Abstract
Background
Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) has been implicated in tumor development and progression. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of TWEAK in colorectal cancer (CRC) progression.
Methods
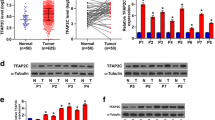
To investigate the involvement of TWEAK in the progression of human CRC, normal, and tumor specimens from 174 patients were analyzed immunohistochemically for the expression of TWEAK. TWEAK recombinant protein treatment, transfection of expression plasmids, and small interfering RNA to knockdown TWEAK expression were performed to test invasive ability with a Boyden chamber. The mRNA expression profile in recombinant TWEAK treatment was compared to a control group by microarray analysis. To identify downstream effectors, Raf kinase inhibitor (RKIP) and its correlation with TWEAK in vitro and in vivo were examined by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and invasion assays.
Results
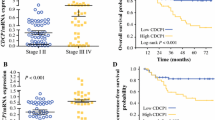
CRC patients whose tumors displayed high TWEAK expression had a statistically significantly higher overall survival and a disease-free advantage over those with a low TWEAK expression. In in vitro invasion assays, alterations in TWEAK expression in CRC cell lines inversely modulated their invasive ability. By means of integrated genomics, we identified RKIP as a downstream effector in TWEAK-mediated invasion inhibition. Knockout of RKIP expression in HCT116 cells by short hairpin RNA (shRKIP) resulted in increased invasiveness. Clinically, RKIP and TWEAK mRNA expression showed strong positive correlations in CRC patient samples.
Conclusions
Our results implicate TWEAK as a key regulator of CRC invasion, and it appears to be a useful prognostic factor for patients with CRC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–49.
Lin BR, Chang CC, Che TF, Chen ST, Chen RJ, Yang CY, et al. Connective tissue growth factor inhibits metastasis and acts as an independent prognostic marker in colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:9–23.
Manfredi S, Bouvier AM, Lepage C, Hatem C, Dancourt V, Faivre J. Incidence and patterns of recurrence after resection for cure of colonic cancer in a well defined population. Br J Surg. 2006;93:1115–22.
Burkly LC, Michaelson JS, Hahm K, Jakubowski A, Zheng TS. TWEAKing tissue remodeling by a multifunctional cytokine: role of TWEAK/Fn14 pathway in health and disease. Cytokine. 2007;40:1–16.
Winkles JA. The TWEAK-Fn14 cytokine-receptor axis: discovery, biology and therapeutic targeting. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7:411–25.
Chicheportiche Y, Bourdon PR, Xu H, Hsu YM, Scott H, Hession C, et al. TWEAK, a new secreted ligand in the tumor necrosis factor family that weakly induces apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:32401–10.
Jakubowski A, Ambrose C, Parr M, Lincecum JM, Wang MZ, Zheng TS, et al. TWEAK induces liver progenitor cell proliferation. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:2330–40.
Dogra C, Changotra H, Mohan S, Kumar A. Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis inhibits skeletal myogenesis through sustained activation of nuclear factor-kappaB and degradation of MyoD protein. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:10327–36.
Tiller G, Fischer-Posovszky P, Laumen H, Finck A, Skurk T, Keuper M, et al. Effects of TWEAK (TNF superfamily member 12) on differentiation, metabolism, and secretory function of human primary preadipocytes and adipocytes. Endocrinology. 2009;150:5373–83.
Perper SJ, Browning B, Burkly LC, Weng S, Gao C, Giza K, et al. TWEAK is a novel arthritogenic mediator. J Immunol. 2006;177:2610–20.
Meighan-Mantha RL, Hsu DK, Guo Y, Brown SA, Feng SL, Peifley KA, et al. The mitogen-inducible Fn14 gene encodes a type I transmembrane protein that modulates fibroblast adhesion and migration. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:33166–76.
Michaelson JS, Burkly LC. Therapeutic targeting of TWEAK/Fnl4 in cancer: exploiting the intrinsic tumor cell killing capacity of the pathway. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2009;49:145–60.
Winkles JA, Tran NL, Brown SA, Stains N, Cunliffe HE, Berens ME. Role of TWEAK and Fn14 in tumor biology. Front Biosci. 2007;12:2761–71.
Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC. Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:563–72.
Steeg PS. Tumor metastasis: mechanistic insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med. 2006;12:895–904.
Yeung K, Seitz T, Li S, Janosch P, McFerran B, Kaiser C, et al. Suppression of Raf-1 kinase activity and MAP kinase signalling by RKIP. Nature. 1999;401:173–7.
O’Connell JB, Maggard MA, Ko CY. Colon cancer survival rates with the new American Joint Committee on Cancer sixth edition staging. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004;96:1420–5.
Marsters SA, Sheridan JP, Pitti RM, Brush J, Goddard A, Ashkenazi A. Identification of a ligand for the death-domain-containing receptor Apo3. Curr Biol. 1998;8:525–8.
Baxter FO, Came PJ, Abell K, Kedjouar B, Huth M, Rajewsky K, et al. IKKβ/2 induces TWEAK and apoptosis in mammary epithelial cells. Development. 2006;133;3385–94.
De A, Park JI, Kawamura K, Chen R, Klein C, Rauch R, et al. Intraovarian tumor necrosis factor-related weak inducer of apoptosis/ fibroblast growth factor-inducible-14 ligand-receptor system limits ovarian preovulatory follicles from excessive luteinization. Mol Endocrinol. 2006;20:2528–38.
Chacon MR, Richart C, Gómez JM, Megía A, Vilarrasa N, Fernández-Real JM, et al. Expression of TWEAK and its receptor Fn14 in human subcutaneous adipose tissue. Relationship with other inflammatory cytokines in obesity. Cytokine. 2006;33:129–37.
Ho DH, Vu H, Brown SA, Donohue PJ, Hanscom HN, Winkles JA. Soluble tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis overexpression in HEK293 cells promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis in athymic nude mice. Cancer Res. 2004;64:8968–72.
Zhao H, Langerod A, Ji Y, Nowels KW, Nesland JM, Tibshirani R, et al. Different gene expression patterns in invasive lobular and ductal carcinomas of the breast. Mol Biol Cell. 2004;15:2523–36.
Kawakita T, Shiraki K, Yamanaka Y, Yamaguchi Y, Saitou Y, Enokimura N, et al. Functional expression of TWEAK in human hepatocellular carcinoma: possible implication in cell proliferation and tumor angiogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;318:726–33.
Tran NL, McDonough WS, Donohue PJ, Winkles JA, Berens TJ, Ross KR, et al. The human Fn14 receptor gene is up-regulated in migrating glioma cells in vitro and overexpressed in advanced glial tumors. Am. J. Pathol. 2003:162:1313–21.
Kawakita T, Shiraki K, Yamanaka Y, Yamaguchi Y, Saitou Y, Enokimura N, et al. Functional expression of TWEAK in human colonic adenocarcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 2005;26:87–93.
Wang D, Fung JN, Tuo Y, Hu L, Chen C. TWEAK/Fn14 promotes apoptosis of human endometrial cancer cells via caspase pathway. Cancer Lett. 2010:294:91–100.
Dionne S, Levy E, Levesque D, Seidman EG. PPARgamma ligand 15-deoxy-delta 12,4-prostaglandin J2 sensitizes human colon carcinoma cells to TWEAK-induced apoptosis. Anticancer Res. 2010;30:157–66.
Nakayama M, Ishidoh K, Kojima Y, Harada N, Kominami E, Okumura K, et al. Fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 mediates multiple pathways of TWEAK-induced cell death. J Immunol. 2003;170:341–8.
Tran NL, McDonough WS, Savitch BA, Fortin SP, Winkles JA, Symons M, et al. Increased fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14ex pression levels promote glioma cell invasion via Rac1 and nuclear factor-κB and correlate with poor patient outcome. Cancer Res. 2006;66:9535–42.
Fortin SP, Ennis MJ, Savitch BA, Carpentieri D, McDonough WS, Winkles JA, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis stimulation of glioma cell survival is dependent on Akt2 function. Mol Cancer Res. 2009;7:1871–81.
Dai L, Gu L, Ding C, Qiu L, Di W. TWEAK promotes ovarian cancer cell metastasis via NF-kappaB pathway activation and VEGF expression. Cancer Lett. 2009;283:159–67.
Lynch CN, Wang YC, Lund JK, Chen YW, Leal JA, Wiley SR. TWEAK induces angiogenesis and proliferation of endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:8455–9.
Wiley SR, Cassiano L, Lofton T, Davis-Smith T, Winkles JA, Lindner V, et al. A novel TNF receptor family member binds TWEAK and is implicated in angiogenesis. Immunity. 2001;15:837–46.
Yeung KC, Rose DW, Dhillon AS, Yaros D, Gustafsson M, Chatterjee D, et al. Raf kinase inhibitor protein interacts with NF-kappaBinducing kinase and TAK1 and inhibits NF-kappaB activation. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21:7207–17.
Chatterjee D, Bai Y, Wang Z, Beach S, Mott S, Roy R, et al. RKIP sensitizes prostate and breast cancer cells to drug induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:17515–23.
Fu Z, Smith PC, Zhang L, Rubin MA, Dunn RL, Yao Z, et al. Effects of raf kinase inhibitor protein expression on suppression of prostate cancer metastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003;95:878–89.
Schuierer MM, Bataille F, Hagan S, Kolch W, Bosserhoff AK. Reduction in Raf kinase inhibitor protein expression is associated with increased Ras-extracellular signal regulated kinase signaling in melanoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 2004;64:5186–92.
Al-Mulla F, Hagan S, Behbehani AI, Bitar MS, George SS, Going JJ, et al. Raf kinase inhibitor protein expression in a survival analysis of colorectal cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:5672–9.
Prenen H, Tejpar S, Van Cutsem E. New strategies for treatment of KRAS mutant metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:2921–6.
Benvenuti S, Sartore-Bianchi A, Di Nicolantonio F, Zanon C, Moroni M, Veronese S, et al. Oncogenic activation of the RAS/RAF signaling pathway impairs the response of metastatic colorectal cancers to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody therapies. Cancer Res. 2007;67:2643–8.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by grants from National Science Council, Taiwan (NSC 97-2314-B-002-031-MY2). We thank Dr. Tung-Tien Sun (Department of Surgery and Physiology, Center for Vascular and Inflammatory Diseases, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD) for providing the soluble form of TWEAK plasmid.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, BR., Huang, MT., Chen, ST. et al. Prognostic Significance of TWEAK Expression in Colorectal Cancer and Effect of Its Inhibition on Invasion. Ann Surg Oncol 19 (Suppl 3), 385–394 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-011-1825-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-011-1825-x