Abstract
Background
Breast cancer liver metastases (BCLM) are considered the most lethal compared with other sites of metastases in patients with breast cancer. This study aimed to evaluate the outcome after hepatectomy for BCLM within current multidisciplinary treatment and to develop a clinically useful nomogram to predict survival.
Methods
Between January 1985 and December 2012, 139 consecutive female patients underwent liver resection for BCLM at the authors’ institution. Clinicopathologic data were collected and analyzed for survival outcome with determination of prognostic factors. A nomogram to predict survival was developed based on a multivariate Cox model. The predictive performance of the model was assessed according to the C-statistic and calibration plots.
Results
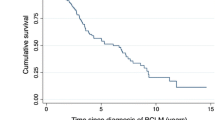
After a median follow-up period of 55 months, the overall 3- and 5-year survival rates after hepatectomy were respectively 58 and 47 %. The median overall survival period was 56 months, and the median disease-free survival period after surgical resection was 33 months. A single hepatic metastasis, no triple negative tumors, no microscopic vascular invasion, and perioperative hormonal or targeted therapy were related to improved overall survival. The model achieved good discrimination and calibration, with a C-statistic of 0.80.
Conclusions
Liver resection for selected patients with breast cancer metastases can provide significant survival benefit. It should be part of a multidisciplinary treatment program in experienced liver surgery centers. The authors’ nomogram facilitates personalized assessment of prognosis for these patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods, and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–86.
Ge Q-D, Lv N, Kong Y-N, et al. Clinical characteristics and survival analysis of breast cancer molecular subtypes with hepatic metastases. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev. 2012;13:5081–6.
Lobbezoo DJ, van Kampen RJ, Voogd AC, et al. Prognosis of metastatic breast cancer subtypes: the hormone receptor/HER2-positive subtype is associated with the most favorable outcome. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013;141:507–14.
O’Reilly SM, Richards MA, Rubens RD. Liver metastases from breast cancer: the relationship between clinical, biochemical, and pathological features and survival. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1990;26:574–7.
Andre F, Slimane K, Bachelot T, et al. Breast cancer with synchronous metastases: trends in survival during a 14-year period. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:3302–8.
Chia SK, Speers CH, D’Yachkova Y, et al. The impact of new chemotherapeutic and hormone agents on survival in a population-based cohort of women with metastatic breast cancer. Cancer. 2007;110:973–9.
Choti MA, Sitzmann JV, Tiburi MF, et al. Trends in long-term survival following liver resection for hepatic colorectal metastases. Ann Surg. 2001;235:759–66.
Adam R, Aloia T, Krissat J, et al. Is liver resection justified for patients with hepatic metastases from breast cancer? Ann Surg. 2006;244:897–907 (discussion 907–8).
Caralt M, Bilbao I, Cortes J, et al. Hepatic resection for liver metastases as part of the “oncosurgical” treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15:2804–10.
Kollmar O, Moussavian MR, Richter S, et al. Surgery of liver metastasis in gynecological cancer: indication and results. Onkologie. 2008;31:375–9.
Lubrano J, Roman H, Tarrab S, et al. Liver resection for breast cancer metastasis: does it improve survival? Surg Today. 2008;38:293–9.
Thelen A, Benckert C, Jonas S, et al. Liver resection for metastases from breast cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2008;97:25–9.
Hoffmann K, Franz C, Hinz U, et al. Liver resection for multimodal treatment of breast cancer metastases: identification of prognostic factors. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:1546–54.
Rubino A, Doci R, Foteuh JC, et al. Hepatic metastases from breast cancer. Updates Surg. 2010;62:143–8.
Cassera MA, Hammill CW, Ujiki MB, et al. Surgical management of breast cancer liver metastases. HPB Oxford. 2011;13:272–8.
Abbott DE, Brouquet A, Mittendorf EA, et al. Resection of liver metastases from breast cancer: estrogen receptor status and response to chemotherapy before metastasectomy define outcome. Surgery. 2012;151:710–6.
Duan XF, Dong NN, Zhang T, et al. Comparison of surgical outcomes in patients with colorectal liver metastases versus noncolorectal liver metastases: a Chinese experience. Hepatol Res. 2012;42:296–303.
Groeschl RT, Nachmany I, Steel JL, et al. Hepatectomy for noncolorectal non-neuroendocrine metastatic cancer: a multi-institutional analysis. J Am Coll Surg. 2012;214:769–77.
van Walsum GA, de Ridder JA, Verhoef C, et al. Resection of liver metastases in patients with breast cancer: survival and prognostic factors. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2012;38:910–7.
Dittmar Y, Altendorf-Hofmann A, Schule S, et al. Liver resection in selected patients with metastatic breast cancer: a single-centre analysis and review of literature. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013;139:1317–25.
Kostov DV, Kobakov GL, Yankov DV. Prognostic factors related to surgical outcome of liver metastases of breast cancer. J Breast Cancer. 2013;16:184–92.
Polistina F, Costantin G, Febbraro A, et al. Aggressive treatment for hepatic metastases from breast cancer: results from a single center. World J Surg. 2013;37:1322–32.
Kim JY, Park JS, Lee SA, et al. Does liver resection provide long-term survival benefits for breast cancer patients with liver metastasis? A single hospital experience. Yonsei Med J. 2014;55:558–62.
Weinrich M, Weiss C, Schuld J, et al. Liver resections of isolated liver metastasis in breast cancer: results and possible prognostic factors. HPB Surg. 2014;2014:893829.
Couinaud C. Variations of the right bile ducts: the futility of complete anatomical classifications. Chirurgie. 1993;1993; 119:354–6.
Ruiz A, Castro-Benitez C, Sebagh M, et al. Repeat Hepatectomy for Breast Cancer Liver Metastases. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22:1057–66.
Zlotnik A, Abraira V. A general-purpose nomogram generator for predictive logistic regression models. Stata J. 2015;15:537–46.
Abuzallouf S, Motawy M, Thotathil Z. Baseline staging of newly diagnosed breast cancer: Kuwait cancer control center experience. Med Princ Pract. 2007;16:22–4.
Schuetz F, Diel IJ, Pueschel M, et al. Reduced incidence of distant metastases and lower mortality in 1072 patients with breast cancer with a history of hormone replacement therapy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007;196:342 e1–9.
Kennecke H, Yerushalmi R, Woods R, et al. Metastatic behavior of breast cancer subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:3271–7.
Pogoda K, Niwinska A, Murawska M, et al. Analysis of pattern, time, and risk factors influencing recurrence in triple-negative breast cancer patients. Med Oncol. 2013;30:388.
Berman AT, Thukral AD, Hwang WT, et al. Incidence and patterns of distant metastases for patients with early-stage breast cancer after breast conservation treatment. Clin Breast Cancer. 2013;13:88–94.
Follana P, Barriere J, Chamorey E, et al. Prognostic factors in 401 elderly women with metastatic breast cancer. Oncology. 2014;86:143–51.
Acknowledgments
The Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO) provided funding for a research fellow.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruiz, A., Wicherts, D.A., Sebagh, M. et al. Predictive Profile-Nomogram for Liver Resection for Breast Cancer Metastases: An Aggressive Approach with Promising Results. Ann Surg Oncol 24, 535–545 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-016-5522-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-016-5522-7