Summary
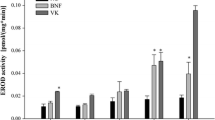
Endothelial cells are a structural barrier and an active regulator of many bodily processes. Cytochrome P4501A (CYPIA) activity is induced in the endothelium of teleosts and mammals exposed to lipophilic xenobiotics, such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and can have significant consequences for endothelial functions. We exposed cultures of characterized endothelial cells from the heart, kidney, and rete mirabile of the eel, Anguilla rostrata, to aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) agonists. In heart endothelial cells, the maximum response (based on O-deethylation of 7-ethoxyresorufin to resorufin [EROD] activity) to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), 113 pmol/mg/min, was at 1 nM TCDD and the peak response to β-napthoflavone (βNF), 135 pmol/mg/min, was at 3 μM βNF. The maximum response to TCDD in the kidney endothelial cells is 12 pmol/mg/min at 0.3 nM TCDD. The rete mirabile capillary endothelial cells responded minimally or not at all to exposure to TCDD and βNF. Both the heart and kidney endothelial cells (but not the rete mirabile capillary cells) have a low level of EROD activity (12.7 and 5.2 pmol/mg/min, respectively) in untreated or dimethylsulfoxide-treated cells. The robust response of the heart endothelial cells to induction and the lack of response in the rete mirabile capillary endothelial cells indicate that these cells are a good resource to use to investigate the physiological consequences of AhR agonist exposure and CYP1A induction in different areas of the vasculature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annas, A.; Brittebo, E. B. Localization of cytochrome P4501A1 and covalent binding of a mutagenic heterocyclic amine in blood vessel endothelia of rodents. Toxicology 129:145–156; 1998.
Annas, A.; Brittebo, E. B.; Hellman, B. Evaluation of benzo(a)pyrene-induced DNA damage in human endothelial cells using alkaline single cell gel electrophoresis. Mutat. Res. 471:145–155; 2000a.
Annas, A.; Cranberg, A. L.; Brittebo, E. B. Differential response of cultured human umbilical vein and artery endothelial cells to AhR receptor agonist treatment: CYP-dependent activation of food and environmental mutagens. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 169:94–101; 2000b.
Bayou-Denizot, C.; Daval, J.-L.; Netter, P.; Minn, A. Xenobiotic-mediated production of superoxide by primary cultures of rat cerebral endothelial cells, astrocytes and neurons. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1497:115–126; 2000.
Borlak, J.; Walles, M.; Levsen, K.; Thum, T. Verapamil: metabolism in cultures of primary human coronary arterial endothelial cells. Drug Metab. Dispos. 31(7):888–891; 2003.
Cantrell, S. M.; Joy-Schlezinger, J.; Stegeman, J. J.; Tillitt, D. E.; Hannink, M. Correlation of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced apoptotic cell death in the embryonic vasculature with embryotoxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 148(1):24–34; 1998.
Carlsson, C.; Part, P. 7-ethoxyresorufin o-deethylase induction in rainbow trout gill epithelium cultured on permeable supports: asymmetrical distribution of substrate metabolites. Aquat. Toxicol. 54:29–38; 2001.
Celander, M.; Weisbrod, R.; Stegeman, J. J. Glucocorticoid potentiation of cytochrome P4501A1 induction by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in procine and human endothelial cells in culture. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 232(3):749–753; 1997.
Chat, M.; Bayol-Denizoi, C.; Suleman, G.; Roux, F.; Minn, A. Drug metabolizing enzyme activities and superoxide formation in primary and immortalized rat brain endothelial cells. Life Sci. 62(2):151–163; 1998.
Chi, J.-T.; Chang, H. Y.; Haraldsen, G., et al. Endothelial cell diversity revealed by global expression profiling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100(19):10623–10628; 2003.
Dugas, T. R.; Morel, D. W.; Harrison, E. H. Novel cell culture medium for use in oxidation experiments provides insights into mechanisms of endothelial cell-mediated oxidation of LDL. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 36A:571–577; 2000.
Farin, F. M.; Pohlman, T. H.; Omiencinski, C. J. Expression of cytochrome P450s and microsomal epoxide hydrolase in primary cultures of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 124:1–9; 1994.
Ganassin, R. C.; Schirmer, K.; Bols, N. C. Cell and tissue culture. In: Ostrander, G. K., ed. The laboratory fish. San Diego, CA: Academic Press; 2000:631–651.
Gannon, M.; Gilday, D.; Rifkind, A. B. TCDD induces CYP1A4 and CYP1A5 in chick liver and kidney and onlyCYP1A4, an enzyme lacking arachidonic acid epoxygenase activity, in myocardium and vascular endothelium. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 164:24–37; 2000.
Garrick, R. A. Isolation and culture of capillary endothelial cells from the eel, Anguilla rostrata. Microvasc. Res. 59:377–385; 2000.
Granberg, L.; Ostergren, A.; Brandt, I.; Brittebo, E. B. CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 in blood-brain interfaces: CYP1A1-dependent bioactivation of 7,12-dimethylbenz(a) anthracene in endothelial cells. Drug Metab. Dispos. 31(3):259–265; 2003.
Guiney, P. D.; Smolowitz, R. M.; Peterson, R. E.; Stegeman, J. J. Correlation of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin induction of cytochrome P4501A in vascular endothelium with toxicity in early life stages of lake trout. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 143(2):256–273; 1997.
Hahn, M. E. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: a comparative perspective. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 121:23–53; 1998.
Hahn, M. E.; Lamb, T. M.; Schultz, M. E.; Smolowitz, R. M.; Stegeman, J. J. Cytochrome P4501A induction and inhibition by 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl in an ah receptor-containing fish hepatoma cell line (PLHC-1). Aquat. Toxicol. 26:185–208; 1993.
Hahn, M. E.; Woodin, B. R.; Stegeman, J. J.; Tillitt, D. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor function in early vertebrates: inducibility of cytochrome P450 1a in agnathan and elasmobranch fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 120:67–75; 1998.
Hahn, M. E.; Woodward, B. L.; Stegeman, J. J.; Kennedy, S. W. Rapid assessment of induced cytochrome P4501A (CYP1a) protein and catalytic activity in fish hepatoma cells grown in multi-well plates. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 15(4):582–591; 1996.
Hennig, B.; Hammonck, B. D.; Slim, R.; Toberak, M.; Saraswathi, V.; Robertson, L. W. Pcb-induced oxidative stress in endothelial cell: modulation by nutrients. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 205:95–102; 2002a.
Hennig, B.; Meerarani, P.; Slim, R.; Toberak, M.; Daugherty, A.; Silverstone, A.; Robertson, L. W. Proinflammatory properties of coplanar PCBs: in vitro and in vivo evidence. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 181:174–183; 2002b.
Hestermann, E. V.; Stegeman, J. J.; Hahn, M. E. Serum alters the uptake and relative potencies of halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons in cell culture bioassays. Toxicol. Sci. 53(2):316–325; 2000.
Hestermann, E. V.; Stegeman, J. J.; Hahn, M. E. Serum withdrawal leads to reduced aryl hydrocarbon receptor expression and loss of cytochrome P4501A inducibility in PLHC-1 cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 63(8):1405–1414; 2002.
Kennedy, S. W.; Jones, S. P.; Bastien, L. J. Efficient analysis of cytochrome P4501A catalytic activity, porphyrins, and total proteins in chicken embryo hepatocyte cultures with a fluorescence plate reader. Anal. Biochem. 226(2):362–370; 1995.
Kennedy, S. W.; Lorenzen, A.; James, C. A.; Collins, B. T. Ethoxyresorufin o-deethylase and porphyrin analysis in chicken embryo hepatocyte cultures with a fluorescence multi-well plate reader. Anal. Biochem. 211:102–112; 1993.
Lorenzen, A.; Kennedy, S. W. A fluorescence-based protein assay for use with a microplate reader. Anal. Biochem. 214:346–348; 1993.
Lou, Y.; Oberpriller, J.; Carlson, E. C. Effect of hypoxia on the proliferation of retinal microvessel endothelial cells in culture. Anat. Rec. 248:366–373; 1997.
Mimura, J.; Fujii-Kuriyama, Y. Functional role of AhR in the expression of toxic effects by TCDD. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1619:263–268; 2003.
Morrison, H. G.; Olesiak, F.; Cornell, N.; Sogin, M.; Stegeman, J. J. Identification of cytochrome P4501A (CYP1A) genes from two teleost fish. toadfish (Opsanus tua) and scup (Stenotomus chrysops) and phylogenetic analysis of CYP1a genes. Biochem. J. 308:97–104; 1995.
Nebert, D. W.; Roe, A. L.; Dieter, M. Z.; Solis, W. A.; Ysng, Y.; Dalton, T. P. Role of the aromatic hydrocarbon receptor and [ah] gene battery in the oxidative stress response, cell cycle, and apoptosis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 59(1):65–85; 2000.
Ogino, Y.; Itakura, T.; Kato, H.; Aoki, J.; Sato, M. Functional analysis of promoter region from eel cytochrome P4501A1 gene in transgenic medaka. Mar. Biotech. 1:364–370; 1999a.
Ogino, Y.; Itakura, T.; Mitsuo, R.; Sato, M. Induction of two forms of eel cytochrome P4501A genes by 3-methylcholanthrene. Mar. Biotechnol. 1:342–345; 1999b.
Park, S. S.; Miller, H.; Klotz, A. V.; Kloepper-Sams, P. J.; Stegeman, J. J.; Gelboin, H. V. Monoclonal antibodies to liver microsomal cytochrome P-450E of the marine fish Stenotomus chrysops (scup): cross reactivity with 3-methylcholanthrene induced rat cytochrome P-450. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 249(2):339–350; 1986.
Ramadass, P.; Meerarani, P.; Toberak, M.; Robertson, L. W.; Hennig, B. Dietary flavonoids modulate pcb-induced oxidative stress, CYP1a1 induction, and AhR-DNA binding activity in vascular endothelial cells. Toxicol. Sci. 76:212–219; 2003.
Sadar, M. D.; Andersson, T. B. Regulation of cytychrome P450 ina primary culture of rainbow trout hepatocytes. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 37A(3):180–184; 2001.
Savouret, J.-F.; Antenos, M.; Quesne, M.; Xu, J.; Milgrom, E.; Casper, R. F. 7-ketocholesterol is an endogenous modulator for the arylhydrocarbon receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 276(5):3054–3059; 2001.
Schlezinger, J. J.; Keller, J.; Verbrugge, L. A.; Stegeman, J. J. 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl oxidation in fish, bird and reptile species: relationship to cytochrome P4501A inactivation and reactive oxygen production. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 125(3):273–286; 2000.
Schlezinger, J. J.; Parker, C.; Zeldin, D. C.; Stegeman, J. J. Arachidonic acid metabolism in the marine fish stenotomus chrysops (scup) and the effects of cytochrome P4501A inducers. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 353(2):265–275; 1998.
Schlezinger, J. J.; Stegeman, J. J. Dose and inducer-dependent induction of cytochrome P450 1A in endothelia of the eel, including in the swimbladder rete mirabile, a model microvascular structure. Drug Metab. Dispos. 28(6):701–708; 2000a.
Schlezinger, J. J.; Stegeman, J. J. Induction of cytochrome P450 1A in the american eel by model halogenated and non-halogenated aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists. Aquat. Toxicol. 50(4):375–386; 2000b.
Shimada, T.; Fujii-Kuriyama, Y. Metabolic activation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to carcinogens by cytochromes P4501A1 and 1B1. Cancer Sci. 95(1):1–6; 2004.
Smolowitz, R. M.; Hahn, M. E.; Stegeman, J. J. Immunohistochemical localization of cytochrome P4501A1 induced by 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl and by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzofuran in liver and extrahepatic tissues of the teleost Stenotomus chrysops (scup). Drug Metab. Dispos. 19(1):113–123; 1991.
Stegeman, J. J.; Hahn, M. E.; Weisbrod, R.; Woodin, B. R.; Joy, J. S.; Najibi, S.; Cohen, R. A. Induction of cytochrome P4501A1 by aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists in porcine aorta endothelial cells in culture and cytochrome P4501A1 activity in intact cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 47(2):296–306; 1995.
Stegeman, J. J.; Miller, M. R.; Hinton, D. E. Cytochrome P450E induction and localization in liver and endothelial of vertebrate (teloost) heart. Mol. Pharmacol. 36:723–729; 1989.
Stegeman, J. J.; Miller, M.; Singh, H.; Hinton, D. Cytochrome P450E induction and localization in liver and endothelial tissue of extrahepatic organs of scup. Fed. Proc. 46:379; 1987.
Stegeman, J. J.; Smolowitz, R. M.; Hahn, M. E. Immunohistochemical localization of environmentally induced cytochrome P4501A1 in multiple organs of the marine teleost Stenotomus chrysops (scup). Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 110:486–504; 1991.
Steinhorn, R.; Morin, F. C., III; Gugino, S. F.; Giese, E. C.; Russell, J. A. Developmental differences in endothelium-dependent responses in isolated ovine pulmonary arteries and veins. Am. J. Physiol. 264:H2162-H2167; 1993.
Teraoka, H.; Dong, W.; Tsujimoto, Y., et al. Induction of cytochrome P4501A is required for circulation failure and edema by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in zebrafish. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 304:223–228; 2003.
Thum, T.; Haverich, A.; Borlak, J. Cellular dedifferentiation of endothelium is linked to activation and silencing of certain nuclear transcription factors: implication for endothelial dysfunction and vascular biology. FASEB J. 14:740–751; 2000.
Tom, D. J.; Lee, L. E.; Lew, J.; Bols, N. C. Induction of 7-ethoxyresorufin-o-deethylase activity by planar chlorinated hydrocarbons and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in cell lines from the rainbow trout pituitary. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 128(2):185–198; 2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garrick, R.A., Woodin, B.R. & Stegeman, J.J. Cytochrome P4501A induced differentially in endothelial cells cultured from different organs of Anguilia rostrata . In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 41, 57–63 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1290/0409063.1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1290/0409063.1