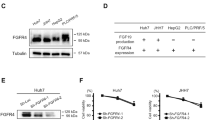
Abstract
Purpose
There is no standardized treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with portal vein tumor thrombus. We previously reported the efficacy of interferon-alpha and 5-fluorouracil combination (IFN/5-FU) therapy for these patients and the potential mechanism via the regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). In this study, we showed the VEGF-related effects of IFN/5-FU therapy using VEGF-receptor (VEGFR) selective inhibitor, PTK787/ZK222584 (PTK/ZK), in HCC cells.
Methods
Using two VEGF secreting and VEGFR expressing human HCC cell lines, PLC/PRF/5 and HuH7, we performed growth inhibitory assays in vitro and in vivo, apoptosis assay, cell cycle analysis, and Western blot analysis for the mechanism, with or without PTK/ZK in IFN/5-FU therapy.
Results
The combination of PTK/ZK and IFN/5-FU significantly inhibited cell growth in vitro and tended to reduce tumor growth in vivo in a HuH7 xenograft model in nude mice—in both cases without affecting VEGF secretion. PTK/ZK enhanced the IFN/5-FU induced apoptosis, based on increased proteins levels of Bax and reduced Bcl-xL and Bcl-2. Cell cycle analysis showed different results between the HCC cell lines following the combination therapy, possibly due to differences in p21 protein.
Conclusions
VEGF signaling inhibition would support an antitumor effect of IFN/5-FU therapy against HCC cell lines via induction of apoptosis and cell cycle delay.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ikai I, Hatano E, Hasegawa S, et al. Prognostic index for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma combined with tumor thrombosis in the major portal vein. J Am Coll Surg. 2006;202:431–8.
Le Treut YP, Hardwigsen J, Ananian P, et al. Resection of hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombus in the major vasculature. A European case-control series. J Gastrointest Surg. 2006;10:855–62.
Minagawa M, Makuuchi M. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma accompanied by portal vein tumor thrombus. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:7561–7.
Sakon M, Nagano H, Dono K, et al. Combined intraarterial 5-fluorouracil and subcutaneous interferon-alpha therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombi in the major portal branches. Cancer. 2002;94:435–42.
Ota H, Nagano H, Sakon M, et al. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with major portal vein thrombosis by combined therapy with subcutaneous interferon-alpha and intra-arterial 5-fluorouracil; role of type 1 interferon receptor expression. Br J Cancer. 2005;93:557–64.
Nagano H, Sakon M, Eguchi H, et al. Hepatic resection followed by IFN-alpha and 5-FU for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombus in the major portal branch. Hepatogastroenterology. 2007;54:172–9.
Nagano H, Miyamoto A, Wada H, et al. Interferon-alpha and 5-fluorouracil combination therapy after palliative hepatic resection in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, portal venous tumor thrombus in the major trunk, and multiple nodules. Cancer. 2007;110:2493–501.
Wada H, Nagano H, Yamamoto H, et al. Combination of interferon-alpha and 5-fluorouracil inhibits endothelial cell growth directly and by regulation of angiogenic factors released by tumor cells. BMC Cancer. 2009;9:361.
Wada H, Nagano H, Yamamoto H, et al. Combination therapy of interferon-alpha and 5-fluorouracil inhibits tumor angiogenesis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by regulating vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietins. Oncol Rep. 2007;18:801–9.
Ribatti D, Vacca A, Nico B, Sansonno D, Dammacco F. Angiogenesis and anti-angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 2006;32:437–44.
Sun HC, Tang ZY. Angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma: the retrospectives and perspectives. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2004;130:307–19.
Moon WS, Rhyu KH, Kang MJ, et al. Overexpression of VEGF and angiopoietin 2: a key to high vascularity of hepatocellular carcinoma? Mod Pathol. 2003;16:552–7.
Yoshiji H, Noguchi R, Kuriyama S, et al. Different cascades in the signaling pathway of two vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors for the VEGF-mediated murine hepatocellular carcinoma development. Oncol Rep. 2005;13:853–7.
Wada H, Nagano H, Yamamoto H, et al. Expression pattern of angiogenic factors and prognosis after hepatic resection in hepatocellular carcinoma: importance of angiopoietin-2 and hypoxia-induced factor-1 alpha. Liver Int. 2006;26:414–23.
Tanaka S, Arii S. Molecularly targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2009;100:1–8.
Marijon H, Faivre S, Raymond E. Targeted therapies in hepatocellular carcinomas: recent results and future development. Bull Cancer. 2009;96:553–61.
Liu Y, Poon RT, Li Q, Kok TW, Lau C, Fan ST. Both antiangiogenesis- and angiogenesis-independent effects are responsible for hepatocellular carcinoma growth arrest by tyrosine kinase inhibitor PTK787/ZK222584. Cancer Res. 2005;65:3691–9.
Eguchi H, Nagano H, Yamamoto H, et al. Augmentation of antitumor activity of 5-fluorouracil by interferon alpha is associated with up-regulation of p27Kip1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:2881–90.
Nakamura M, Nagano H, Sakon M, et al. Role of the Fas/FasL pathway in combination therapy with interferon-alpha and fluorouracil against hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro. J Hepatol. 2007;46:77–88.
Kondo M, Nagano H, Wada H, et al. Combination of IFN-alpha and 5-fluorouracil induces apoptosis through IFN-alpha/beta receptor in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:1277–86.
Yamamoto T, Nagano H, Sakon M, et al. Partial contribution of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)/TRAIL receptor pathway to antitumor effects of interferon-alpha/5-fluorouracil against Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:7884–95.
Noda T, Nagano H, Takemasa I, et al. Activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway induces chemoresistance to interferon-alpha/5-fluorouracil combination therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2009;100:1647–58.
Wood JM, Bold G, Buchdunger E, et al. PTK787/ZK 222584, a novel and potent inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases, impairs vascular endothelial growth factor-induced responses and tumor growth after oral administration. Cancer Res. 2000;60:2178–89.
Gerber HP, McMurtrey A, Kowalski J, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor regulates endothelial cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3’-kinase/Akt signal transduction pathway. Requirement for Flk-1/KDR activation. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:30336–43.
Nor JE, Christensen J, Liu J, et al. Up-Regulation of Bcl-2 in microvascular endothelial cells enhances intratumoral angiogenesis and accelerates tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2001;61:2183–8.
Platanias LC. The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway and its role in interferon signaling. Pharmacol Ther. 2003;98:129–42.
Hata T, Yamamoto H, Ngan CY, et al. Role of p21waf1/cip1 in effects of oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005;4:1585–94.
Lee TK, Man K, Poon RT, Lo CM, Ng IO, Fan ST. Disruption of p53-p21/WAF1 cell cycle pathway contributes to progression and worse clinical outcome of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2004;12:25–31.
Martin J, Dufour JF. Tumor suppressor and hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:1720–33.
Qin LF, Ng IO, Fan ST, Ng M. p21/WAF1, p53 and PCNA expression and p53 mutation status in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1998;79:424–8.
Hsu IC, Tokiwa T, Bennett W, et al. p53 gene mutation and integrated hepatitis B viral DNA sequences in human liver cancer cell lines. Carcinogenesis. 1993;14:987–92.
Michieli P, Chedid M, Lin D, Pierce JH, Mercer WE, Givol D. Induction of WAF1/CIP1 by a p53-independent pathway. Cancer Res. 1994;54:3391–5.
Nakaji M, Yano Y, Ninomiya T, et al. IFN-alpha prevents the growth of pre-neoplastic lesions and inhibits the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in the rat. Carcinogenesis. 2004;25:389–97.
Puisieux A, Galvin K, Troalen F, et al. Retinoblastoma and p53 tumor suppressor genes in human hepatoma cell lines. FASEB J. 1993;7:1407–13.
Fan G, Ma X, Wong PY, Rodrigues CM, Steer CJ. p53 dephosphorylation and p21(Cip1/Waf1) translocation correlate with caspase-3 activation in TGF-beta1-induced apoptosis of HuH-7 cells. Apoptosis. 2004;9:211–21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murakami, M., Kobayashi, S., Marubashi, S. et al. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor PTK/ZK Enhances the Antitumor Effects of Interferon-α/5-Fluorouracil Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Ann Surg Oncol 18, 589–596 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-010-1310-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-010-1310-y