a few rotational periods. The different colors correspond to different values of the density, while the computation was done in full general relativity. Movie produced at the University of Illinois by T.W. Baumgarte, S.L. Shapiro, and M. Shibata, with the assistance of the Illinois Undergraduate Research Team [29]; used with permission. (For video see appendix)
mpg-Movie (*** MB)Still from a movie showing the gravitational wave emission during the development of the dynamical bar-mode instability in a rapidly rotating relativistic star. The gravitational wave amplitude in a plane containing the rotation axis is shown. At large distances, the waves assume a quadrupole-like angular dependence. Movie produced at the University of Illinois by T.W. Baumgarte, S.L. Shapiro, and M. Shibata, with the assistance of the Illinois Undergraduate Research Team [29]; used with permission. (For video see appendix)
4.2 Pulsations of rotating stars
Pulsations of rotating relativistic stars are traditionally studied (when possible) as a time independent, linear eigenvalue problem, but recent advances in numerical relativity also allow the study of such pulsations via numerical time evolutions. The first quasi-radial mode frequencies of rapidly rotating stars in full general relativity have been recently obtained in [105], something that has not been achieved yet with linear perturbation theory. The fundamental quasi-radial mode in full general relativity has a similar rotational dependence as in the relativistic Cowling approximation, and an empirical relation between the full GR computation and the Cowling approximation can be constructed (Figure 18). For higher order modes, apparent intersections of mode sequences near the mass-shedding limit do not allow for such empirical relations to be constructed.
The first fully relativistic, quasi-radial pulsation frequencies for a sequence of rapidly rotating stars (solid lines). The frequencies of the fundamental mode F (filled squares) and of the first overtone H 1 (filled circles) are obtained through coupled hydrodynamical and spacetime evolutions. The corresponding frequencies obtained from computations in the relativistic Cowling approximation [ 104 ] are shown as dashed lines. (Figure 16 of Font, Goodale, Iyer, Miller, Rezzolla, Seidel, Stergioulas, Suen, and Tobias [ 105 ].)
In the relativistic Cowling approximation, 2D time evolutions have yielded frequencies for the l=0 to l=3 axisymmetric modes of rapidly rotating relativistic polytropes with N=1.0 [104]. The higher order overtones of these modes show characteristic apparent crossings near mass-shedding (as was observed for the quasi-radial modes in [330]).
Numerical relativity has also enabled the first study of nonlinear r-modes in rapidly rotating relativistic stars (in the Cowling approximation) by Stergioulas and Font [294]. For several dozen dynamical timescales, the study shows that nonlinear r-modes with amplitudes of order unity can exist in a star rotating near mass-shedding. However, on longer timescales, nonlinear effects may limit the r-mode amplitude to smaller values (see Section 3.5.3).
4.3 Rotating core collapse
4.3.1 Collapse to a rotating black hole
Black hole formation in relativistic core collapse was first studied in axisymmetry by Nakamura [232, 233], using the (2+1)+1 formalism [217]. The outcome of the simulation depends on the rotational parameter
A rotating black hole is formed only if q<1, indicating that cosmic censorship holds. Stark and Piran [290, 244] use the 3+1 formalism and the radial gauge of Bardeen-Piran [25] to study black hole formation and gravitational wave emission in axisymmetry. In this gauge, two metric functions used in determining \({g_{\theta \theta }}\) and \({g_{\phi \phi }}\) can be chosen such that at large radii they tend directly to h+ and h× (the even and odd transverse traceless amplitudes of the gravitational waves, with 1/r fall-off at large radii; note that h+ defined in [290] has the opposite sign as that commonly used, e.g. in [306]). In this way, the gravitational waveform is obtained at large radii directly in the numerical evolution. It is also easy to compute the gravitational energy emitted, as a simple integral over a sphere far from the source: \(\Delta E \sim {r^2}\int {dt(h_{ + ,r}^2} + h_{ \times ,r}^2)\). Using polar slicing, black hole formation appears as a region of exponentially small lapse, when \(q < {\mathcal O}(1)\). The initial data consists of a nonrotating, pressure deficient TOV solution, to which angular momentum is added by hand. The obtained waveform is nearly independent of the details of the collapse: It consists of a broad initial peak (since the star adjusts its initial spherical shape to a flattened shape, more consistent with the prescribed angular momentum), the main emission (during the formation of the black hole), and an oscillatory tail, corresponding to oscillations of the formed black hole spacetime. The energy of the emitted gravitational waves during the axisymmetric core collapse is found not to exceed 7×10-4M⊙c2 (to which the broad initial peak has a negligible contribution). The emitted energy scales as q4, while the energy in the even mode exceeds that in the odd mode by at least an order of magnitude.
More recently, Shibata [272] carried out axisymmetric simulations of rotating stellar collapse in full general relativity, using a Cartesian grid, in which axisymmetry is imposed by suitable boundary conditions. The details of the formalism (numerical evolution scheme and gauge) are given in [271]. It is found that rapid rotation can prevent prompt black hole formation. When \(q = {\mathcal O}(1)\), a prompt collapse to a black hole is prevented even for a rest mass that is 70–80% larger than the maximum allowed mass of spherical stars, and this depends weakly on the rotational profile of the initial configuration. The final configuration is supported against collapse by the induced differential rotation. In these axisymmetric simulations, shock formation for q<0.5 does not result in a significant heating of the core; shocks are formed at a spheroidal shell around the high density core. In contrast, when the initial configuration is rapidly rotating \((q = {\mathcal O}(1))\), shocks are formed in a highly nonspherical manner near high density regions, and the resultant shock heating contributes in preventing prompt collapse to a black hole. A qualitative analysis in [272] suggests that a disk can form around a black hole during core collapse, provided the progenitor is nearly rigidly rotating and \(q = {\mathcal O}(1)\) for a stiff progenitor EOS. On the other hand, q≪1 still allows for a disk formation if the progenitor EOS is soft. At present, it is not clear how much the above conclusions depend on the restriction to axisymmetry or on other assumptions — 3-dimensional simulations of the core collapse of such initially axisymmetric configurations have still to be performed.
A new numerical code for axisymmetric gravitational collapse in the (2+1)+1 formalism is presented in [63].
4.3.2 Formation of rotating neutron stars
First attempts to study the formation of rotating neutron stars in axisymmetric collapse were initiated by Evans [96, 97]. Recently, Dimmelmeier, Font and Müller [90, 89] have successfully obtained detailed simulations of neutron star formation in rotating collapse. In the numerical scheme, HRSC methods are employed for the hydrodynamical evolution, while for the spacetime evolution the conformal flatness approximation [324] is used. Surprisingly, the gravitational waves obtained during the neutron star formation in rotating core collapse are weaker in general relativity than in Newtonian simulations. The reason for this result is that relativistic rotating cores bounce at larger central densities than in the Newtonian limit (for the same initial conditions). The gravitational waves are computed from the time derivatives of the quadrupole moment, which involves the volume integration of ρr4. As the density profile of the formed neutron star is more centrally condensed than in the Newtonian case, the corresponding gravitational waves turn out to be weaker. Details of the numerical methods and of the gravitational wave extraction used in the above studies can be found in [91, 92].
New, fully relativistic axisymmetric simulations with coupled hydrodynamical and spacetime evolution in the light-cone approach, have been obtained by Siebel et al. [282, 281]. One of the advantages of the light-cone approach is that gravitational waves can be extracted accurately at null infinity, without spurious contamination by boundary conditions. The code by Siebel et al. combines the light-cone approach for the spacetime evolution with HRSC methods for the hydrodynamical evolution. In [281] it is found that gravitational waves are extracted more accurately using the Bondi news function than by a quadrupole formula on the null cone.
A new 2D code for axisymmetric core collapse, also using HRSC methods, has recently been introduced in [273].
References
International Numerical Relativity Group, “Jean-Luc Movies: /AEI2001/NeutronStars”, (June, 2002), [Online HTML Document]: cited on 19 June 2002, http://jean-luc.ncsa.uiuc.edu/Movies/AEI2001/NeutronStars/. 14
Abramowicz, M.A., and Kluźniak, W., “A precise determination of angular momentum in the black hole candidate GRO J1655-40”, Astron. Astrophys., 374, L19–L20, (2001). For a related online version see: M.A. Abramowicz, et al., “A precise determination of angular momentum in the black hole candidate GRO J1655-40”, (May, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0105077. 2.10.1
Abramowicz, M.A., Kluźniak, W., and Lasota, J.-P., “The Centrifugal Force Reversal and X-ray Bursts”, Astron. Astrophys., 374, L16–L18, (2001). For a related online version see: M.A. Abramowicz, et al., “The Centrifugal Force Reversal and X-ray Bursts”, (May, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0105324. 2.10.2
Alcubierre, M., Brügmann, B., Dramlitsch, T., Font, J.A., Papadopoulos, P., Seidel, E., Stergioulas, N., and Takahashi, R., “Towards a stable numerical evolution of strongly gravitating systems in general relativity: The conformal treatments”, Phys. Rev. D, 62, 044034–1–044034–16, (2000). For a related online version see: M. Alcubierre, et al., “Towards a Stable Numerical Evolution of Strongly Gravitating Systems in General Relativity: The Conformal Treatments”, (March, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 5 June 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0003071. 4
Amsterdamski, P., Bulik, T., Gondek-Rosińska, D., and Kluźniak, W., “Low-mass Quark Stars as Maclaurin Spheroids”, Astron. Astrophys., 381, L21–L24, (2002). For a related online version see: P. Amsterdamski, et al., “Low-mass Quark Stars as Maclaurin Spheroids”, (December, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0012547. 2.10.1
Andersson, N., “A New Class of Unstable Modes of Rotating Relativistic Stars”, Astrophys. J., 502, 708–713, (1998). For a related online version see: N. Andersson, “A New Class of Unstable Modes of Rotating Relativistic Stars”, (June, 1997), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9706075. 3.5.1, 3.5.3
Andersson, N., “Gravitational waves from instabilities in relativistic stars”, Class. Quantum Grav., 20, R105–R144, (2003). For a related online version see: N. Andersson, “Gravitational waves from instabilities in relativistic stars”, (February, 2002), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 3 April 2003, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/astro-ph/0211151. 3.5.3
Andersson, N., and Comer, G.L., “Probing neutron star superfluidity with gravitational-wave data”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 87, 241101, (2001). For a related online version see: N. Andersson, et al., “Probing neutron star superfluidity with gravitational-wave data”, (October, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc0110112. 3.2
Andersson, N., and Comer, G.L., “Slowly Rotating General Relativistic Superfluid Neutron Stars”, Class. Quantum Grav., 18, 969–1002, (2001). For a related online version see: N. Andersson, et al., “Slowly Rotating General Relativistic Superfluid Neutron Stars”, (September, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0009089. 2.6.2
Andersson, N., Comer, G.L., and Langlois, D., “Oscillations of general relativistic superfluid neutron stars”, Phys. Rev. D, 66, 104002–1–104002–22, (2002). For a related online version see: N. Andersson, et al., “Oscillations of General Relativistic Superfluid Neutron Stars”, (March, 2002), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0203039. 3.2
Andersson, N., Jones, D.I., and Kokkotas, K.D., “Strange stars as persistent sources of gravitational wave”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 337, 1224–1232, (2002). For a related online version see: N. Andersson, et al., “Strange stars as persistent sources of gravitational waves”, (November, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 5 June 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0111582. 9, 3.5.3, 3.5.3
Andersson, N., Jones, D.I., Kokkotas, K.D., and Stergioulas, N., “R-Mode Runaway and Rapidly Rotating Neutron Stars”, Astrophys. J., 534, L75–L78, (2000). For a related online version see: N. Andersson, et al., “R-Mode Runaway and Rapidly Rotating Neutron Stars”, (February, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0002114. 2.9.3, 3.5.3
Andersson, N., and Kokkotas, K.D., “Gravitational Waves and Pulsating Stars: What Can We Learn from Future Observations?”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 77, 4134–4137, (1996). For a related online version see: N. Andersson, et al., “Gravitational Waves and Pulsating Stars: What Can We Learn from Future Observations?”, (October, 1996), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9610035. 3
Andersson, N., and Kokkotas, K.D., “The R-Mode Instability in Rotating Neutron Stars”, Int. J. Mod. Phys. D, 10, 381–441, (2001). For a related online version see: N. Andersson, et al., “The R-Mode Instability in Rotating Neutron Stars”, (October, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0010102. 3.5.3
Andersson, N., Kokkotas, K.D., and Schutz, B.F., “A new numerical approach to the oscillation modes of relativistic stars”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 274, 1039–1048, (1995). For a related online version see: N. Andersson, et al., “A new numerical approach to the oscillation modes of relativistic stars”, (March, 1995), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9503014. 3.4.1
Andersson, N., Kokkotas, K.D., and Schutz, B.F., “Gravitational Radiation Limit on the Spin of Young Neutron Stars”, Astrophys. J., 510, 846–853, (1999). For a related online version see: N. Andersson, et al., “Gravitational Radiation Limit on the Spin of Young Neutron Stars”, (May, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9805225. 3.5.3
Andersson, N., Kokkotas, K.D., and Stergioulas, N., “On the Relevance of the r-mode Instability for Accreting Neutron Stars and White Dwarfs”, Astrophys. J., 516, 307–314, (1999). For a related online version see: N. Andersson, et al., “On the Relevance of the r-mode Instability for Accreting Neutron Stars and White Dwarfs”, (June, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9806089. 3.5.3
Ansorg, M., Kleinwächter, A., and Meinel, R., “Highly Accurate Calculation of Rotating Neutron Stars: Detailed Description of the Numerical Methods”, (January, 2003), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 7 February 2003, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0301173. 2.7.6
Ansorg, M., Kleinwächter, A., and Meinel, R., “Highly accurate calculation of rotating neutron stars”, Astron. Astrophys., 381, L49–L52, (2002). For a related online version see: M. Ansorg, et al., “Highly accurate calculation of rotating neutron stars”, (November, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/011108. 2.7, 2.7.6, 2.7.7, 2.7.8
Arnett, W.D., and Bowers, R.L., “A Microscopic Interpretation of Neutron Star Structure”, Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser., 33, 415–436, (1977). 2.6.2, 2.9.3
Arras, P., Flanagan, E.E., Morsink, S.M., Schenk, A.K., Teukolsky, S.A., and Wasserman, I., “Saturation of the R-mode Instability”, (February, 2002), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0202345. 3.5.3, 3.5.3
Asada, H., and Shibata, M., “Formulation for Nonaxisymmetric Uniformly Rotating Equilibrium Configurations in the Second Post-Newtonian Approximation of General Relativity”, Prog. Theor. Phys., 96, 81–112, (1996). For a related online version see: H. Asada, et al., “Formulation for Nonaxisymmetric Uniformly Rotating Equilibrium Configurations in the Second Post-Newtonian Approximation of General Relativity”, (September, 1996), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9609024. 2.7.8
Bardeen, J.M., “A variational principle for rotating stars in general relativity”, Astrophys. J., 162, 71–95, (1970). 2.2
Bardeen, J.M., “Rapidly rotating stars, disks, and black holes”, in DeWitt, C., and DeWitt, B.S., eds., Black Holes, Les Houches 1972, 241–289, (Gordon & Breach, New York, 1973). 2.2, 2.2
Bardeen, J.M., and Piran, T., “General relativistic axisymmetric rotating systems: Coordinates and equations”, Phys. Rep., 96, 205-250, (1983). 4, 4.3.1
Bardeen, J.M., and Wagoner, R.V., “Relativistic Disks. I. Uniform Rotation”, Astrophys. J., 167, 359–423, (1971). 2.2
Battiston, L., Cazzola, P., and Lucaroni, L., “Stability of nonradial oscillations of cold nonrotating neutron stars”, Nuovo Cimento B, 3, 295–317, (1971). 3.4.2
Baumgarte, T.W., and Shapiro, S.L., “Radiation of Angular Momentum by Neutrinos from Merged Binary Neutron Stars”, Astrophys. J., 504, 431–441, (1998). For a related online version see: T.W. Baumgarte, et al., “Radiation of Angular Momentum by Neutrinos from Merged Binary Neutron Stars”, (January, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9801294. 3.5.5
Baumgarte, T.W., Shapiro, S.L., and Shibata, M., “Stuart L. Shapiro’s Movies”, (June, 2002), [Online HTML Document]: cited on 19 June 2002, http://www.physics.uiuc.edu/Research/cta/Shapiro/movies.html. With the assistance of the Illinois Undergraduate Research Team. 16, 17
Baumgarte, T.W., Shapiro, S.L., and Shibata, M., “On the maximum mass of differentially rotating neutron stars”, Astrophys. J., 528, L29–L32, (2000). For a related online version see: T.W. Baumgarte, et al., “On the maximum mass of differentially rotating neutron stars”, (October, 1999), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9910565. 2.9.3
Baumgarte, T.W., Shapiro, S.L., and Teukolsky, S.A., “Computing the Delayed Collapse of Hot Neutron Stars to Black Holes”, Astrophys. J., 458, 680–691, (1996). 2.9.7
Baumgarte, T.W., and S.L., Shapiro, “Numerical integration of Einstein’s field equations”, Phys. Rev. D, 59, 024007–1–024007–7, (1999). For a related online version see: T.W. Baumgarte, et al., “On the Numerical Integration of Einstein’s Field Equations”, (October, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 5 June 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9810065. 4
Bhattacharyya, S., Temperature Profiles and Spectra of Accretion Disks around Rapidly Rotating Neutron Stars, PhD Thesis, (Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, India, 2001). For a related online version see: S. Bhattacharyya, “Temperature Profiles and Spectra of Accretion Disks around Rapidly Rotating Neutron Stars”, (May, 2002), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0205133. 2.10.2
Bhattacharyya, S., “A study of accretion discs around rapidly rotating neutron stars in general relativity and its applications to four low mass X-ray binaries”, Astron. Astrophys., 383, 524–532, (2002). For a related online version see: S. Bhattacharyya, “A study of accretion discs around rapidly rotating neutron stars in general relativity and its applications to four Low Mass X-ray Binaries”, (December, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0112178. 2.10.2
Bildsten, L., “Gravitational Radiation and Rotation of Accreting Neutron Stars”, Astrophys. J., 501, L89–L93, (1998). For a related online version see: L. Bildsten, “Gravitational Radiation and Rotation of Accreting Neutron Stars”, (April, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9804325. 2.9.3, 3.5.3
Blanchet, L., “Post-Newtonian Theory and its Application”, in Shibata, M., ed., Proceedings of the 12th Workshop on General Relativity and Gravitation. in press, (2003). For a related online version see: L. Blanchet, “Post-Newtonian Theory and its Application”, (April, 2003), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 4 April 2003, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0304014. 3.4.3
Bocquet, M., Bonazzola, S., Gourgoulhon, E., and Novak, J., “Rotating neutron star models with a magnetic field”, Astron. Astrophys., 301, 757–775, (1995). For a related online version see: M. Bocquet, et al., “Rotating neutron star models with magnetic field”, (March, 1995), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9503044. 2.9.6
Bodmer, A.R., “Collapsed Nuclei”, Phys. Rev. D, 4, 1601–1606, (1971). 2.6.3, 2.9.8
Bonazzola, S. Frieben, J., and Gourgoulhon, E., “Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking of Rapidly Rotating Stars in General Relativity: Influence of the 3D-shift Vector”, Astron. Astrophys., 331, 280–290, (1998). For a related online version see: J. Bonazzola, S. Frieben, et al., “Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking of Rapidly Rotating Stars in General Relativity: Influence of the 3D-shift Vector”, (October, 1997), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9710121. 3.5.2, 3.5.6
Bonazzola, S., “The virial theorem in general relativity”, Astrophys. J., 182, 335–340, (1973). 2.7.7
Bonazzola, S., Frieben, J., and Gourgoulhon, E., “Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking of Rapidly Rotating Stars in General Relativity”, Astrophys. J., 460, 379–389, (1996). For a related online version see: S. Bonazzola, et al., “Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking of Rapidly Rotating Stars in General Relativity”, (September, 1995), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9509023. 3.5.4, 3.5.6
Bonazzola, S., Frieben, J., Gourgoulhon, E., and Marck, J.-A., “Spectral Methods in General Relativity — Towards the Simulation of 3D-Gravitational Collapse of Neutron Stars”, in Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Spectral and High Order Methods, Houston Journal of Mathematics, (1996). For a related online version see: S. Bonazzola, et al., “Spectral Methods in General Relativity — Towards the Simulation of 3D-Gravitational Collapse of Neutron Stars”, (April, 1996), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9604029. 2.7.8
Bonazzola, S., and Gourgoulhon, E., “A virial identity applied to relativistic stellar models”, Class. Quantum Grav., 11, 1775–1784, (1994). 2.7.4, 2.7.7
Bonazzola, S., and Gourgoulhon, E., “Gravitational Waves from Pulsars: Emission by the Magnetic Field Induced Distortion”, Astron. Astrophys., 312, 675–690, (1996). For a related online version see: S. Bonazzola, et al., “Gravitational Waves from Pulsars: Emission by the Magnetic Field Induced Distortion”, (February, 1996), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9602107. 3.5.5
Bonazzola, S., and Gourgoulhon, E., “Gravitational Waves from Neutron Stars”, in Marck, J.-A., and Lasota, J.-P., eds., Relativistic Gravitation and Gravitational Radiation: Proceedings of the Les Houches School of Physics, 26 September–6 October, 1995, Cambridge Contemporary Astrophysics, 151, (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1997). For a related online version see: S. Bonazzola, et al., “Gravitational Waves from Neutron Stars”, (May, 1996), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9605187. 3.5.5
Bonazzola, S., Gourgoulhon, E., and Marck, J.-A., “Numerical Approach for High Precision 3-D Relativistic Star Models”, Phys. Rev. D, 58, 104020, (1998). For a related online version see: S. Bonazzola, et al., “Numerical Approach for High Precision 3-D Relativistic Star Models”, (March, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9803086. 2.7, 2.7.5
Bonazzola, S., Gourgoulhon, E., Salgado, M., and Marck, J.-A., “Axisymmetric rotating relativistic bodies: A new numerical approach for’ exact’ solutions”, Astron. Astrophys., 278, 421–443, (1993). 2.7, 2.7.4, 2.7.7, 2.9.6, 4
Bonazzola, S., and Schneider, S., “An Exact Study of Rigidly and Rapidly Rotating Stars in General Relativity with Application to the Crab Pulsar”, Astrophys. J., 191, 195–290, (1974). 2.7
Boyer, R.H., and Lindquist, R.W., “A variational principle for a rotating relativistic fluid”, Phys. Lett., 20, 504–506, (1966). 2.5
Brecher, K., and Caporaso, G., “Obese’ neutron’ stars”, Nature, 259, 377, (1976). 2.6.3
Brown, G.E., and Bethe, H.A., “A Scenario for a Large Number of Low-Mass Black Holes in the Galaxy”, Astrophys. J., 423, 659–664, (1994). 2.6.2, 2.9.7
Burderi, L., and D’Amico, N., “Probing the Equation of State of Ultradense Matter with a Submillisecond Pulsar Search Experiment”, Astrophys. J., 490, 343–352, (1997). 2.9.3
Burderi, L., Possenti, A., D’Antona, F., Di Salvo, T., Burgay, M., Stella, L., Menna, M.T., Iaria, R., Campana, S., and d’Amico, N., “Where May Ultrafast Rotating Neutron Stars Be Hidden?”, Astrophys. J., 560, L71–L74, (2001). For a related online version see: L. Burderi, et al., “Where May Ultrafast Rotating Neutron Stars Be Hidden?”, (September, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0109088. 2.9.3
Butterworth, E.M., “On the structure and stability of rapidly rotating fluid bodies in general relativity. II — The structure of uniformly rotating pseudopolytropes”, Astrophys. J., 204, 561–572, (1976). 2.7.2
Butterworth, E.M., and Ipser, J.R., “On the structure and stability of rapidly rotating fluid bodies in general relativity. I — The numerical method for computing structure and its application to uniformly rotating homogeneous bodies”, Astrophys. J., 204, 200–223, (1976). 2.4, 2.4, 2.7, 2.7.2
Carroll, B.W., Zweibel, E.G., Hansen, C.J., McDermott, P.N., Savedoff, M.P., Thomas, J.H., and Van Horn, H.M., “Oscillation Spectra of Neutron Stars with Strong Magnetic Fields”, Astrophys. J., 305, 767–783, (1986). 3.1
Carter, B., “Killing Horizons and Orthogonally Transitive Groups in Space-Time”, J. Math. Phys., 10, 70–81, (1969). 2.2
Carter, B., “The Commutation Property of a Stationary, Axisymmetric System”, Commun. Math. Phys., 17, 233–238, (1970). 2.2
Chandrasekhar, S., An introduction to the study of stellar structure, (University of Chicago Press, Chicago, 1939). 2.7.7
Chandrasekhar, S., “Solutions of Two Problems in the Theory of Gravitational Radiation”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 24, 611–615, (1970). 3.5.1, 3.5.2
Chandrasekhar, S., and Ferrari, V., “On the non-radial oscillations of slowly rotating stars induced by the Lense-Thirring effect”, Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A, 433, 423–440, (1991). 3, 3.4.1, 3.4.2
Cheng, K.S., and Harko, T., “Approximate mass and radius formulas for static and rotating strange stars”, Phys. Rev. D, 62, 083001–1–083001–9, (2000). 2.9.8
Choptuik, M.W., Hirschmann, E.W., Liebling, S.L., and Pretorius, F., “An Axisymmetric Gravitational Collapse Code”, (January, 2003), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 7 February 2003, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0301006. 4.3.1
Clement, M.J., “Normal modes of oscillation for rotating stars. I — The effect of rigid rotation on four low-order pulsations”, Astrophys. J., 249, 746–760, (1981). 3
Colella, P., and Woodward, P.R., “The Piecewise Parabolic Method (PPM) for Gas-Dynamical Simulations”, J. Comput. Phys., 54, 174–201, (1984). 4.1.1
Colpi, M., and Miller, J.C., “Rotational properties of strange stars”, Astrophys. J., 388, 513–520, (1992). 2.9.8
Comer, G.L., Langlois, D., and Lin, L.M., “Quasinormal modes of general relativistic superfluid neutron stars”, Phys. Rev. D, 60, 104025–1–104025–20, (1999). For a related online version see: G.L. Comer, et al., “Quasi-Normal Modes of General Relativistic Superfluid Neutron Stars”, (August, 1999), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9908040. 3.2
Comins, N., and Schutz, B.F., “On the ergoregion instability”, Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 364, 211–226, (1978). 2.2
Cook, G.B., Shapiro, S.L., and Teukolsky, S.A., “Spin-up of a rapidly rotating star by angular momentum loss — Effects of general relativity”, Astrophys. J., 398, 203–223, (1992). 2.7.3, 2.9.1, 2.9.5, 3.3.1
Cook, G.B., Shapiro, S.L., and Teukolsky, S.A., “Rapidly rotating neutron stars in general relativity: Realistic equations of state”, Astrophys. J., 424, 823–845, (1994). 2.7.3, 2.9.1, 2.9.3, 2.9.5
Cook, G.B., Shapiro, S.L., and Teukolsky, S.A., “Rapidly rotating polytropes in general relativity”, Astrophys. J., 422, 227–242, (1994). 2.7.3, 2.9.1, 2.9.5
Cook, G.B., Shapiro, S.L., and Teukolsky, S.A., “Recycling pulsars to millisecond periods in general relativity”, Astrophys. J., 423, L117–L120, (1994). 2.10.1
Cook, G.B., Shapiro, S.L., and Teukolsky, S.A., “Testing a simplified version of Einstein’s equations for numerical relativity”, Phys. Rev. D, 53, 5533–5540, (1996). For a related online version see: G.B. Cook, et al., “Testing a simplified version of Einstein’s equations for numerical relativity”, (December, 1995), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9512009. 4.1.2
Cottam, J., Paerels, F., and Mendez, M., “Gravitationally redshifted absorption lines in the X-ray burst spectra of a neutron star”, Nature, 420, 51–54, (2002). For a related online version see: J. Cottam, et al., “Gravitationally redshifted absorption lines in the X-ray burst spectra of a neutron star”, (November, 2002), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 7 February 2003, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0211126. 2.6.2
Crawford, F., Kaspi, V.M., and Bell, J.F., “A Search for Sub-millisecond Pulsations in Unidentified FIRST and NVSS Radio Sources”, in Kramer, M., Wex, N., and Wielebinski, N., eds., Pulsar Astronomy — 2000 and beyond, volume 202 of ASP Conference Series, 31, (Astronomical Society of the Pacific, San Francisco, 2000). 2.9.3
Cumming, A., Morsink, S.M., Bildsten, L., Friedman, J.L., and Holz, D., “Hydrostatic Expansion and Spin Changes during Type I X-Ray Bursts”, Astrophys. J., 564, 343–352, (2002). For a related online version see: A. Cumming, et al., “Hydrostatic Expansion and Spin Changes During Type I X-ray Bursts”, (August, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0108009. 2.10.2
Cutler, C., “Post-Newtonian effects on the modes of rotating stars”, Astrophys. J., 374, 248–254, (1991). 3.4.3
Cutler, C., and Lindblom, L., “The effect of viscosity on neutron star oscillations”, Astrophys. J., 314, 234–241, (1987). 2.1
Cutler, C., and Lindblom, L., “Post-Newtonian frequencies for the pulsations of rapidly rotating neutron stars”, Astrophys. J., 385, 630–641, (1992). 3.4.3, 3.5.2
Cutler, C., and Thorne, K.S., “An Overview of Gravitational-Wave Sources”, in Proceedings of GR16, (2003). For a related online version see: C. Cutler, et al., “An Overview of Gravitational-Wave Sources”, (April, 2002), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 5 June 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0204090. 3.5.5
D’Amico, N., “The Bologna submillisecond pulsar survey”, in Kramer, M., Wex, N., and Wielebinski, N., eds., Pulsar Astronomy — 2000 and beyond, volume 202 of ASP Conference Series, 27, (Astronomical Society of the Pacific, San Francisco, 2000). 2.9.3
Datta, B., “Recent developments in neutron star physics”, Fundam. Cosmic Phys., 12, 151–239, (1988). 2.7.1
Datta, B., Hasan, S.S., Sahu, P.K., and Prasanna, A.R., “Radial modes of rotating neutron stars in the Chandrasekhar-Friedman formalism”, Int. J. Mod. Phys. D, 7, 49–59, (1998). 3.3.2
Datta, B., Thampan, A.V., and Bombaci, I., “Equilibrium sequences of rotating neutron stars for new microscopic equations of state”, Astron. Astrophys., 334, 943–952, (1998). For a related online version see: B. Datta, et al., “Equilibrium sequences of rotating neutron stars for new microscopic equations of state”, (January, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9801312. 2.6.2
Detweiler, S.L., and Ipser, J.R., “A Variational Principle and a Stability Criterion for the Non-radial Modes of Pulsation of Stellar Models in General Relativity”, Astrophys. J., 185, 685–708, (1973). 3.4.1
Detweiler, S.L., and Lindblom, L., “On the nonradial pulsations of general relativistic stellar models”, Astrophys. J., 292, 12–15, (1985). 3.4.1
Dey, M., Bombaci, I., Dey, J., Ray, S., and Samanta, B.C., “Strange stars with realistic quark vector interaction and phenomenological density-dependent scalar potential”, Phys. Lett. B, 438, 123–128, (1998). For a related online version see: M. Dey, et al., “Strange stars with realistic quark vector interaction and phenomenological density-dependent scalar potential”, (October, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9810065. 2.6.3, 2.9.8
Di Girolamo, T., and Vietri, M., “Post-Newtonian Treatment of Bar Mode Instability in Rigidly Rotating Equilibrium Configurations for Polytropic Stars”, Astrophys. J., 581, 519–549, (2002). For a related online version see: T. Di Girolamo, et al., “Post-Newtonian treatment of bar mode instability in rigidly rotating equilibrium configurations for neutron stars”, (May, 2002), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 5 June 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0205398. 3.5.6
Dimmelmeier, H., General Relativistic Collapse of Rotating Stellar Cores in Axisymmetry, PhD Thesis, (Technische Universität München, München, Germany, 2001). 4.3.2
Dimmelmeier, H., Font, J.A., and E., Müller, “Gravitational waves from relativistic rotational core collapse”, Astrophys. J., 560, L163–L166, (2001). For a related online version see: H. Dimmelmeier, et al., “Gravitational waves from relativistic rotational core collapse”, (March, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0103088. 4.3.2
Dimmelmeier, H., Font, J.A., and E., Müller, “Relativistic simulations of rotational core collapse I. Methods, initial models, and code tests”, Astron. Astrophys., 388, 917–935, (2002). For a related online version see: H. Dimmelmeier, et al., “Relativistic simulations of rotational core collapse. I. Methods, initial models, and code tests”, (April, 2002), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0204288. 4.3.2
Dimmelmeier, H., Font, J.A., and E., Müller, “Relativistic simulations of rotational core collapse II. Collapse dynamics and gravitational radiation”, Astron. Astrophys., 393, 523–542, (2002). For a related online version see: H. Dimmelmeier, et al., “Relativistic simulations of rotational core collapse. II. Collapse dynamics and gravitational radiation”, (April, 2002), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0204289. 4.3.2
Duez, M.D., Marronetti, P., Shapiro, S.L., and Baumgarte, T.W., “Hydrodynamic simulations in 3+1 general relativity”, Phys. Rev. D, 67, 024004–1–024004–22, (2003). For a related online version see: M.D. Duez, et al., “Hydrodynamic Simulations in 3+1 General Relativity”, (September, 2003), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 7 February 2003, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0209102. 4.1.1
Edwards, R.T., van Strate, W., and Bailes, M., “A Search for Submillisecond Pulsars”, Astrophys. J., 560, 365–370, (2001). For a related online version see: R.T. Edwards, et al., “A Search for Submillisecond Pulsars”, (June, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0106353. 2.9.3
Eriguchi, Y., Hachisu, I., and Nomoto, K., “Structure of Rapidly Rotating Neutron Stars”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 266, 179–185, (1994). 2.7.3, 2.7.8
Evans, C.R., A method for numerical relativity: Simulation of axisymmetric gravitational collapse and gravitational radiation generation, PhD Thesis, (Texas University, Austin, USA, 1984). 4.3.2
Evans, C.R., “An Approach for Calculating Axisymmetric Gravitational Collapse”, in Centrella, J.M., ed., Dynamical Spacetimes and Numerical Relativity, 3–39, (Cambrigde University Press, Cambridge, England, 1986). 4.3.2
Farhi, E., and Jaffe, R.L., “Strange matter”, Phys. Rev. D, 30, 2379–2390, (1984). 2.6.3, 2.9.8
Finn, L.S., “Relativistic stellar pulsations in the Cowling approximation”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 232, 259–275, (1988). 3.4.4
Flanagan, E.E., “Astrophysical Sources of Gravitational Radiation and Prospects for their Detection”, in Dadhich, N., and Narlikar, J., eds., Gravitation and Relativity: At the turn of the Millennium. Proceedings of the GR-15 Conference, Pune, December 16–21, 1997, 177–197, (IUCAA, Pune, 1998). For a related online version see: E.E. Flanagan, “Sources of Gravitational Radiation and Prospects for their Detection”, (April, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9804024. 3.5.5
Flowers, E., and Itoh, N., “Transport properties of dense matter”, Astrophys. J., 206, 218–242, (1976). 2.1, 3.5.4
Flowers, E., and Itoh, N., “Transport properties of dense matter. II”, Astrophys. J., 230, 847–858, (1979). 2.1
Font, J.A., “Numerical Hydrodynamics in General Relativity”, (2000), [Article in Online Journal Living Reviews in Relativity]: cited on 5 June 2002, http://www.livingreviews.org/Articles/Volume3/2000-2font. 4.1.1
Font, J.A., Dimmelmeier, H., Gupta, A., and Stergioulas, N., “Axisymmetric Modes of Rotating Relativistic Stars in the Cowling Approximation”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 325, 1463–1470, (2001). For a related online version see: J.A. Font, et al., “Axisymmetric Modes of Rotating Relativistic Stars in the Cowling Approximation”, (April, 2002), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0204289. 3.3.2, 5, 4.2, 18
Font, J.A., Goodale, T., Iyer, S., Miller, M., Rezzolla, L., Seidel, E., Stergioulas, N., Suen, W.-M., and Tobias, M., “Three-dimensional general relativistic hydrodynamics. II. Long-term dynamics of single relativistic stars”, Phys. Rev. D, 65, 084024–1–084024–18, (2002). For a related online version see: J.A. Font, et al., “Three-dimensional general relativistic hydrodynamics II: long-term dynamics of single relativistic stars”, (October, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0110047. 3.2, 3.3.2, 4, 4.1.1, 4.2, 18
Font, J.A., Stergioulas, N., and Kokkotas, K.D., “Nonlinear hydrodynamical evolution of rotating relativistic stars: Numerical methods and code tests”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 313, 678–688, (2000). For a related online version see: J.A. Font, et al., “Nonlinear hydrodynamical evolution of rotating relativistic stars: Numerical methods and code tests”, (August, 1999), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9908010. 3.3.2, 4, 4.1.1
Friedman, J.L., unpublished, quoted in Glendenning, N.K., ”PSR1987A: the case for strong quarks”, J. Phys. G., 15, L255–L260, (1989). 2.9.8
Friedman, J.L., “Ergosphere Instability”, Commun. Math. Phys., 63, 243–255, (1978). 2.2
Friedman, J.L., “How fast can pulsars spin?”, in Ashby, N., Bartlett, D.F., and Wyssed, W., eds., General Relativity and Gravitation, 1989: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on General Relativity and Gravitation, University of Colorado at Boulder, July 2–8, 1989, 21–39, (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1990). 2.9.2
Friedman, J.L., “Upper Limit on the Rotation of Relativistic Stars”, in Fruchter, A.S., Tavani, M., and Backer, D.C., eds., Millisecond Pulsars. A Decade of Surprise, volume 72 of ASP Conference Series, 177–185, (Astronomical Society of the Pacific, San Francisco, California, 1995). 2.9.3
Friedman, J.L., and Ipser, J.R., “On the maximum mass of a uniformly rotating neutron star”, Astrophys. J., 314, 594–597, (1987). 2.9.4
Friedman, J.L., and Ipser, J.R., “Rapidly rotating relativistic stars”, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London, Ser. A, 340, 391–422, (1992). 2.1, 2.9.1
Friedman, J.L., Ipser, J.R., and Parker, L., “Rapidly rotating neutron star models”, Astrophys. J., 304, 115–139, (1986). Erratum: Astrophys. J., 351, 705 (1990). 2.7.2
Friedman, J.L., Ipser, J.R., and Parker, L., “Implications of a halfmillisecond pulsar”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 62, 3015–3019, (1989). 2.7.2, 2.9.2
Friedman, J.L., Ipser, J.R., and Sorkin, R.D., “Turning-point method for axisymmetric stability of rotating relativistic stars”, Astrophys. J., 325, 722–724, (1988). 3.3.1
Friedman, J.L., and Lockitch, K.H., “Implications of the r-mode instability of rotating relativistic stars”, in Gurzadyan, V.G., Jantzen, R.T., and Ruffini, R., eds., Proceedings of the 9th Marcel Grossmann Meeting, 163–181, (World Scientific, Singapore, 2002). 3.5.3
Friedman, J.L., and Morsink, S.M., “Axial Instability of Rotating Relativistic Stars”, Astrophys. J., 502, 714–720, (1998). For a related online version see: J.L. Friedman, et al., “Axial Instability of Rotating Relativistic Stars”, (June, 1997), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9706073. 3.5.1, 3.5.3
Friedman, J.L., and Schutz, B.F., “Secular instability of rotating Newtonian stars”, Astrophys. J., 222, 281–296, (1978). 3, 3.5.1, 3.5.2
Fryer, C.L., and Heger, A., “Core-Collapse Simulations of Rotating Stars”, Astrophys. J., 541, 1033–1050, (2000). For a related online version see: C.L. Fryer, et al., “Core-Collapse Simulations of Rotating Stars”, (July, 1999), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9907433. 2.9.3
Geroch, R., and Lindblom, L., “Causal Theories of Dissipative Relativistic Fluids”, Ann. Phys. (N. Y.), 207, 394–416, (1991). 2.9.4
Giazotto, A., Bonazzola, S., and Gourgoulhon, E., “On gravitational waves emitted by an ensemble of rotating neutron stars”, Phys. Rev. D, 55, 2014–2023, (1997). For a related online version see: A. Giazotto, et al., “On gravitational waves emitted by an ensemble of rotating neutron stars”, (November, 1996), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9611188. 3.5.5
Glendenning, N.K., “Fast pulsar in SN 1987A: Candidate for strange-quark matter”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 63, 2629–2632, (1989). 2.9.8
Glendenning, N.K., “PSR 1987A: the case for strange-quark stars”, J. Phys. G, 15, L255–260, (1989). 2.9.8
Glendenning, N.K., “Limiting rotational period of neutron stars”, Phys. Rev. D, 46, 4161–4168, (1992). 2.9.4
Glendenning, N.K., Compact Stars, Nuclear Physics, Particle Physics, and General Relativity, (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1997). 2.6.2, 2.6.3
Glendenning, N.K., and Weber, F., “Nuclear solid crust on rotating strange quarks stars”, Astrophys. J., 400, 647–658, (1992). 2.9.8
Gondek, D., Haensel, P., and Zdunik, J.L., “Radial pulsations and stability of protoneutron stars”, Astron. Astrophys., 325, 217–227, (1997). For a related online version see: D. Gondek, et al., “Radial pulsations and stability of protoneutron stars”, (May, 1997), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9705157. 2.9.7, 3.3.1
Gondek-Rosińska, D., Bulik, T., Zdunik, J.L., Gourgoulhon, E., Ray, S., Dey, J., and Dey, M., “Rotating compact strange stars”, Astron. Astrophys., 363, 1005–1012, (2000). For a related online version see: D. Gondek-Rosińska, et al., “Rotating compact strange stars”, (July, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0007004. 2.6.3, 2.9.8
Gondek-Rosińska, D., and E., Gourgoulhon, “Jacobi-like bar mode instability of relativistic rotating bodies”, Phys. Rev. D, 66, 044021–1–044021–11, (2002). For a related online version see: D. Gondek-Rosińska, et al., “Jacobi-like bar mode instability of relativistic rotating bodies”, (May, 2002), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 5 June 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0205102. 2.7.5, 2.7.8, 3.5.6
Gondek-Rosińska, D., Gourgoulhon, E., and Haensel, P., “Rapidly Rotating Strange Quark Stars as Sources of Gravitational Waves”, preprint, submitted to Astron. Astrophys., (2003). 3.5.6
Gondek-Rosińska, D., Stergioulas, N., Bulik, T., Kluźniak, W., and Gourgoulhon, E., “Lower Limits on the Maximum Orbital Frequency Around Rotating Strange Stars”, Astron. Astrophys., 380, 190–197, (2001). For a related online version see: D. Gondek-Rosińska, et al., “Lower Limits on the Maximum Orbital Frequency Around Rotating Strange Stars”, (October, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0110209. 2.9.8
Gourgoulhon, E., and Bonazzola, S., “A formulation of the virial theorem in general relativity”, Class. Quantum Grav., 11, 443–452, (1994). 2.7.4, 2.7.7
Gourgoulhon, E., Haensel, P., Livine, R., Paluch, E., Bonazzola, S., and Marck, J.-A., “Fast rotation of strange stars”, Astron. Astrophys., 349, 851–862, (1999). For a related online version see: E. Gourgoulhon, et al., “Fast rotation of strange stars”, (July, 1999), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9907225. 2.7.5, 2.9.8, 3, 2.9.8
Goussard, J.O., Haensel, P., and Zdunik, J.L., “Rapid Uniform Rotation of Protoneutron Stars”, Astron. Astrophys., 321, 822–834, (1997). For a related online version see: J.O. Goussard, et al., “Rapid Uniform Rotation of Protoneutron Stars”, (October, 1996), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9610265. 2.9.7, 3.3.1
Goussard, J.O., Haensel, P., and Zdunik, J.L., “Rapid Differential Rotation of Protoneutron Stars and Constraints on Radio Pulsars Periods”, Astron. Astrophys., 330, 1005–1016, (1998). For a related online version see: J.O. Goussard, et al., “Rapid Differential Rotation of Protoneutron Stars and Constraints on Radio Pulsars Periods”, (November, 1997), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9711347. 2, 2.9.7
Gressman, P., Lin, L-M., Suen, W-M., Stergioulas, N., and Friedman, J.L., “Nonlinear r-modes in neutron stars: Instability of an unstable mode”, Phys. Rev. D, 66, 041303–1–041303–5, (2002). For a related online version see: P. Gressman, et al., “Nonlinear r-modes in Neutron Stars: Instability of an unstable mode”, (March, 2003), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 3 April 2003, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0301014. 3.5.3
Gupta, A., Mishra, A., Mishra, H., and Prasanna, A.R., “Rotating Compact Objects with Magnetic Fields”, Class. Quantum Grav., 15, 3131–3145, (1998). For a related online version see: A. Gupta, et al., “Rotating Compact Objects with Magnetic Fields”, (May, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9805146. 2.9.6
Haensel, P., “Equation of State of Dense Matter and Maximum Mass of Neutron Stars”, in Hameury, J.-M., and Motch, C., eds., Final Stages of Stellar Evolution, EAS Publication Series, (EDP Sciences, Les Ulis, France, 2003). For a related online version see: P. Haensel, “Equation of state of dense matter and maximum mass of neutron stars”, (January, 2003), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 10 January 2003, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0301073.
Haensel, P., Lasota, J.-P., and Zdunik, J.L., “On the minimum period of uniformly rotating neutron stars”, Astron. Astrophys., 344, 151–153, (1999). For a related online version see: P. Haensel, et al., “On the minimum period of uniformly rotating neutron stars”, (January, 1999), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9901118. 2.9.4
Haensel, P., Levenfish, K.P., and Yakovlev, D.G., “Bulk viscosity in super-fluid neutron star cores. III. Effects of ∑- hyperons”, Astron. Astrophys., 381, 1080–1089, (2002). For a related online version see: P. Haensel, et al., “Bulk viscosity in superfluid neutron star cores. III. Effects of ∑- hyperons”, (October, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0110575. 3.5.3
Haensel, P., Salgado, M., and Bonazzola, S., “Equation of state of dense matter and maximum rotation frequency of neutron stars”, Astron. Astrophys., 296, 746–751, (1995). 2.9.2
Haensel, P., and Zdunik, J.L., “A submillisecond pulsar and the equation of state of dense matter”, Nature, 340, 617–619, (1989). 2.9.2
Hartle, J.B., “Slowly Rotating Relativistic Stars. I. Equations of Structure”, Astrophys. J., 150, 1005–1029, (1967). 2.2, 2.7.1
Hartle, J.B., “Bounds on the mass and moment of inertia of non-rotating neutron stars”, Phys. Rep., 46, 201–247, (1978). 2.9.4
Hartle, J.B., and Friedman, J.L., “Slowly rotating relativistic stars. VIII. Frequencies of the quasi-radial modes of an n=3/2 polytrope”, Astrophys. J., 196, 653–660, (1975). 3.3.2
Hartle, J.B., and Sabbadini, A.G., “The equation of state and bounds on the mass of nonrotating neutron stars”, Astrophys. J., 213, 831–835, (1977). 2.9.4
Hartle, J.B., and Sharp, D.H., “Variational Principle for the Equilibrium of a Relativistic, Rotating Star”, Astrophys. J., 147, 317–333, (1967). 2.5
Hartle, J.B., and Thorne, K.S., “Slowly Rotating Relativistic Stars. II. Models for Neutron Stars and Supermassive Stars”, Astrophys. J., 153, 807–834, (1968). 2.7.1
Hartle, J.B., and Thorne, K.S., “Slowly Rotating Relativistic Stars. III. Static Criterion for Stability”, Astrophys. J., 158, 719–726, (1969). 2.8
Hashimoto, M., Oyamatsu, K., and Eriguchi, Y., “Upper limit of the angular velocity of neutron stars”, Astrophys. J., 436, 257–261, (1994). 2.9.7
Heger, A., Langer, N., and Woosley, S.E., “Presupernova Evolution of Rotating Massive Stars. I. Numerical Method and Evolution of the Internal Stellar Structure”, Astrophys. J., 528, 368–396, (2000). For a related online version see: A. Heger, et al., “Presupernova Evolution of Rotating Massive Stars. I. Numerical Method and Evolution of the Internal Stellar Structure”, (May, 1999), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9905058. 2.9.3
Heger, A., Woosley, S.E., Langer, N., and Spruit, H.C., “Presupernova Evolution of Rotating Massive Stars and the Rotation Rate of Pulsars”, in Maeder, A., and Eenens, P., eds., Stellar Rotation, Proceedings of the IAU Symposium 215 on Stellar Rotation, (2003). For a related online version see: A. Heger, et al., “Presupernova Evolution of Rotating Massive Stars and the Rotation Rate of Pulsars”, (January, 2003), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 7 February 2003, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0301374. 2.9.3
Hegyi, D.J., “The upper mass limit for neutron stars including differential rotation”, Astrophys. J., 217, 244–247, (1977). 2.1
Heyl, J., “Low-Mass X-Ray Binaries May Be Important Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory Sources After All”, Astrophys. J., 574, L57–L60, (2002). For a related online version see: J. Heyl, “LMXBs may be important LIGO sources after all”, (June, 2002), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 14 June 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0206174. 3.5.3
Houser, J.L., Centrella, J.M., and Smith, S.C., “Gravitational radiation from nonaxisymmetric instability in a rotating star”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 72, 1314–1317, (1994). For a related online version see: J.L. Houser, et al., “Gravitational radiation from nonaxisymmetric instability in a rotating star”, (September, 1994), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9409057. 3.5.1
Imamura, J.N., Friedman, J.L., and Durisen, R.H., “Secular stability limits for rotating polytropic stars”, Astrophys. J., 294, 474–478, (1985). 3, 3.5.2
Ipser, J.R., Kislinger, M.B., and Morley, P.D., unpublished. 2.6.3
Ipser, J.R., and Lindblom, L., “The oscillations of rapidly rotating Newtonian stellar models”, Astrophys. J., 355, 226–240, (1990). 3, 3.5.2
Ipser, J.R., and Lindblom, L., “On the adiabatic pulsations of accretion disks and rotating stars”, Astrophys. J., 379, 285–289, (1991). 3, 3.5.1, 3.5.4
Ipser, J.R., and Lindblom, L., “The oscillations of rapidly rotating Newtonian stellar models. II — Dissipative effects”, Astrophys. J., 373, 213–221, (1991). 3, 3.5.1, 3.5.4
Ipser, J.R., and Lindblom, L., “On the pulsations of relativistic accretion disks and rotating stars — The Cowling approximation”, Astrophys. J., 389, 392–399, (1992). 3.5.1, 3.5.2
Ipser, J.R., and Managan, R.A., “An Eulerian variational principle and a criterion for the occurrence of nonaxisymmetric neutral modes along rotating axisymmetric sequences”, Astrophys. J., 292, 517–521, (1985). 3, 3.5.2
Ipser, J.R., and Price, R.H., “Nonradial pulsations of stellar models in general relativity”, Phys. Rev. D, 43, 1768–1773, (1991). 3.4.1
James, R.A., “The Structure and Stability of Rotating Gas Masses”, Astrophys. J., 140, 552–582, (1964). 3.5.2, 3.5.6
Jones, D.I., “Gravitational waves from rotating neutron stars”, Class. Quantum Grav., 19, 1255–1266, (2002). For a related online version see: D.I. Jones, “Gravitational waves from rotating neutron stars”, (November, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0111007. 2.9.1
Jones, P.B., “Comment on ‘Gravitational radiation instability in hot young neutron stars’”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 86, 1384–1384, (2001). 3.5.3
Kaaret, P., Ford, E.C., and Chen, K., “Strong-Field General Relativity and Quasi-periodic Oscillations in X-Ray Binaries”, Astrophys. J., 480, L27–L29, (1997). For a related online version see: P. Kaaret, et al., “Strong-Field General Relativity and Quasi-periodic Oscillations in X-Ray Binaries”, (January, 1997), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9701101. 2.9.3, 2.9.8
Klis, M. van der, “Millisecond Oscillations in X-Ray Binaries”, Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys., 38, 717–760, (2000). For a related online version see: M. van der Klis, “Millisecond Oscillations in X-Ray Binaries”, (January, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0001167. 2.10.1, 2.10.2
Kluźniak, W., and Abramowicz, M.A., “Parametric epicyclic resonance in black hole disks: QPOs in micro-quasars”, (March, 2002), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0203314. 2.10.1
Kluźniak, W., Bulik, T., and Gondek-Rosińska, D., “Quark stars in Low-Mass X-ray Binaries: for and against”, in Exploring the Gamma-Ray Universe, Proceedings of the 4th Integral Workshop, ESA SP-459, 301–304, (2001). For a related online version see: W. Kluźniak, et al., “Quark stars in Low-Mass X-ray Binaries: for and against”, (November, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0011517. 2.10.1
Kluźniak, W., Michelson, P., and Wagoner, R.V., “Determining the properties of accretion-gap neutron stars”, Astrophys. J., 358, 538–544, (1990). 2.10.1
Kluźniak, W., and Wilson, J.R., “Hard X-ray Spectra from Gap Accretion onto Neutron Stars”, Astrophys. J., 372, L87–L90, (1991). 2.10.2
Kojima, Y., “Equations governing the nonradial oscillations of a slowly rotating relativistic star”, Phys. Rev. D, 46, 4289–4303, (1992). 3.4.2
Kojima, Y., “Coupled Pulsations between Polar and Axial Modes in a Slowly Rotating Relativistic Star”, Prog. Theor. Phys., 90, 977–990, (1993). 3.4.2
Kojima, Y., “Normal modes of relativistic stars in slow rotation limit”, Astrophys. J., 414, 247–253, (1993). 3.4.2
Kojima, Y., “Quasi-toroidal oscillations in rotating relativistic stars”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 293, 49–52, (1998). For a related online version see: Y. Kojima, “Quasi-toroidal oscillations in rotating relativistic stars”, (June, 1997), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9709003. 3.5.3
Kokkotas, K., and Schmidt, B., “Quasi-normal Modes of Black Holes and Stars”, (1999), [Article in Online Journal Living Reviews in Relativity]: cited on 5 June 2002, http://www.livingreviews.org/Articles/Volume2/1999-2kokkotas. 3.1
Kokkotas, K.D., “Pulsating relativistic stars”, in Marck, J.-A., and Lasota, J.-P., eds., Relativistic Gravitation and Gravitational Radiation: Proceedings of the Les Houches School of Physics, 26 September–6 October, 1995, Cambridge Contemporary Astrophysics, 89–102, (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1997). For a related online version see: K.D. Kokkotas, “Pulsating Relativistic Stars”, (March, 1996), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 19 November 1997, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9603024. 3.1
Kokkotas, K.D., “Stellar Pulsations and Gravitational Waves”, in Krolak, A., ed., Mathematics of Gravitation, Gravitational Wave Detection, volume 41(II) of Banach Center Publications, 31–41, (Banach Center Publications, Warsaw, 1997). 3.1
Kokkotas, K.D., and Ruoff, J., “Instabilities of Relativistic Stars”, in 2001: A relativistic spacetime Odyssey, 25th Johns Hopkins Workshop, (2002). For a related online version see: K.D. Kokkotas, et al., “Instabilities of Relativistic Stars”, (December, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 7 February 2003, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0212105. Firenze 2001. 3.4.2, 3.5.3
Kokkotas, K.D., and Schutz, B.F., “W-modes: A new Family of Normal Modes for Pulsating Relativistic Stars”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 225, 119–128, (1992). 3.4.1
Kokkotas, K.D., and Stergioulas, N., “Analytic Desctription of the r-mode Instability in Uniform Density Stars”, Astron. Astrophys., 341, 110–116, (1999). For a related online version see: K.D. Kokkotas, et al., “Analytic Desctription of the r-mode Instability in Uniform Density Stars”, (May, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9805297. 3.5.3
Kokkotas, K.D., Ruoff J., and Andersson, N., “The w-mode instability of ultracompact relativistic stars”, (December, 2002), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 7 February 2003, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-qc/0212429. 3.5.3
Komatsu, H., Eriguchi, Y., and Hachisu, I., “Rapidly rotating general relativistic stars. I — Numerical method and its application to uniformly rotating polytropes”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 237, 355–379, (1989). 2.5, 2.7, 2.7.3
Komatsu, H., Eriguchi, Y., and Hachisu, I., “Rapidly rotating general relativistic stars. II — Differentially rotating polytropes”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 239, 153–171, (1989). 2.5, 2.7, 2.7.3
Koranda, S., Stergioulas, N., and Friedman, J.L., “Upper limit Set by Causality on the Rotation and Mass of Uniformly Rotating Relativistic Stars”, Astrophys. J., 488, 799–806, (1997). For a related online version see: S. Koranda, et al., “Upper limit Set by Causality on the Rotation and Mass of Uniformly Rotating Relativistic Stars”, (August, 1996), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9608179. 2.9.4, 2.9.4, 2.9.4
Kulkarni, S.R., “The First Decade of Millisecond Pulsars: An Overview”, in Fruchter, A.S., Tavani, M., and Backer, D.C., eds., Millisecond Pulsars. A Decade of Surprise, volume 72 of ASP Conference Series, 79–101, (Astronomical Society of the Pacific, San Francisco, California, 1995). 2.6.2, 2.9.3
Laarakkers, W.G., and Poisson, E., “Quadrupole moments of rotating neutron stars”, Astrophys. J., 512, 282–287, (1999). For a related online version see: W.G. Laarakkers, et al., “Quadrupole moments of rotating neutron stars”, (September, 1997), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9709033. 2.9.1
Lai, D., Rasio, F.A., and Shapiro, S.L., “Ellipsoidal figures of equilibrium — Compressible models”, Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser., 88, 205–252, (1993). 3.5.5
Lai, D., Rasio, F.A., and Shapiro, S.L., “Hydrodynamics of Rotating Stars and Close Binary Interactions: Compressible Ellipsoid Models”, Astrophys. J., 437, 742–769, (1994). For a related online version see: D. Lai, et al., “Hydrodynamics of Rotating Stars and Close Binary Interactions: Compressible Ellipsoid Models”, (April, 1994), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9404031. 3.5.5
Lai, D., and Shapiro, S.L., “Gravitational radiation from rapidly rotating nascent neutron stars”, Astrophys. J., 442, 259–272, (1995). For a related online version see: D. Lai, et al., “Gravitational radiation from rapidly rotating nascent neutron stars”, (August, 1994), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9408053. 3.5.4, 3.5.5
Lamb, F.K., Miller, M.C., and Psaltis, D., “The Origin of Kilohertz QPOs and Implications for Neutron Stars”, in Shibazaki, N., Kawai, N., Shibata, S., and Kifune, T., eds., Neutron Stars and Pulsars: Thirty Years after the Discovery, number 24 in Frontiers science series, 89, (Universal Academy Press, Tokyo, Japan, 1998). Proceedings of the International Conference on Neutron Stars and Pulsars held on November 17–20, 1997, at Tachikawa Hall, Rikkyo University, Tokyo, Japan. 2.10.1
Lasota, J.-P., Haensel, P., and Abramowicz, M.A., “Fast Rotation of Neutron Stars”, Astrophys. J., 456, 300–304, (1996). 2.9.2
Lattimer, J.M., Prackash, M., Pethick, C.J., and Haensel, P., “Direct URCA process in neutron stars”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 66, 2701–2704, (1991). 3.5.4
Lattimer, J.M., and Swesty, F.D., “A Generalized Equation of State for Hot, Dense Matter”, Nucl. Phys. A, 535, 331–376, (1991). 2.9.7
Lattimer, L.M., Prakash, M., Masak, D., and Yahil, A., “Rapidly rotating pulsars and the equation of state”, Astrophys. J., 355, 241–254, (1990). 2.7.2, 2.9.8, 2.9.8
Leins, M., Nollert, H.-P., and Soffel, M.H., “Nonradial Oscillations of Neutron Stars: A New Branch of Strongly Damped Normal Modes”, Phys. Rev. D, 48, 3467–3472, (1993). 3.4.1
Lewin, W.H.G., van Paradijs, J., and Taam, R.E., “X-ray bursts”, in Lewin, W.H.G., van Paradijs, J., and van den Heuvel, E.P.J., eds., X-ray binaries, volume 26 of Cambridge Astrophysics Series, 175–232, (Cambridge University. Press, Cambridge, 1995
Lindblom, L., “Critical angular velocities of rotating neutron stars”, Astrophys. J., 438, 265–268, (1995). 3.4.3, 3.5.2, 3.5.4
Lindblom, L., “The Relaxation Effect in Dissipative Relativistic Fluid Theories”, Ann. Phys. (N. Y.), 247, 1–18, (1996). For a related online version see: L. Lindblom, “The Relaxation Effect in Dissipative Relativistic Fluid Theories”, (August, 1995), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9508058. 2.6.3
Lindblom, L., “Neutron Star Pulsations and Instabilities”, in Ferrari, V., Miller, J.C., and Rezzolla, L., eds., Gravitational Waves: A Challenge to Theoretical Astrophysics, volume 3 of ICTP Lecture Notes Series, 257–275, (ICTP, Trieste, Italy, 2001). For a related online version see: L. Lindblom, “Neutron Star Pulsations and Instabilities”, (January, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0101136. 3.5.3
Lindblom, L., and Detweiler, S.L., “The quadrupole oscillations of neutron stars”, Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser., 53, 73–92, (1983). 3.4.1
Lindblom, L., and Mendell, G., “The Oscillations of Superfluid Neutron Stars”, Astrophys. J., 421, 689–704, (1994). 3.2
Lindblom, L., and Mendell, G., “Does gravitational radiation limit the angular velocities of superfluid neutron stars?”, Astrophys. J., 444, 804–809, (1995). 3.5.1, 3.5.4
Lindblom, L., and Mendell, G., “R-modes in Superfluid Neutron Stars”, Phys. Rev. D, 61, 104003–1–104003–15, (2000). For a related online version see: L. Lindblom, et al., “R-modes in Superfluid Neutron Stars”, (September, 1999), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 5 June 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9909084. 3.5.4
Lindblom, L., Mendell, G., and Ipser, J.R., “Relativistic stellar pulsations with near-zone boundary conditions”, Phys. Rev. D, 56, 2118–2126, (1997). For a related online version see: L. Lindblom, et al., “Relativistic stellar pulsations with near-zone boundary conditions”, (April, 1997), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9704046. 3.4.1
Lindblom, L., and Owen, B.J., “Effect of hyperon bulk viscosity on neutron-star r-modes”, Phys. Rev. D, 65, 063006–1–063006–15, (2002). For a related online version see: L. Lindblom, et al., “Effect of hyperon bulk viscosity on neutron-star r-modes”, (October, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0110558. 3.5.3, 3.5.3
Lindblom, L., Owen, B.J., and Morsink, S.M., “Gravitational Radiation Instability in Hot Young Neutron Stars”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 80, 4843–4846, (1998). For a related online version see: L. Lindblom, et al., “Gravitational Radiation Instability in Hot Young Neutron Stars”, (March, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9803053. 3.5.3
Lindblom, L., and Splinter, R.J., “The accuracy of the relativistic Cowling approximation”, Astrophys. J., 348, 198–202, (1990). 3.4.4
Lindblom, L., Tohline, J.E., and Vallisneri, M., “Non-linear evolution of the r-modes in neutron stars”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 86, 1152–1155, (2001). For a related online version see: L. Lindblom, et al., “Non-linear evolution of the r-modes in neutron stars”, (October, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/. 3.5.3, 3.5.3
Lindblom, L., Tohline, J.E., and Vallisneri, M., “Numerical evolutions of nonlinear r-modes in neutron stars”, Phys. Rev. D, 65, 084039, (2002). For a related online version see: L. Lindblom, et al., “Numerical evolutions of nonlinear r-modes in neutron stars”, (September, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0109352. 3.5.3
Liu, Y.T., and Lindblom, L., “Models of rapidly rotating neutron stars: Remnants of accretion induced collapse”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 324, 1063–1073, (2001). For a related online version see: Y.T. Liu, et al., “Models of rapidly rotating neutron stars: Remnants of accretion induced collapse”, (December, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0012198. 2.9.3
Livio, M., and Pringle, J.E., “The Rotation Rates of White Dwarfs and Pulsars”, Astrophys. J., 505, 339–343, (1998). 2.9.3
Lockitch, K.H., Andersson, N., and Friedman, J.L., “Rotational modes of relativistic stars: Analytic results”, Phys. Rev. D, 63, 024019–1–024019–26, (2001). For a related online version see: K.H. Lockitch, et al., “The rotational modes of relativistic stars: Analytic results”, (August, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0008019. 3.4.2
Lyford, N.D., Baumgarte, T.W., and Shapiro, S.L., “Effects of Differential Rotation on the Maximum Mass of Neutron Stars”, Astrophys. J., 583, 410–415, (2003). For a related online version see: N.D. Lyford, et al., “Effects of Differential Rotation on the Maximum Mass of Neutron Stars”, (October, 2002), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 7 February 2003, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0210012. 2.9.5
Lynden-Bell, D., and Ostriker, J.P., “On the stability of differentially rotating bodies”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 136, 293–310, (1967). 3
Maeda, K., Sasaki, M., Nakamura, T., and Miyama, S., “A New Formalism of the Einstein Equations for Relativistic Rotating Systems”, Prog. Theor. Phys., 63, 719–721, (1980). 4.3.1
Managan, R.A., “On the secular instability of axisymmetric rotating stars to gravitational radiation reaction”, Astrophys. J., 294, 463–473, (1985). 3, 3.5.2
Manko, V.S., Martin, J., Ruiz, E., Sibgatullin, N.R., and Zaripov, M.N., “Metric of a rotating, charged, magnetized, deformed mass”, Phys. Rev. D, 49, 5144–5149, (1994). 2.8
Manko, V.S., Mielke, E.W., and Sanabria-Gómez, J.D., “Exact solution for the exterior field of a rotating neutron star”, Phys. Rev. D, 61, 081501–1–081501–5, (2000). For a related online version see: V.S. Manko, et al., “Exact solution for the exterior field of a rotating neutron star”, (January, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0001081. 2.8
Manko, V.S., Sanabria-Gómez, J.D., and Manko, O.V., “Nine-parameter electrovac metric involving rational functions”, Phys. Rev. D, 62, 044048–1–044048–10, (2000). 2.8
Marković, D., “Bound near-equatorial orbits around neutron stars”, (September, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0009450. 2.10.1
Marković, D., “Eccentric orbits and QPOs in neutron star X-ray binaries”, (September, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0009169. 2.10.1
Marshall, F.E., Gotthelf, E.V., Zhang, W., Middleditch, J., and Wang, Q.D., “Discovery of an ultra-fast pulsar in the supernova remnant N157B”, Astrophys. J., 499, L179–L182, (1998). For a related online version see: F.E. Marshall, et al., “Discovery of an ultra-fast pulsar in the supernova remnant N157B”, (March, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9803214. 3.5.3, 3.5.5
McDermott, P.N., Van Horn, H.M., and Hansen, C.J., “Nonradial Oscillations of Neutron Stars”, Astrophys. J., 325, 725–748, (1988). 3.1
McDermott, P.N., Van Horn, H.M., and Scholl, J.F., “Nonradial g-mode oscillations of warm neutron stars”, Astrophys. J., 268, 837–848, (1983). 3.4.4
Mendell, G., “Magnetohydrodynamics in Superconducting-Superfluid Neutron Stars”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 296, 903–912, (1998). For a related online version see: G. Mendell, “Magnetohydrodynamics in Superconducting-Superfluid Neutron Stars”, (February, 1997), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9702032. 2.1
Migdal, Z., Zh. Eskp. Teor. Fiz., 61, 2209, (1971). 2.6.2
Miller, M.C., Lamb, F.K., and G.B., Cook, “Effects of Rapid Stellar Rotation on Equation-of-State Constraints Derived from Quasi-periodic Brightness Oscillations”, Astrophys. J., 509, 793–801, (1998). For a related online version see: M.C. Miller, et al., “Effects of Rapid Stellar Rotation on Equation-of-State Constraints Derived from Quasi-periodic Brightness Oscillations”, (May, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9805007. 2.10.1
Morsink, S., Stergioulas, N., and Blattning, S., “Quasi-normal Modes of Rotating Relativistic Stars — Neutral Modes for Realistic Equations of State”, Astrophys. J., 510, 854–861, (1999). For a related online version see: S. Morsink, et al., “Quasi-normal Modes of Rotating Relativistic Stars — Neutral Modes for Realistic Equations of State”, (June, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9806008. 7, 3.5.2
Morsink, S.M., and Stella, L.M., “Relativistic precession around rotating neutron stars: Effects due to frame-dragging and stellar oblateness”, Astrophys. J., 513, 827–844, (1999). For a related online version see: S.M. Morsink, et al., “Relativistic precession around rotating neutron stars: Effects due to frame-dragging and stellar oblateness”, (August, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9808227. 2.10.1
Nakamura, T., “General Relativistic Collapse of Axially Symmetric Stars”, Prog. Theor. Phys., 65, 1876–1890, (1981). 4.3.1
Nakamura, T., “General Relativistic Collapse of Accreting Neutron Stars with Rotation”, Prog. Theor. Phys., 70, 1144–1147, (1983). 4.3.1
Nakamura, T., Oohara, K., and Kojima, Y., “General Relativistic Collapse to Black Holes and Gravitational Waves from Black Holes”, Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl., 90, 1–12, (1987). 4
Neugebauer, G., and Herold, H., “Gravitational Fields of Rapidly Rotating Neutron Stars: Theoretical Foundation”, in Ehlers, J., and Schäfer, G., eds., Relativistic Gravity Research: Proceedings of the 81 WE-Heraeus-Seminar Held at the Physikzentrum Bad Honnef, Germany, 2–6 September 1991, volume 410 of Lecture Notes in Physics, 305–318, (Springer, Berlin, 1992). 2.7
Nozawa, T., Stergioulas, N., Gourgoulhon, E., and Eriguchi, Y., “Construction of Highly Accurate Models of Rotating Neutron Stars — Comparison of Three Different Numerical Schemes”, Astron. Astrophys. Suppl., 132, 431–454, (1998). For a related online version see: T. Nozawa, et al., “Construction of Highly Accurate Models of Rotating Neutron Stars — Comparison of Three Different Numerical Schemes”, (April, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9804048. 2.6.2, 2.7.7, 2.7.8, 2
Ouyed, R., “Rotating Skyrmion stars”, Astron. Astrophys., 382, 939–946, (2002). For a related online version see: R. Ouyed, “Rotating skyrmion stars”, (July, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0107154. 2.6.2
Owen, B.J., Lindblom, L., Cutler, C., Schutz, B.F., Vecchio, A., and Andersson, N., “Gravitational waves from hot young rapidly rotating neutron stars”, Phys. Rev. D, 58, 084020–1–084020–15, (1998). For a related online version see: B.J. Owen, et al., “Gravitational waves from hot young rapidly rotating neutron stars”, (April, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9804044. 3.5.3
Oyamatsu, K., “Nuclear shapes in the inner crust of a neutron star”, Nucl. Phys. A, 561, 431–452, (1993). 2.9.7
Page, D., “Geminga: A cooling superfluid neutron star”, Astrophys. J., 428, 250–260, (1994). 3.5.4
Pandharipande, V.R., Pethick, C.J., and Thorsson, V., “Kaon energies in dense matter”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 75, 4567–4570, (1995). 2.6.2
Papaloizou, J., and Pringle, J.E., “Non-radial oscillations of rotating stars and their relevance to the short-period oscillations of cataclysmic variables”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 182, 423–442, (1978). 3.5.3
Phinney, E.S., and Kulkarni, S.R., “Binary and Millisecond Pulsars”, Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys., 32, 591–639, (1994). 2.6.2, 2.9.6
Piran, T., and Stark, R.F., “Numerical Relativity, Rotating Gravitational Collapse and Gravitational Radiation”, in Centrella, J.M., ed., Dynamical Spacetimes and Numerical Relativity: Proceedings of a Workshop held at Drexel University, October 7–11, 1985, 40–73, (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1986). 4.3.1
Price, R., and Thorne, K.S., “Non-Radial Pulsation of General-Relativistic Stellar Models. II. Properties of the Gravitational Waves”, Astrophys. J., 155, 163–182, (1969). 3.4.1
Price, R.H., and Ipser, J.R., “Relation of gauge formalisms for pulsations of general-relativistic stellar models”, Phys. Rev. D, 44, 307–313, (1991). 3.4.1
Priou, D., “The Perturbations of a Fully General Relativistic and Rapidly Rotating Neutron Star — I. Equations of Motion for the Solid Crust”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 254, 435–452, (1992). 3.2
Prix, R., Novak, J., and Comer, G.L., “Stationary structure of relativistic superfluid neutron stars”, in Proceedings of the 26th Spanish Relativity Meeting (ERE 2002), (2003). For a related online version see: R. Prix, et al., “Stationary structure of relativistic superfluid neutron stars”, (November, 2002), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 7 February 2003, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0211105. 2.6.2
Psaltis, D., “Models of quasi-periodic variability in neutron stars and black holes”, Adv. Space Res., 28, 481–491, (2001). For a related online version see: D. Psaltis, “Models of quasi-periodic variability in neutron stars and black holes”, (December, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0012251. 2.10.1, 2.10.2
Psaltis, D., and Norman, C., “On the origin of quasi-periodic oscillations and broad-band noise in accreting neutron stars and black holes”, (2000, January), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0001391. 2.10.1
Regge, T., and Wheeler, J.A., “Stability of a Schwarzschild Singularity”, Phys. Rev., 108, 1063–1069, (1957). 3.4.1
Rezzolla, L., Ahmedov, B.J., and Miller, J.C., “General Relativistic Electromagnetic Fields of a Slowly Rotating Magnetized Neutron Star. I. Formulation of the equations”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 322, 723–740, (2001). For a related online version see: L. Rezzolla, et al., “General Relativistic Electromagnetic Fields of a Slowly Rotating Magnetized Neutron Star. I. Formulation of the equations”, (August, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0108057. 2.9.6
Rezzolla, L., Lamb, F.K., Marković, D., and Shapiro, S.L., “Properties of r modes in rotating magnetic neutron stars. I. Kinematic Secular Effects and Magnetic Evolution Equations”, Phys. Rev. D, 64, 104013–1–104013–12, (2001). For a related online version see: L. Rezzolla, et al., “Properties of r modes in rotating magnetic neutron stars. I. Kinematic Secular Effects and Magnetic Evolution Equations”, (July, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0107061. 11, 3.5.3
Rezzolla, L., Lamb, F.K., Marković, D., and Shapiro, S.L., “Properties of r modes in rotating magnetic neutron stars. II. Evolution of the r modes and stellar magnetic field”, Phys. Rev. D, 64, 104014–1–104014–13, (2001). For a related online version see: L. Rezzolla, et al., “Properties of r modes in rotating magnetic neutron stars. II. Evolution of the r modes and stellar magnetic field”, (July, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0107062. 3.5.3
Rezzolla, L., Lamb, F.K., and Shapiro, S.L., “R-Mode Oscillations in Rotating Magnetic Neutron Stars”, Astrophys. J., 531, L139–L142, (2000). For a related online version see: L. Rezzolla, et al., “R-Mode Oscillations in Rotating Magnetic Neutron Stars”, (November, 1999), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9911188. 3.5.3
Roberts, P.H., and Stewartson, K., “On the Stability of a Maclaurin Spheroid of Small Viscosity”, Astrophys. J., 137, 777–790, (1963). 3.5.6
Ruoff, J., Stavridis, A., and Kokkotas, K.D., “Evolution Equations for the Perturbations of Slowly Rotating Relativistic Stars”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 332, 676–688, (2002). For a related online version see: J. Ruoff, et al., “Evolution Equations for the Perturbations of Slowly Rotating Relativistic Stars”, (September, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0109065. 3.4.2
Ruoff, J., Stavridis, A., and Kokkotas, K.D., “Inertial modes of slowly rotating relativistic stars in the Cowling approximation”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 339, 1170–1182, (2003). For a related online version see: J. Ruoff, et al., “Inertial modes of slowly rotating relativistic stars in the Cowling approximation”, (March, 2002), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0203052. 3.4.2, 10, 3.5.3
Saijo, M., Shibata, M., Baumgarte, T.W., and Shapiro, S.L., “Dynamical Bar Instability in Rotating Stars: Effect of General Relativity”, Astrophys. J., 548, 919–931, (2001). For a related online version see: M. Saijo, et al., “Dynamical Bar Instability in Rotating Stars: Effect of General Relativity”, (October, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0010201. 4.1.3
Saio, H., “R-mode oscillations in uniformly rotating stars”, Astrophys. J., 256, 717–735, (1982). 3.5.3
Salgado, M., Bonazzola, S., Gourgoulhon, E., and Haensel, P., “High precision rotating netron star models 1: Analysis of neutron star properties”, Astron. Astrophys., 291, 155–170, (1994). 2.6.2, 2.7.1, 2.7.4, 2.7.7
Salgado, M., Bonazzola, S., Gourgoulhon, E., and Haensel, P., “High precision rotating neutron star models. II. Large sample of neutron star properties.”, Astron. Astrophys. Suppl., 108, 455–459, (1994). 2.7.4, 2.7.7
Sawyer, R.F., “Bulk viscosity of hot neutron-star matter and the maximum rotation rates of neutron stars”, Phys. Rev. D, 39, 3804–3806, (1989). 3.5.4
Sawyer, R.F., and Scalapino, D.J., “Pion Condensation in Superdense Nuclear Matter”, Phys. Rev. D, 7, 953–964, (1973). 2.6.2
Schöbel, K., and Ansorg, M., “Maximal Mass of Uniformly Rotating Homogeneous Stars in Einsteinian Gravity”, (January, 2003), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 7 February 2003, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0301618. 2.7.6
Schutz, B.F., “Gravitational wave astronomy”, Class. Quantum Grav., 16, A131–A156, (1999). For a related online version see: B.F. Schutz, “Gravitational wave astronomy”, (November, 1999), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9911034. 3.5.5
Shapiro, S.L., “Differential rotation in neutron stars: Magnetic braking and viscous damping”, Astrophys. J., 544, 397–408, (2000). For a related online version see: S.L. Shapiro, “Differential rotation in neutron stars: Magnetic braking and viscous damping”, (October, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0010493. 2.1
Shapiro, S.L., and Teukolsky, S.A., Black Holes, White Dwarfs and Neutron Stars, (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1983). 2.9.2
Shapiro, S.L., and Zane, S., “Bar Mode Instability in Relativistic Rotating Stars: A Post-Newtonian Treatment”, Astrophys. J., 460, 379–389, (1996). For a related online version see: S.L. Shapiro, et al., “Bar Mode Instability in Relativistic Rotating Stars: A Post-Newtonian Treatment”, (November, 1997), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9711050. 3.5.6
Shibata, M., “Fully general relativistic simulation of coalescing binary neutron stars: Preparatory tests”, Phys. Rev. D, 60, 104052–1–104052–25, (1999). For a related online version see: M. Shibata, “Fully general relativistic simulation of coalescing binary neutron stars: Preparatory tests”, (August, 1999), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9908027. 4.1.1
Shibata, M., “Fully General Relativistic Simulation of Merging Binary Clusters — Spatial Gauge Condition”, Prog. Theor. Phys., 101, 1199–1233, (1999). For a related online version see: M. Shibata, “Fully General Relativistic Simulation of Merging Binary Clusters — Spatial Gauge Condition”, (May, 1999), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9905058. 4.3.1
Shibata, M., “Axisymmetric Simulations of Rotating Stellar Collapse in Full General Relativity — Criteria for Prompt Collapse to Black Holes”, Prog. Theor. Phys., 104, 325–358, (2000). For a related online version see: M. Shibata, “Axisymmetric Simulations of Rotating Stellar Collapse in Full General Relativity — Criteria for Prompt Collapse to Black Holes”, (July, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/007049. 4.3.1
Shibata, M., “Axisymmetric general relativistic hydrodynamics: Longterm evolution of neutron stars and stellar collapse to neutron stars and black holes”, Phys. Rev. D, 67, 024033–1–024033–24, (2003). For a related online version see: M. Shibata, “Axisymmetric general relativistic hydrodynamics: Long-term evolution of neutron stars and stellar collapse to neutron stars and black holes”, (January, 2003), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 7 February 2003, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0301103. 4.1.1, 4.3.2
Shibata, M., Baumgarte, T.W., and Shapiro, S.L., “The bar-mode instability in differentially rotating neutron stars: Simulations in full general relativity”, Astrophys. J., 542, 453–463, (2000). For a related online version see: M. Shibata, et al., “The bar-mode instability in differentially rotating neutron stars: Simulations in full general relativity”, (May, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0005378. 3.3.1, 3.5.1, 4.1.3, 15
Shibata, M., Baumgarte, T.W., and Shapiro, S.L., “Stability and collapse of rapidly rotating, supramassive neutron stars: 3D simulations in general relativity”, Phys. Rev. D, 61, 044012–1–044012–11, (2000). For a related online version see: M. Shibata, et al., “Stability and collapse of rapidly rotating, supramassive neutron stars: 3D simulations in general relativity”, (November, 1999), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9911308. 4.1.2
Shibata, M., and Sasaki, M., “Innermost stable circular orbits around relativistic rotating stars”, Phys. Rev. D, 58, 104011–1–104011–10, (1998). For a related online version see: M. Shibata, et al., “Innermost stable circular orbits around relativistic rotating stars”, (July, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9807046. 2.8, 2.10.1
Shibata, M., and T., Nakamura, “Evolution of three-dimensional gravitational waves: Harmonic slicing case”, Phys. Rev. D, 52, 5428–5444, (1995). 4
Sibgatullin, N., “Nodal and periastron precession of inclined orbits in the field of a rapidly rotating neutron star”, Astron. Lett., 28, 83–88, (2002). For a related online version see: N. Sibgatullin, “Nodal and periastron precession of inclined orbits in the field of a rapidly rotating neutron star”, (January, 2002), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0201155. 2.10.1
Sibgatullin, N.R., and Sunyaev, R.A., “Disk accretion in the gravitational field of a rapidly rotating neutron star with a rotationally induced quadrupole mass distribution”, Astron. Lett., 24, 774–787, (1998). For a related online version see: N.R. Sibgatullin, et al., “The disk accretion in the gravitational field of a rapidly rotating neutron star with a rotationally induced quadrupole mass distribution”, (November, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9811028. 2.8, 2.10.2
Sibgatullin, N.R., and Sunyaev, R.A., “Energy Release During Disk Accretion onto a Rapidly Rotating Neutron Star”, Astron. Lett., 26, 699–724, (2000). For a related online version see: N.R. Sibgatullin, et al., “Energy Release During Disk Accretion onto a Rapidly Rotating Neutron Star”, (November, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0011253. 2.8, 2.10.2
Siebel, F., Font, J.A., Müller, E., and Papadopoulos, P., “Axisymmetric core collapse simulations using characteristic numerical relativity”, (January, 2003), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 7 February 2003, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0301127. 4.3.2
Siebel, F., Font, J.A., Müller, E., and Papadopoulos, P., “Simulating the dynamics of relativistic stars via a light-cone approach”, Phys. Rev. D, 65, 064038–1–064038–15, (2002). For a related online version see: F. Siebel, et al., “Simulating the dynamics of relativistic stars via a light-cone approach”, (November, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 10 June 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0111093. 4.3.2
Skinner, D., and Lindblom, L., “On the Viscosity-driven Secular Instability in Rotating Neutron Star”, Astrophys. J., 461, 920–926, (1996). 3.5.2, 3.5.6
Smarr, L., and York Jr., J.W., “Kinematical conditions in the construction of spacetime”, Phys. Rev. D, 17, 2529–2551, (1978). 4
Sonin, E.B., “Vortex oscillations and hydrodynamics of rotating superfluids”, Rev. Mod. Phys., 59, 87–155, (1987). 2.1
Sorkin, R.D., “A Stability Criterion for Many Parameter Equilibrium Families”, Astrophys. J., 257, 847–854, (1982). 3.3.1
Spruit, H.C., “Gamma-ray bursts from X-ray binaries”, Astron. Astrophys., 341, L1–L4, (1999). For a related online version see: H.C. Spruit, “Gamma-ray bursts from X-ray binaries”, (November, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9811007. 3.5.3
Spruit, H.C., and Phinney, E.S., “Birth kicks as the origin of pulsar rotation”, Nature, 393, 139–141, (1998). For a related online version see: H.C. Spruit, et al., “Why pulsars rotate and move: kicks at birth”, (March, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9803201. 2.9.3
Spyrou, N.K., and Stergioulas, N., “Spin-down of Relativistic Stars with Phase Transitions and PSR J0537-6910”, Astron. Astrophys., 395, 151–160, (2002). For a related online version see: N.K. Spyrou, et al., “Spindown of Relativistic Stars with Phase Transitions and PSR J0537-6910”, (April, 2002), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 7 February 2003, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0204380. 2.9.5
Stark, R.F., and Piran, T., “Gravitational-wave emission from rotating gravitational collapse”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 55, 891–894, (1985). Erratum: Phys. Rev. Lett. 55, 891 (1985). 4.3.1
Stella, L.M., Vietri, M., and Morsink, S.M., “Correlations in the QPO Frequencies of Low-Mass X-Ray Binaries and the Relativistic Precession Model”, Astrophys. J., 524, L63–L66, (1999). For a related online version see: L.M. Stella, et al., “Correlations in the QPO Frequencies of Low-Mass X-Ray Binaries and the Relativistic Precession Model”, (July, 1999), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9907346. 2.10.1
Stergioulas, N., “Rapidly Rotating Neutron Star”, (November, 1997), [Public Domain Code]: cited on 19 November 1997, http://www.gravity.phys.uwm.edu/rns. 2.7.3, 2.9.1
Stergioulas, N., The Structure and Stability of Rotating Relativistic Stars, PhD Thesis, (University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, Milwaukee, USA, 1996). 2.7.3, 3, 3.2, 3.5.1, 3.5.2, 3.5.2
Stergioulas, N., and Font, J.A., “Nonlinear r-modes in rapidly rotating relativistic stars”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 86, 1148–1151, (2001). For a related online version see: N. Stergioulas, et al., “Nonlinear r-modes in rapidly rotating relativistic stars”, (July, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0007086. 3.4.2, 3.5.3, 12, 3.5.3, 4, 4.1.1, 13, 4.2
Stergioulas, N., and Friedman, J.L., “Comparing Models of Rapidly Rotating Relativistic Stars Constructed by Two Numerical Methods”, Astrophys. J., 444, 306–311, (1995). For a related online version see: N. Stergioulas, et al., “Comparing Models of Rapidly Rotating Relativistic Stars Constructed by Two Numerical Methods”, (November, 1994), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9411032. 2.7.3, 2.7.8, 1, 2.9.1
Stergioulas, N., and Friedman, J.L., “Nonaxisymmetric Neutral Modes in Rotating Relativistic Stars”, Astrophys. J., 492, 301–322, (1998). For a related online version see: N. Stergioulas, et al., “Nonaxisymmetric Neutral Modes in Rotating Relativistic Stars”, (May, 1997), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9705056. 3.2, 3.5.1, 3.5.2, 3.5.2, 8, 3.5.5
Stergioulas, N., Kluźniak, W., and Bulik, T., “Keplerian frequencies and innermost stable circular orbits of rapidly rotating strange stars”, Astron. Astrophys., 352, L116–L120, (1999). For a related online version see: N. Stergioulas, et al., “Keplerian frequencies and innermost stable circular orbits of rapidly rotating strange stars”, (September, 1999), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9909152. 2.9.8, 2.9.8
Strobel, K., Schaab, C., and Weigel, M.K., “Properties of non-rotating and rapidly rotating protoneutron stars”, Astron. Astrophys., 350, 497–512, (1999). For a related online version see: K. Strobel, et al., “Properties of non-rotating and rapidly rotating protoneutron stars”, (August, 1999), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9908132. 2.9.7
Strohmayer, T.E., “Oscillations during thermonuclear x-ray bursts”, Adv. Space Res., 28, 511–522, (2001). For a related online version see: T.E. Strohmayer, “Oscillations during thermonuclear x-ray bursts”, (December, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0012516. 2.10.2
Sumiyoshi, K., Ibáñez, J.M., and Romero, J.V., “Thermal history and structure of rotating protoneutron stars with relativistic equation of state”, Astron. Astrophys. Suppl., 134, 39–52, (1999). 2.9.7
Swesty, F.D., “Thermodynamically Consistent Interpolation for Equation of State Tables”, J. Comput. Phys., 127, 118–127, (1996). 2.6.2
Tassoul, J.-L., Theory of Rotating Stars, (Princeton University Press, Princeton, USA, 1978). 2.4
Thampan, A.V., and Datta, B., “A general relativistic calculation of boundary layer and disk luminosity for accreting non-magnetic neutron stars in rapid rotation”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 297, 570–578, (1998). For a related online version see: A.V. Thampan, et al., “A general relativistic calculation of boundary layer and disk luminosity for accreting non-magnetic neutron stars in rapid rotation”, (December, 1997), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9712120. 2.10.2
Thorne, K.S., “Nonradial Pulsation of General-Relativistic Stellar Models. IV. The Weak-Field Limit”, Astrophys. J., 158, 997–1019, (1969). 3.4.1
Thorne, K.S., “Multipole expansions of gravitational radiation”, Rev. Mod. Phys., 52, 299–340, (1980). 2.9.1
Thorne, K.S., “The theory of gravitational radiation — an introductory review”, in Deruelle, N., and Piran, T., eds., Gravitational Radiation, Proceedings of the Advanced Study Institute, Les Houches, 1–57, (North Holland, Amsterdam, 1983). 4.3.1
Thorne, K.S., “Gravitational Waves”, in Kolb, E.W., and Peccei, R., eds., Proceedings of the Snowmass 94 Summer Study on Particle and Nuclear Astrophysics and Cosmology, 398–425, (World Scientific, Singapore, 1995). For a related online version see: K.S. Thorne, “Gravitational Waves”, (June, 1995), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9506086. 3.5.5
Thorne, K.S., “Tidal stabilization of rigidly rotating, fully relativistic neutron stars”, Phys. Rev. D, 58, 124031–1–124031–9, (1998). For a related online version see: K.S. Thorne, “Tidal Stabilization of Rigidly Rotating, Fully Relativistic Neutron Stars”, (June, 1997), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9706057. 3.3.2
Thorne, K.S., and Campolattaro, A., “Non-Radial Pulsation of General-Relativistic Stellar Models. I. Analytic Analysis for L ≥ 2”, Astrophys. J., 149, 591–611, (1967). 3.4.1
Timmes, F.X., Woosley, S.E., and Weaver, T.A., “The Neutron Star and Black Hole Initial Mass Function”, Astrophys. J., 457, 834–843, (1996). For a related online version see: F.X. Timmes, et al., “The Neutron Star and Black Hole Initial Mass Function”, (October, 1995), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9510136. 2.9.3
Tooper, R.F., “General Relativistic Polytropic Fluid Spheres”, Astrophys. J., 140, 434–459, (1964). 2.6.1
Tooper, R.F., “Adiabatic Fluid Spheres in General Relativity”, Astrophys. J., 142, 1541–1562, (1965). 2.6.1
Ushomirsky, G., Cutler, C., and Bildsten, L., “Deformations of accreting neutron star crusts and gravitational wave emission”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 319, 902–932, (2000). For a related online version see: G. Ushomirsky, et al., “Deformations of accreting neutron star crusts and gravitational wave emission”, (January, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0001136. 2.9.3
van Kerkwijk, M.H., van Paradijs, J., and Zuiderwijk, E.J., “On the masses of neutron stars”, Astron. Astrophys., 303, 497–501, (1995). For a related online version see: M.H. van Kerkwijk, et al., “On the masses of neutron stars”, (May, 1995), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9505071. 2.9.3
van Leer, B., “Towards the Ultimate Conservative Difference Scheme. IV. A New Approach to Numerical Convection”, J. Comput. Phys., 23, 276–299, (1977). 4.1.1
Villain, L., and Bonazzola, S., “Inertial modes in slowly rotating stars: An evolutionary description”, Phys. Rev. D, 66, 123001–1–123001–25, (2002). For a related online version see: L. Villain, et al., “Inertial modes in slowly rotating stars: an evolutionary description”, (March, 2002), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 5 June 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0203106. 3.5.3
Weber, F., and Glendenning, N.K., “Exact versus approximate solution to Einstein’s equations for rotating neutron stars”, Phys. Lett. B, 265, 1–5, (1991). 2.7.1, 2.9.2
Weber, F., and Glendenning, N.K., “Application of the improved Hartle method for the construction of general relativistic rotating neutron star models”, Astrophys. J., 390, 541–549, (1992). 2.7.1, 2.9.2
Weber, F., Glendenning, N.K., and Weigel, M.K., “Structure and stability of rotating relativistic neutron stars”, Astrophys. J., 373, 579–591, (1991). 2.7.1
Weber, F., Schaab, C., Weigel, M.K., and Glendenning, N.K., “From Quark Matter to Strange MACHOS”, in Giovannelli, F., and Mannocchi, G., eds., Frontier Objects in Astrophysics and Particle Physics, Proceedings of the Vulcano Workshop 1996, volume 57 of Italian Physical Society Conference Proceedings Series, 87–106, (Italian Physical Society, Bologna, Italy, 1998). For a related online version see: F. Weber, et al., “From Quark Matter to Strange MACHOS”, (September, 1996), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9609067. 2.6.3
Weinberg, S., Gravitation and Cosmology: Principles and Applications of the General Theory of Relativity, (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1972). 2.2
White, N.E., and Zhang, W., “Millisecond X-Ray Pulsars in Low-mass X-Ray Binaries”, Astrophys. J., 490, L87–L90, (1997). 2.9.3
Wilson, J.R., “Models of Differentially Rotating Stars”, Astrophys. J., 176, 195–204, (1972). 2.7
Wilson, J.R., and Mathews, G.J., “Instabilities in close neutron star binaries”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 75, 4161–4164, (1995). 4.3.2
Witten, E., “Cosmic separation of phases”, Phys. Rev. D, 30, 272–285, (1984). 2.6.3, 2.9.8
Yoshida, S., and Eriguchi, Y., “Gravitational radiation driven secular instability of rotating polytropes”, Astrophys. J., 438, 830–840, (1995). 3.5.1, 3.5.2, 3.5.4
Yoshida, S., and Eriguchi, Y., “Ergoregion instability revisited — a new and general method for numerical analysis of stability”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 282, 580–586, (1996). 3.5.1
Yoshida, S., and Eriguchi, Y., “Neutral Points of Oscillation Modes along Equilibrium Sequences of Rapidly Rotating Polytropes in General Relativity: Application of the Cowling Approximation”, Astrophys. J., 490, 779–784, (1997). For a related online version see: S. Yoshida, et al., “Neutral Points of Oscillation Modes along Equilibrium Sequences of Rapidly Rotating Polytropes in General Relativity: Application of the Cowling Approximation”, (April, 1997), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9704111. 3.4.4, 3.5.2
Yoshida, S., and Eriguchi, Y., “A Numerical Study of Normal Modes of Rotating Neutron Star Models by the Cowling Approximation”, Astrophys. J., 515, 414–422, (1999). For a related online version see: S. Yoshida, et al., “A Numerical Study of Normal Modes of Rotating Neutron Star Models by the Cowling Approximation”, (July, 1998), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9807254. 3.4.4, 6
Yoshida, S., and Eriguchi, Y., “Quasi-radial modes of rotating stars in general relativity”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 322, 389–396, (2001). For a related online version see: S. Yoshida, et al., “Quasi-radial modes of rotating stars in general relativity”, (August, 1999), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9908359. 4, 3.3.2, 3.3.2, 4.2
Yoshida, S., and Kojima, Y., “Accuracy of the Relativistic Cowling Approximation in Slowly Rotating Stars”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 289, 117–122, (1997). For a related online version see: S. Yoshida, et al., “Accuracy of the Relativistic Cowling Approximation in Slowly Rotating Stars”, (May, 1997), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9705081. 3.4.4
Yoshida, S., and Lee, U., “Relativistic r-modes in Slowly Rotating Neutron Stars: Numerical Analysis in the Cowling Approximation”, Astrophys. J., 567, 1112–1120, (2002). For a related online version see: S. Yoshida, et al., “Relativistic r-modes in Slowly Rotating Neutron Stars: Numerical Analysis in the Cowling Approximation”, (October, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0110038. 3.5.3
Yoshida, S., Rezzolla, L., Karino, S., and Eriguchi, Y., “Frequencies of f-modes in differentially rotating relativistic stars and secular stability limits”, Astrophys. J., 568, L41–L44, (2002). For a related online version see: S. Yoshida, et al., “Frequencies of f-modes in differentially rotating relativistic stars and secular stability limits”, (December, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0112032. 8, 3.5.2
Yuan, Y.F., and Zhang, J.L., “Cooling of a rotating strange star with a crust”, Astron. Astrophys., 344(1), 371–375, (1999). 2.9.8
Zahn, J.-P., in Zahn, J.-P., and Zinn-Justin, J., eds., Astrophysical fluid dynamics, Proceedings of the Les Houches Summer School, Course XLVII, 29 June–31 July, 1987, (Elsevier, Oxford, 1993). 2.5
Zanotti, O., and Rezzolla, L., “General relativistic electromagnetic fields of a slowly rotating magnetized neutron star — II. Solution of the induction equations”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 331, 376–388, (2001). For a related online version see: O. Zanotti, et al., “General relativistic electromagnetic fields of a slowly rotating magnetized neutron star — II. Solution of the induction equations”, (December, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0112032. 2.9.6
Zdunik, J.L., “Damping of GRR Instability by Direct URCA Reactions”, Astron. Astrophys., 308, 828–832, (1996). For a related online version see: J.L. Zdunik, “Damping of GRR Instability by Direct URCA Reactions”, (November, 1995), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 2 May 1998, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9511136. 3.5.4
Zdunik, J.L., Bulik, T., Kluźniak, W., Haensel, P., and Gondek-Rosińska, D., “On the mass of moderately rotating strange stars in the MIT bag model and LMXBs”, Astron. Astrophys., 359, 143–147, (2000). For a related online version see: J.L. Zdunik, et al., “On the mass of moderately rotating strange stars in the MIT bag model and LMXBs”, (April, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0004278. 2.9.8
Zdunik, J.L., and Gourgoulhon, E., “Small strange stars and marginally stable orbit in Newtonian theory”, Phys. Rev. D, 63, 087501–1–087501–4, (2001). For a related online version see: J.L. Zdunik, et al., “Small Strange Stars and Marginally Stable Orbit in Newtonian Theory”, (November, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0011028. 2.10.1
Zdunik, J.L., Haensel, P., and E., Gourgoulhon, “The crust of rotating strange quark stars”, Astron. Astrophys., 372, 535–543, (2001). For a related online version see: J.L. Zdunik, et al., “The crust of rotating strange quark stars”, (April, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0104116. 2.9.8, 2.9.8
Zdunik, J.L., Haensel, P., and E., Gourgoulhon, “Recycling strange stars to millisecond periods”, Astron. Astrophys., 381, 933–940, (2002). For a related online version see: J.L. Zdunik, et al., “Recycling strange stars to millisecond periods”, (November, 2001), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0111162. 2.9.8, 2.10.1
Zdunik, J.L., Haensel, P., Gondek-Rosińska, D., and E., Gourgoulhon, “Innermost stable circular orbits around strange stars and kHz QPOs in low-mass X-ray binaries”, Astron. Astrophys., 356, 612–618, (2001). For a related online version see: J.L. Zdunik, et al., “Innermost stable circular orbits around strange stars and kHz QPOs in low-mass X-ray binaries”, (February, 2000), [Online Los Alamos Archive Preprint]: cited on 23 April 2002, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0002394. 2.9.8
Acknowledgements
I am grateful to Emanuele Berti, John L. Friedman, Wlodek Kluźniak, Kostas D. Kokkotas, and Luciano Rezzolla for a careful reading of the manuscript and for many valuable comments. Many thanks to Dorota Gondek-Rosińska and Eric Gourgoulhon for comments and for supplying numerical results obtained with the Lorene/rotstar code, that were used in the comparison in Table 2. I am also grateful to Marcus Ansorg for discussions and to all authors of the included figures for granting permission for reproduction. This work was supported, in part, by the EU Programme “Improving the Human Research Potential and the Socio-Economic Knowledge Base” (Research Training Network Contract HPRN-CT-2000-00137), KBN-5P03D01721, and the Greek GSRT Grant EPANM. 43/2013555.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
41114_2016_9037_MOESM1_ESM.mpg
mpg-Movie (*** MB)Still from a movie showing the simulation of a stationary, rapidly rotating neutron star model in full general relativity, for 3 rotational periods (shown are iso-density contours, in dimensionless units). The stationary shape is well preserved at a resolution of 1293. Simulation by Font, Goodale, Iyer, Miller, Rezzolla, Seidel, Stergioulas, Suen, and Tobias. Visualization by W. Benger and L. Rezzolla at the Albert Einstein Institute, Golm [1].
Electronic supplementary material
41114_2016_9037_MOESM2_ESM.mpg
mpg-Movie (*** MB)Still from a movie showing the development of the dynamical barmode instability in a rapidly rotating relativistic star. Spiral arms form within a few rotational periods. The different colors correspond to different values of the density, while the computation was done in full general relativity. Movie produced at the University of Illinois by T.W. Baumgarte, S.L. Shapiro, and M. Shibata, with the assistance of the Illinois Undergraduate Research Team [29]; used with permission.
Electronic supplementary material
41114_2016_9037_MOESM3_ESM.mpg
mpg-Movie (*** MB)Still from a movie showing the gravitational wave emission during the development of the dynamical bar-mode instability in a rapidly rotating relativistic star. The gravitational wave amplitude in a plane containing the rotation axis is shown. At large distances, the waves assume a quadrupole-like angular dependence. Movie produced at the University of Illinois by T.W. Baumgarte, S.L. Shapiro, and M. Shibata, with the assistance of the Illinois Undergraduate Research Team [29]; used with permission.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits use, duplication, adaptation, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Stergioulas, N. Rotating Stars in Relativity. Living Rev. Relativ. 6, 3 (2003). https://doi.org/10.12942/lrr-2003-3
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12942/lrr-2003-3
Keywords
Article history
- Rotating Stars in Relativity
- Published:
- 16 June 2003
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12942/lrr-2003-3
Original
Rotating Stars in Relativity- Published:
- 18 June 1998
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12942/lrr-1998-8