Abstract
Introduction
The clinical relevance of primary tumor sidedness is not fully understood in colon cancer patients with peritoneal metastasis treated with cytoreductive surgery (CRS) and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC).
Methods
This was a retrospective cohort study of a multi-institutional database of patients with peritoneal surface malignancy at 12 participating high-volume academic centers from the US HIPEC Collaborative.
Results
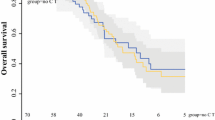
Overall, 336 patients with colon primary tumors who underwent curative-intent CRS with or without HIPEC were identified; 179 (53.3%) patients had right-sided primary tumors and 157 (46.7%) had left-sided primary tumors. Patients with right-sided tumors were more likely to be older, male, have higher Peritoneal Cancer Index (PCI), and have a perforated primary tumor, but were less likely to have extraperitoneal disease. Patients with complete cytoreduction (CC-0/1) had a median disease-free survival (DFS) of 11.5 months (95% confidence interval [CI] 7.6–15.3) versus 13.1 months (95% CI 9.5–16.8) [p = 0.158] and median overall survival (OS) of 30 months (95% CI 23.5–36.6) versus 45.4 months (95% CI 35.9–54.8) [p = 0.028] for right- and left-sided tumors; respectively. Multivariate analysis revealed that right-sided primary tumor was an independent predictor of worse DFS (hazard ratio [HR] 1.75, 95% CI 1.19–2.56; p =0.004) and OS (HR 1.72, 95% CI 1.09–2.73; p = 0.020).
Conclusion
Right-sided primary tumor was an independent predictor of worse DFS and OS. Relevant clinicopathologic criteria, such as tumor sidedness and PCI, should be considered in patient selection for CRS with or without HIPEC, and guide stratification for clinical trials.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benedix F, Kube R, Meyer F, et al. Comparison of 17,641 patients with right- and left-sided colon cancer: differences in epidemiology, perioperative course, histology, and survival. Dis Colon Rectum. 2010;53:57–64.
Benedix F, Meyer F, Kube R, et al. Influence of anatomical subsite on the incidence of microsatellite instability, and KRAS and BRAF mutation rates in patients with colon carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract. 2012;208:592–7.
Gervaz P, Bucher P, Morel P. Two colons-two cancers: paradigm shift and clinical implications. J Surg Oncol. 2004;88:261–6.
Holch JW, Ricard I, Stintzing S, Modest DP, Heinemann V. The relevance of primary tumour location in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of first-line clinical trials. Eur J Cancer. 2017;70:87–98.
Loupakis F, Yang D, Yau L, et al. Primary tumor location as a prognostic factor in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015;107(3):dju427.
Creasy JM, Sadot E, Koerkamp BG, et al. The impact of primary tumor location on long-term survival in patients undergoing hepatic resection for metastatic colon cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018;25:431–8.
Dupre A, Malik HZ, Jones RP, Diaz-Nieto R, Fenwick SW, Poston GJ. Influence of the primary tumour location in patients undergoing surgery for colorectal liver metastases. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018;44:80–6.
Franko J, Shi Q, Meyers JP, et al. Prognosis of patients with peritoneal metastatic colorectal cancer given systemic therapy: an analysis of individual patient data from prospective randomised trials from the Analysis and Research in Cancers of the Digestive System (ARCAD) database. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:1709–19.
Elias D, Gilly F, Boutitie F, et al. Peritoneal colorectal carcinomatosis treated with surgery and perioperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy: retrospective analysis of 523 patients from a multicentric French study. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:63–8.
Glehen O, Kwiatkowski F, Sugarbaker PH, et al. Cytoreductive surgery combined with perioperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy for the management of peritoneal carcinomatosis from colorectal cancer: a multi-institutional study. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:3284–92.
Quenet F. A UNICANCER phase III trial of hyperthermic intra-peritoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) for colorectal peritoneal carcinomatosis (PC): PRODIGE 7. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:LBA3503.
Lim DR, Kuk JK, Kim T, Shin EJ. Comparison of oncological outcomes of right-sided colon cancer versus left-sided colon cancer after curative resection: Which side is better outcome? Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96:e8241.
Lindblom A. Different mechanisms in the tumorigenesis of proximal and distal colon cancers. Curr Opin Oncol. 2001;13:63–9.
Nitsche U, Stogbauer F, Spath C, et al. Right sided colon cancer as a distinct histopathological subtype with reduced prognosis. Dig Surg. 2016;33:157–63.
Tejpar S, Stintzing S, Ciardiello F, et al. Prognostic and predictive relevance of primary tumor location in patients with RAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer: retrospective analyses of the CRYSTAL and FIRE-3 trials. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3(2):194–201.
Ceelen W. HIPEC with oxaliplatin for colorectal peritoneal metastasis: the end of the road? Eur J Surg Oncol. 2019;45(3):400–2.
da Silva RG, Sugarbaker PH. Analysis of prognostic factors in seventy patients having a complete cytoreduction plus perioperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy for carcinomatosis from colorectal cancer. J Am Coll Surg. 2006;203:878–86.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kotha, N.V., Baumgartner, J.M., Veerapong, J. et al. Primary Tumor Sidedness is Predictive of Survival in Colon Cancer Patients Treated with Cytoreductive Surgery With or Without Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy: A US HIPEC Collaborative Study. Ann Surg Oncol 26, 2234–2240 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-019-07373-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-019-07373-0