Abstract
Background
The oncologic safety of sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) alone for clinically node-positive (cN1–2) patients who convert to pathologic node-negativity (ypN0) after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) is not well established.
Methods
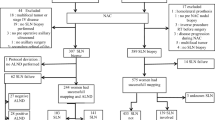
This study retrospectively identified 244 consecutive patients with a diagnosis of cT1–3cN0–2 breast cancer who underwent NAC followed by SLNB at the authors’ institution between 2013 and 2018. The patients were categorized as clinically node-negative (cN0) or cN1–2 before the onset of NAC, and the Kaplan–Meier method was used to compare locoregional and distant recurrence rates after SLNB alone for ypN0 patients.
Results
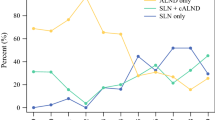
Among 244 patients who underwent NAC followed by surgery with SLNB for axillary staging, 112 (45.9%) were cN0 at presentation, whereas 132 (54.5%) had biopsy-proven cN1–2 disease and converted to cN0 after treatment. Of the patients presenting with cN0 disease, 102 (91.1%) were ypN0 on SLNB pathology compared with 60 cN1/2 patients (45.5%; p < 0.001). Regional nodal irradiation was administered to 5% of the cN0/ypN0 patients compared with 70.7% of the cN1–2/ypN0 patients (p < 0.001). Overall, 211 patients were treated with SLNB alone and had a median follow-up period of 36 months (interquartile range [IQR], 24–53 months). For 101 cN0/ypN0 patients who underwent SLNB alone, the 5-year local and regional recurrence rates were respectively 5.7% (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.4–13.8) and 1% (95% CI 0.1–7.0). For 58 cN1–2/ypN0 patients who underwent SLNB alone, the 5-year local and regional recurrence rates were respectively 4.1% (95% CI 1.0–15.5) and 0%, with no axillary recurrences noted.
Conclusion
For ypN0 patients, SLNB alone after NAC is associated with low and acceptable short-term axillary recurrence rates. Additional follow-up data from prospective clinical trials are needed to confirm long-term oncologic safety and define optimal local therapy recommendations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boileau JF, Poirier B, Basik M, et al. Sentinel node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in biopsy-proven node-positive breast cancer: the SN FNAC study. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:258–64.
Boughey JC, Suman VJ, Mittendorf EA, et al. Sentinel lymph node surgery after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with node-positive breast cancer: the ACOSOG Z1071 (Alliance) clinical trial. JAMA. 2013;310:1455–61.
Classe JM, Loaec C, Gimbergues P, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy without axillary lymphadenectomy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy is accurate and safe for selected patients: the GANEA 2 study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019;173:343–52.
Kuehn T, Bauerfeind I, Fehm T, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy in patients with breast cancer before and after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (SENTINA): a prospective, multicentre cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:609–18.
Caudle AS, Bedrosian I, Milton DR, et al. Use of sentinel lymph node dissection after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with node-positive breast cancer at diagnosis: practice patterns of American Society of Breast Surgeons members. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017;24:2925–34.
Mamtani A, Barrio AV, King TA, et al. How often does neoadjuvant chemotherapy avoid axillary dissection in patients with histologically confirmed nodal metastases? Results of a prospective study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016;23:3467–74.
Wong SM, Weiss A, Mittendorf EA, et al. Surgical management of the axilla in clinically node-positive patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy: a national cancer database analysis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019;26:3517–25.
Galimberti V, Ribeiro Fontana SK, Maisonneuve P, et al. Sentinel node biopsy after neoadjuvant treatment in breast cancer: five-year follow-up of patients with clinically node-negative or node-positive disease before treatment. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2016;42:361–8.
Mamounas EP, White JR, Bandos H, et al. NSABP B-51/RTOG 1304: randomized phase III clinical trial evaluating the role of postmastectomy chest wall and regional nodal XRT (CWRNRT) and post-lumpectomy RNRT in patients (pts) with documented positive axillary (Ax) nodes before neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NC) who convert to pathologically negative Ax nodes after NC. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:TPS1141. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2014.32.15_suppl.tps1141.
Morency D, Dumitra S, Parvez E, et al. Axillary lymph node ultrasound following neoadjuvant chemotherapy in biopsy-proven node-positive breast cancer: results from the SN FNAC study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019;26:4337–45.
Schwentner L, Helms G, Nekljudova V, et al. Using ultrasound and palpation for predicting axillary lymph node status following neoadjuvant chemotherapy: results from the multi-center SENTINA trial. Breast. 2017;31:202–7.
Moo TA, Jochelson MS, Zabor EC, et al. Is clinical exam of the axilla sufficient to select node-positive patients who downstage after NAC for SLNB? A comparison of the accuracy of clinical exam versus MRI. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019;26:4238–43.
Hyun SJ, Kim EK, Moon HJ, et al. Preoperative axillary lymph node evaluation in breast cancer patients by breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): can breast MRI exclude advanced nodal disease? Eur Radiol. 2016;26:3865–73.
Weber JJ, Jochelson MS, Eaton A, et al. MRI and Prediction of pathologic complete response in the breast and axilla after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. J Am Coll Surg. 2017;225:740–6.
Le-Petross HT, McCall LM, Hunt KK, et al. Axillary ultrasound identifies residual nodal disease after chemotherapy: results from the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group Z1071 Trial (Alliance). AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2018;210:669–76.
Network NCC. Clinical practice guidelines in oncology. Breast Cancer Version 3.2020. Preoperative systemic therapy: surgical treatment response. 2020.
Xing Y, Foy M, Cox DD, et al. Meta-analysis of sentinel lymph node biopsy after preoperative chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2006;93:539–46.
Boughey JC, Suman VJ, Mittendorf EA, et al. Factors affecting sentinel lymph node identification rate after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer patients enrolled in ACOSOG Z1071 (Alliance). Ann Surg. 2015;261:547–52.
Boughey JC, Ballman KV, Le-Petross HT, et al. Identification and resection of clipped node decreases the false-negative rate of sentinel lymph node surgery in patients presenting with node-positive breast cancer (T0–T4, N1–N2) who receive neoadjuvant chemotherapy: results from ACOSOG Z1071 (Alliance). Ann Surg. 2016;263:802–7.
Caudle AS, Yang WT, Krishnamurthy S, et al. Improved axillary evaluation following neoadjuvant therapy for patients with node-positive breast cancer using selective evaluation of clipped nodes: implementation of targeted axillary dissection. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:1072–8.
Donker M, Straver ME, Wesseling J, et al. Marking axillary lymph nodes with radioactive iodine seeds for axillary staging after neoadjuvant systemic treatment in breast cancer patients: the MARI procedure. Ann Surg. 2015;261:378–82.
Morrow M, Khan AJ. Locoregional management after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:2281–9.
Hunt KK, Yi M, Mittendorf EA, et al. Sentinel lymph node surgery after neoadjuvant chemotherapy is accurate and reduces the need for axillary dissection in breast cancer patients. Ann Surg. 2009;250:558–66.
Nogi H, Uchida K, Mimoto R, et al. Long-term follow-up of node-negative breast cancer patients evaluated via sentinel node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Clin Breast Cancer. 2017;17:644–9.
Stecklein SR, Park M, Liu DD, et al. Long-term impact of regional nodal irradiation in patients with node-positive breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant systemic therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018;102:568–77.
Mamounas EP. Impact of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on locoregional surgical treatment of breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22:1425–33.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wong, S.M., Basik, M., Florianova, L. et al. Oncologic Safety of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Alone After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 28, 2621–2629 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-020-09211-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-020-09211-0